

Tales. The body of stories that we today call “Norse mythology” formed one of the centerpieces of the pagan Norse religion. These are the tales that Viking poets recited in dimly lit halls to the captivated attendees of grand feasts, and which fathers and mothers told to their children around roaring hearth-fires on long winter nights.
They are epic myths of war, magic, love, betrayal, triumph, and ruin. Not only did they provide deep wells of religious meaning for the Vikings; they also speak to much that is timeless and universal in the human condition, and so continue to provide modern audiences from around the world with wonder, entertainment, and even spiritual nourishment for some. Since the pre-Christian Norse never wrote down their myths – theirs was an almost exclusively oral culture – the primary sources upon which our current knowledge of Norse mythology rests were all written while the Norse were converting to Christianity, or generations thereafter. Demographics of Scandinavia - Statistics & Facts.
One such difference concerns population size.
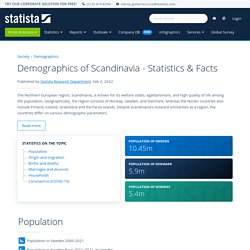
With more than 10.3 million people, Sweden has nearly twice as many inhabitants as Norway, and Denmark. However, the fertility rate has been declining overall in all three countries over the past decade. The lowest fertility rate was recorded in Norway in 2019, with only 1.53 live-born children per woman within the age group 15-49. That year, the fertility rates in Sweden and Denmark were both 1.7. A low fertility rate, combined with constantly enhanced medical science, is often linked to an aging population. A factor that can potentially slow down or even turn around the trend of decreasing population is immigration.
The Swedish system of government. 2018: After a lengthy process, the Social Democratic Party and the Green Party form a government. 2014: A minority left-of-centre coalition takes over after the Alliance. 2010: The ruling centre-right Alliance beats the left-of-centre coalition, but fails to gain an outright majority. 2006: The non-socialist parties form a four-party coalition government called the Alliance. 2002 and 1998: The Social Democrats remain in office after both elections, but in order to implement their policies are forced to form a parliamentary alliance with the Left Party and the Green Party. 1994: The Social Democrats form a new minority government.

Scandinavian languages. History of Old Scandinavian About 125 inscriptions dated from ad 200 to 600, carved in the older runic alphabet (futhark), are chronologically and linguistically the oldest evidence of any Germanic language.
Most are from Scandinavia, but enough have been found in southeastern Europe to suggest that the use of runes was also familiar to other Germanic tribes. Most inscriptions are brief, marking ownership or manufacture, as on the Gallehus Horns (Denmark; c. ad 400): Ek Hlewagastiz Holtijaz horna tawido ‘I, Hlewagastiz, son of Holti, made [this] horn.’ A number of inscriptions are memorials to the dead, while others are magical in content. The earliest were carved on loose wooden or metal objects, while later ones were also chiseled in stone. Scandinavia - New World Encyclopedia.
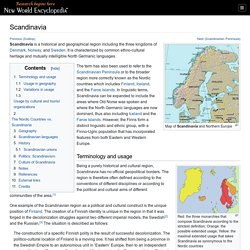
Map of Scandinavia and Northern Europe Scandinavia is a historical and geographical region including the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden.
It is characterized by common ethno-cultural heritage and mutually intelligible North Germanic languages. Weather and climate / Authentic Scandinavia. When is the best time of year to travel?
We offer tours all year round because the Nordic countries are a destination for every season. The Summers are light and the temperatures are mild. Above the Arctic Circle you can experience the Midnight Sun. Much of the Nordic countries are covered in snow during Winter; although snow is much rarer in the south and along the coast. During winter you will experience the dark season; above the Arctic Circle there will be a period without daylight. Autumn offers an explosion of colours while Spring brings nature alive after a long winter. Japanese folklore and mythology - New World Encyclopedia. Japanese folklore are heavily influenced by the two primary religions of Japan, Shinto and Buddhism.
Japanese mythology is a complex system of beliefs that also embraces Shinto and Buddhist traditions as well as agriculture-based folk religion. The Shinto pantheon alone boasts an uncountable number of kami (deities or spirits). One notable aspect of Japanese mythology is that it provided a creation story for Japan and attributed divine origins to the Japanese Imperial family, assigning them godhood.
The Japanese word for the Emperor of Japan, tennō (天皇), means "heavenly emperor. " Contents Japanese folklore has been influenced by foreign literature. Japanese Folklore A young Kintarō battling a giant carp, in a print by Yoshitoshi In the middle years of the twentieth century storytellers would often travel from town to town telling these stories with special paper illustrations called kamishibai. Demographics of Japan. Government - Explore Japan - Kids Web Japan - Web Japan.
The National Diet Building (AFLO)

Religion in Japan. Shinto and Buddhism are Japan's two major religions.
Shinto is as old as the Japanese culture, while Buddhism was imported from the mainland in the 6th century. Since then, the two religions have been co-existing relatively harmoniously and have even complemented each other to a certain degree. Most Japanese consider themselves Buddhist, Shintoist or both. Religion does not play a big role in the everyday life of most Japanese people today. The average person typically follows the religious rituals at ceremonies like birth, weddings and funerals, may visit a shrine or temple on New Year and participates at local festivals (matsuri), most of which have a religious background.
General Information on Climate of Japan. Japan has four distinct seasons with a climate ranging from subarctic in the north to subtropical in the south.
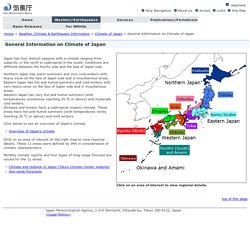
Conditions are different between the Pacific side and the Sea of Japan side. Northern Japan has warm summers and very cold winters with heavy snow on the Sea of Japan side and in mountainous areas. Eastern Japan has hot and humid summers and cold winters with very heavy snow on the Sea of Japan side and in mountainous areas. Western Japan has very hot and humid summers (with temperatures sometimes reaching 35 oC or above) and moderate cold winters. Okinawa and Amami have a subtropical oceanic climate. Click below to see an overview of Japan's climate. Japan Geography. Location.
Tangaroa. Polynesian Mythology - Myth Encyclopedia - god, legend, war, world, creation, life, hero, people, children. Polynesia is a vast region of the Pacific Ocean consisting of many hundreds of widely separated, culturally and politically diverse island groups. Ranging from Midway and Hawaii in the north to New Zealand in the south, the triangular area called Polynesia also includes Tahiti, Samoa, Tonga, Tuamotu, the Cook Islands, and the Pitcairn Islands.
Although the mythology of Polynesia took different forms on various islands, many of the basic stories, themes, and deities were surprisingly similar throughout the region. Foundations of Religion and Myth. Scholars believe that humans first migrated to Polynesia from Southeast Asia about 2,000 years ago. These people carried with them their mythological traditions about events, deities, and heroes. Polynesian religion and mythology placed great emphasis on nature, particularly the ocean environment. Because mana was sacred, Polynesians invented complicated rules to protect it.
Origin of Yams deity god or goddess. Hawaiian Myths and Legends.