

Cryptix. Cyber Security. Web Geek. Bit Coin Review. The Bitcoin Trader: Bitcoin's Liquidity: A Third Look. Back in November 2011, I wrote about Bitcoin's liquidity, and how it had improved from six weeks prior.
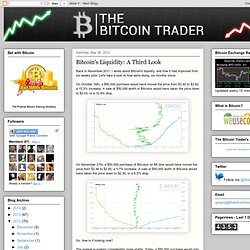
Let's take a look at how we're doing, six months since: On October 16th, a $50,000 purchase would have moved the price from $3.40 to $3.92, a 15.3% increase. A sale of $50,000 worth of Bitcoins would have taken the price down to $3.03, or a 10.9% drop. On November 27th, a $50,000 purchase of Bitcoins on Mt.Gox would have moved the price from $2.46 to $2.60, a 5.7% increase. A sale of $50,000 worth of Bitcoins would have taken the price down to $2.30, or a 6.5% drop. So, how is it looking now? The market is looking considerably more stable. In the last seven months, the Bitcoin market has clearly matured significantly, making it increasingly stable and usable as a currency; something many merchants have been waiting for before deciding to accept Bitcoin. The Proof-of-Work Concept. The Search Perhaps the least intuitive aspect of the Bitcoin network is the proof-of-work concept it uses to define the requirement for the generation of a new set of transactions (“block“) to be added to the distributed transaction database (“block chain“).
This concept, which grew out of ideas from the early cypherpunk movement, is new to monetary theory and feels a little out of place in computer science too. I will show that biology gives us the most suitable framework for understanding it. What Other Flaws Are Lurking In Bitcoin? Down slope: The value of a bitcoin slid quickly after the largest exchange for the currency halted operations.
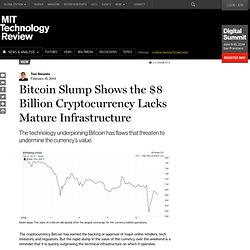
The cryptocurrency Bitcoin has earned the backing or approval of major online retailers, tech investors, and regulators. But the rapid slump in the value of the currency over the weekend is a reminder that it is quickly outgrowing the technical infrastructure on which it operates. The crash began last Friday, when the largest exchange for swapping bitcoins for conventional currency, Mt Gox, abruptly ceased operations, freezing the bitcoin accounts of all its customers. Today it emerged that the Japan-based company did so after realizing that it had failed to properly account for a known flaw in the Bitcoin protocol. Quartz has a good explainer of the quirk, known as transaction malleability. Bitcoin enthusiasts are currently debating how much blame Mt Gox deserves for the slump in bitcoin value. No one comes out of this looking very good. Michael Goldstein Explains How The Bitcoin Block Chain Enables Smart Property. Hidden surprises in the Bitcoin blockchain and how they are stored: Nelson Mandela, Wikileaks, photos, and Python software.
Every Bitcoin transaction is stored in the distributed database known as the Bitcoin blockchain.

However, people have found ways to hack the Bitcoin protocol to store more than just transactions. I've searched through the blockchain and found many strange and interesting things - from images to source code in JavaScript, Python, and Basic. If you're running a Bitcoin client, you probably have all this data stored on your system.[1] Nelson Mandela tribute The Bitcoin blockchain contains this image of Nelson Mandela and the tribute text. Nelson Mandela (1918-2013) "I am fundamentally an optimist. The Blockchain and the Rise of Networked Trust. “We are free to plant our own seeds; we don’t buy the brand nor the patent from a multinational.
In order to plant, we don’t need permission. Also, we don’t ask anyone’s permission for what to do with our money!” Santiago Zaz is an organic farmer from Argentina. Back in 2013, Zaz’s business became the first of its kind to accept bitcoin payments in the country. Like Zaz, many in his community don’t have the possibility of owning a credit card. A similar sentiment is echoed in Shannon County, South Dakota – the second poorest county in the US. Furthermore, he spoke about his passion to free his people from the American government through cryptocurrency. From big cities to villages and Indian reservations – all around the world we are seeing a common current that weaves the diverse actions of ordinary people. Transaction Malleability. While transactions are signed, the signature does not currently cover all the data in a transaction that is hashed to create the transaction hash.
Thus while uncommon it is possible for a node on the network to change a transaction you send in such a way that the hash is invalidated. Note that this just changes the hash, the output of the transaction remains the same and the bitcoins will go to their intended recipient. However this does mean that, for instance, it is not safe to accept a chain of unconfirmed transactions under any circumstance because the later transactions will depend on the hashes of the previous transactions, and those hashes can be changed until they are confirmed in a block.
(and potentially even after a confirmation if the block chain is reorganized) In addition clients must always actively scan for transactions to them; assuming a txout exists because the client created it previously is unsafe. Signature Malleability scriptSig Malleability References. Bitcoin is not Anonymous. Bitcoin is not inherently anonymous.
It may be possible to conduct transactions is such a way so as to obscure your identity, but, in many cases, users and their transactions can be identified. We have performed an analysis of anonymity in the Bitcoin system and published our results in a preprint on arXiv. 584.