

M.habrahabr. Тестирование Android приложений — тема большая и емкая, говорить о ней можно бесконечно.
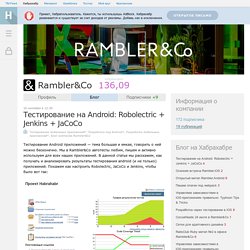
Мы в Rambler&Co автотесты любим, пишем и активно используем для всех наших приложений. В данной статье мы расскажем, как получать и анализировать результаты тестирования android (и не только) приложений. Покажем как настроить Robolectric, JaCoCo и Jenkins, чтобы было вот так: Robolectric Robolectric — это библиотека, которая позволяет запускать тесты для android-приложений на локальной JVM. Robolectric активно развивается, но в ней все еще есть множество проблем, поэтому мы используем robolectric для тестирования бизнес объектов, логики приложения, хранения и обработки данных. Установка С выходом версии 3.0 установка библиотеки умещается в одну строчку (раньше требовался еще и плагин), добавить в dependencies: testCompile 'org.robolectric:robolectric:3.0' Build Variants Дело в том, что для unit тестов (по умолчанию) используется src/test, а для android test — src/androidTest.
Первый тест Запуск тестов. Как работает наш мозг или как смоделировать душу? / Geektimes. Здравствуй, Geektimes!
В ранее опубликованной статье, была представлена модель нервной системы, опишу теорию и принципы, которые легли в её основу. Теория основана на анализе имеющейся информации о биологическом нейроне и нервной системе из современной нейробиологии и физиологии мозга. Сначала приведу краткую информацию об объекте моделирования, вся информация изложена далее, учтена и использована в модели. Нейрон является основным функциональным элементом нервной системы, он состоит из тела нервной клетки и её отростков. Robust Short-Term Memory without Synaptic Learning. Citation: Johnson S, Marro J, Torres JJ (2013) Robust Short-Term Memory without Synaptic Learning.

PLoS ONE 8(1): e50276. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050276 Editor: Dante R. Chialvo, National Research & Technology Council, Argentina Received: May 22, 2012; Accepted: October 23, 2012; Published: January 22, 2013 Copyright: © 2013 Johnson et al. Funding: This work was supported by Junta de Andalucía projects FQM-01505 and P09-FQM4682, by the joint Spanish Research Ministry (MEC) and the European Budget for the Regional Development (FEDER) project FIS2009-08451, and by the Granada Research of Excellence Initiative on Bio-Health (GREIB) traslational project GREIB.PT_2011_19 of the Spanish Science and Innovation Ministry (MICINN) “Campus of International Excellence.”
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. Introduction Slow but sure, or fast and fleeting? Harnessing network structure The mechanism, which we call Cluster Reverberation (CR), is very simple. Digit Span - Cambridge Brain Sciences. The digit span task exercises your verbal working memory.

Scientists refer to working memory as the cognitive system that allows the temporary storage and manipulation of information. According to one influential cognitive theory, this system has specialised components, one of which, the 'phonological loop', underlies verbal working memory abilities (Baddeley & Hitch 1974). The phonological loop is comprised of a verbal storage system and a rehearsal system.
If you do this task, you may find yourself mentally rehearsing the string of digits as they appeared on screen; this is the rehearsal system in action. It allows the visual inputs to be recoded so that they can enter your short term verbal store and it also refreshes decaying representations (that is, any item that is about to be forgotten). Verbal working memory is involved in many everyday tasks, from remembering your friend's telephone number while you enter it into your phone, to understanding long and difficult sentences. Human working memory is based on dynamic interaction networks in the brain.
A research project of the Neuroscience Center of the University of Helsinki sheds light on the neuronal mechanisms sustaining memory traces of visual stimuli in the human brain.

The results show that the maintenance of working memory is associated with synchronisation of neurons, which facilitates communication between different parts of the brain. On the basis of interaction between the brain areas, it was even possible to predict the subject's individual working memory capacity. The results were published last week in the online version of the journal PNAS.
The working memory of an average person can sustain only three of four objects at a time. A taxonomy of external and internal attention. [Annu Rev Psychol. 2011] Insights on Loss of Working Memory. By Rick Nauert PhD Senior News Editor Reviewed by John M.
Grohol, Psy.D. on July 19, 2010 Scientists are studying a genetic disease to gain insights on working memory, i.e., the ability to hold and manipulate information in your mind. The disease, neurofibromatosis type 1, or NF1 is characterized by a loss of working memory. The condition affects one in 3,500 people and is the most common cause of learning disabilities. New research by UCLA scientist has uncovered new clues about how NF1 disrupts memory and how medications may be created to correct NF1-related learning disabilities. The research is published in the online edition of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. NF1 is caused by mutations in a gene called neurofibromin, or Nf1, which makes a protein with the same name. Previous animal studies led by principal investigator Dr. The findings imply that excess GABA hinders the activity of neurons in the brain, thus interfering with working memory.