

Breast-Feeding. Newborn. Midwife. Radiology. Hospice. Sickle-Cell-Disease. Cochrane. Bacteriology. Surgery. Obesity. Vegetarian. Elearning. Year 2000 Position Statement: Principles and Guidelines for Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Programs. Failure to Thrive: Miscellaneous Disorders in Infants and Children: Merck Manual Professional. 2005 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiovascular Care (ECC) of Pediatric and Neonatal Patients: Pediatric Basic Life Support. Abstract This publication presents the 2005 American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and emergency cardiovascular care (ECC) of the pediatric patient and the 2005 American Academy of Pediatrics/AHA guidelines for CPR and ECC of the neonate.

The guidelines are based on the evidence evaluation from the 2005 International Consensus Conference on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science With Treatment Recommendations, hosted by the American Heart Association in Dallas, Texas, January 23–30, 2005. The “2005 AHA Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care” contain recommendations designed to improve survival from sudden cardiac arrest and acute life-threatening cardiopulmonary problems.
The evidence evaluation process that was the basis for these guidelines was accomplished in collaboration with the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR). Injuries Motor Vehicle Injuries. Patients - Health Record, Education Program, Medical Library - Medem. Multiple Sclerosis Video Page-Nystagmus. Group A Streptococcal Infections, NIAID Fact Sheet. Multimedia - Lead Candy. Update of Newborn Screening and Therapy for Congenital Hypothyroidism. American Academy of Pediatrics, Susan R.

Rose, MD, and the Section on Endocrinology and Committee on Genetics, American Thyroid Association, Rosalind S. Brown, MD, and the Public Health Committee, Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrine Society Abstract Unrecognized congenital hypothyroidism leads to mental retardation. Newborn screening and thyroid therapy started within 2 weeks of age can normalize cognitive development. Improvements in screening and therapy have led to improved developmental outcomes in adults with congenital hypothyroidism who are now in their 20s and 30s.
Remaining controversy centers on infants whose abnormality in neonatal thyroid function is transient or mild and on optimal care of very low birth weight or preterm infants. Physicians must not relinquish their clinical judgment and experience in the face of normal newborn thyroid test results. Key Words: Congenital hypothyroidism (CH) is one of the most common preventable causes of mental retardation. In-Toeing in Children. In-Toeing in Children Noticing that your child or grandchild's feet turn in can cause alarm, prompting a visit to the pediatrician or orthopaedist.
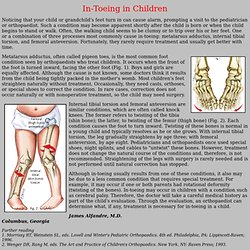
Such a condition may become apparent shortly after the child is born or when the child begins to stand or walk. Often, the walking child seems to be clumsy or to trip over his or her feet. One or a combination of three processes most commonly cause in-toeing: metatarsus adductus, internal tibial torsion, and femoral anteversion. Fortunately, they rarely require treatment and usually get better with time. Metatarsus adductus, often called pigeon toes, is the most common foot condition seen by orthopaedists who treat children. Internal tibial torsion and femoral anteversion are similar conditions, which are often called knock knees. Although in-toeing usually results from one of these conditions, it also may be due to a less common condition that requires special treatment.
James Alfandre, M.D.Columbus, Georgia Further reading1. Crohn's Disease. Johns Hopkins University Internet Learning Center: Log-in. WebCite query result. Poison Ivy, Oak and Sumac: Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention on MedicineNet. Contemporary Pediatrics - Home Page. April 17,2014 Color blindness overwhelming affects non-Hispanic white boys, according to what is perhaps the first population-based study of color vision deficiency (CVD) in preschool children.
Adolescents with sickle cell disease (SCD) are highly knowledgeable about their condition and generally have a positive outlook about transition programs and life beyond, according to a small pilot study. A new study finds that adolescents who report tanning indoors are more likely to engage in unhealthy weight loss practices, suggesting an underlying body image problem may put this group at increased risk of eating disorders. Surprisingly, males may be at higher risk than females. Vaccine Information for the Public and Health Professionals. Calculate your BMI - Metric BMI Calculator. Mental Health America: Children's Mental Health: Resource List. 10-year CVD Risk Calculator (Risk Assessment Tool for Estimating Your 10-year Risk of Having a Heart Attack Version)