Drugs
>
Pag101
>
Education
>
Classes
>
BioPsych
Ayahuasca relieves depression and anxiety, finds study on nearly 12,000 users. Ayahuasca is a powerful hallucinogenic tea that has been brewed in the Amazon rainforest for thousands of years.

Although the brew’s main active ingredient, dimethyltryptamine (DMT), is illegal in most countries, recent research suggests the drug may have significant therapeutic properties in the context of improving depression and anxiety symptoms. A new study published this week — the largest thus far on ayahuasca — adds weight to this body of evidence. The Global Ayahuasca Project was conducted between 2017 and 2020 and involved more than 11,000 individuals, 7,785 of whom suffered from symptoms of depression or anxiety at the time they took the drug.
The participants had to fill an online self-reported questionnaire designed to measure mental health outcomes among Ayahuasca users. The results were impressive, to say the least. Users who reported profound mystical experiences tended to report the greatest improvements in their depression or anxiety symptoms.
Neuroscience study indicates that LSD “frees” brain activity from anatomical constraints - The psychedelic state induced by LSD appears to weaken the association between anatomical brain structure and functional connectivity, finds new fMRI study. : scien. Know Your Amphetamines - Astral Codex Ten. In the 1950s, a shady outfit called Obetrol Pharmaceuticals made a popular over-the-counter diet pill called Obetrol.
If you're familiar with any of: the 1950s, shady pharma, or diet pills, your next question will be "did it contain amphetamines?
" and the answer is yes, loads of them.
His life is too damn perfect. : ContagiousLaughter. Post-Psychedelic Reductions in Experiential Avoidance Are Associated With Decreases in Depression Severity and Suicidal Ideation. Introduction “Afterwards, I allowed myself to experience everything—even if it is sadness.
Now I know how to deal with my feelings rather than repress them” (1) Serotonergic psychedelics, a class of pharmacological agents that act as serotonin 2A receptor (5-HT2AR) agonists, including psilocybin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), and dimethyltryptamine (DMT; contained in the brew ayahuasca), are currently receiving attention within psychiatry and mental health as novel interventions for a wide range of mental health concerns [for reviews, see (2, 3)]. Randomized controlled trials and open-label trials have found promising results for psychedelic therapy in the treatment of distress associated with a life-threatening illness [e.g., (4–6)], substance use disorders [e.g., (7–10)], obsessive-compulsive disorder (11), depression [e.g., (12–14)], and suicidal ideation (13, 15).
Neuroimaging study suggests a single dose of ayahuasca produces lasting changes in two important brain networks. Consuming a single dose of the psychedelic brew ayahuasca can result in lasting changes in higher-order cognitive brain networks, according to a new study published in the Journal of Psychopharmacology.
Ayahuasca, a concoction used for centuries by indigenous Amazon tribes, contains the powerful psychedelic drug dimethyltryptamine (DMT) and monoamine oxidase inhibitors. The brew is typically prepared using leaves from the Psychotria viridis shrub and the bark of the Banisteriopsis caapi vine. The new neuroimaging research suggests that ayahuasca may produce long-lasting effects on mood by altering the functional connectivity of the brain’s salience and default mode networks. “As a clinical neuroscientist, I am interested in approaches that can improve the life of patients with neuropsychiatric disorders,” said study author Lorenzo Pasquini, a postdoctoral fellow at the Memory and Aging Center at the University of California, San Francisco.
Anesthesia-Related Memory Loss Lasts Days, Study Warns. People who are put under general anesthesia may wind up with memory and cognitive deficits for days or weeks after surgery.

But now, a new study in mice reveals a possible way to reverse the ill effects of anesthesia drugs on memory. In the study, scientists gave mice a common anesthetic, and found the drug caused memory impairments that lasted up to a week. But when they gave the mice another drug, after the anesthetic, the memory effects were reversed, the researchers say. The findings suggest that doctors should tell their patients that anesthesia may affect their memory, said Dr. Beverly Orser, a professor of anesthesiology at the University of Toronto, in Canada, co-author of the study published today (Nov. 3) in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Drug-induced amnesia.
Introduction: Skin diseases affect a large percentage of people and can result in a markedly decreased quality of life.
Nearly 25% of all physician office visits are for skin complaints, but only about one third of these visits occur with dermatologists. Most of the remaining visits for skin complaints occur with primary care physicians including Family Physicians, Internists, and Pediatricians. Primary care physicians, however, have an ever-increasing knowledge base of medicine to master and receive little formal training in dermatology. Several studies have shown that non-dermatologists have difficulty diagnosing many diseases of the skin. Improving the diagnostic accuracy and dermatologic care that these physicians provide to a large number of patients will significantly impact healthcare quality and cost-effective care by reducing error.
New opioid douses pain without being addictive or deadly in primates. While the opioid epidemic continues kill more than 40 American every day, researchers and health experts are frantically searching for ways to curtail use of the highly addictive, pain-quenching drugs.
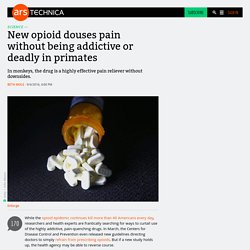
In March, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention even released new guidelines directing doctors to simply refrain from prescribing opioids. But if a new study holds up, the health agency may be able to reverse course. According to a report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, an opioid drug referred to as BU08028 was able to alleviate pain in a dozen monkeys just as well as other opioid painkillers, such as morphine.
Why Is Everyone Freaking Out About MDMA?
Some MDMA (Photo via) MDMA has caused something of a stir here in the US recently.
TheDEA.org: The History of MDMA. Christmas Eve, 1912: The pharmaceutical company Merck files for a patent on MDMA ('ecstasy') as a precursor to a drug that they hoped would be effective in controlling bleeding.

Their patent application is granted two years later (1914.)
Ecstasy History. Early ecstasy.
An Error Occurred Setting Your User Cookie. Neuropsychopharmacology - Abstract of article: Acute Physiological and Behavioral Effects of Intranasal Methamphetamine in Humans. Hormone removes the pleasure of smoking. Waves of Candy Crush Addiction Hit Los Banos, One Man Sues. Los Banos CA – The popular game has taken locals by storm, candy crush is the new crack. If you look and see someone on their phone, it is not Facebook they’re checking, it is Candy Crush they are playing. The hit game features a grid of candies that the player has to match up with at least three or more of a kind. The object of the game varies in each game mode, but the idea is to reach that objective by sliding candy to match it’s color.
Why Candy Crush Saga is EXTREMELY dangerous to your wealth.
I’ve been swamped of late with facebook updates telling me that my friends want me to play Candy Crush Saga. Invites to join them in the game. Requests for lives, requests asking for advice on how to best so-and-so a level.
Pleasure_Addiction
DrugAbuse. Cannabis use and cognitive dysfunction. The Effects of Marijuana on Cognitive Functioning. The Effects of Marijuana on Cognitive Functioning Psychology 20, Spring 2000 April 19, 2000. Harvard Gazette: Study: Intelligence, cognition unaffected by heavy marijuana use. By William J. Cromie Gazette Staff The new study of cognitive changes caused by heavy marijuana use has found no lasting effects 28 days after quitting. Following a month of abstinence, men and women who smoked pot at least 5,000 times in their lives performed just as well on psychological tests as people who used pot sparingly or not at all, according to a report in the latest edition of the Archives of General Psychiatry. That's the good news. The bad news, not included in the study, is that most heavy users admit that pot has had a negative effect on their physical and mental health as well their functioning on the job and socially.
Neuropsychopharmacology - Effects of Acute Smoked Marijuana on Complex Cognitive Performance.
Transtheoretical Model (or Stages of Change) - Health Behavior Change. Think Pregnancy: Alcohol During Pregnancy: What is FAS?
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) is the name given to a group of physical and mental birth defects cause by a woman drinking heavily during pregnancy.
3D Brain Maps Created of People Tripping on LSD. Nimodipine prevents the effects of ethanol... [Neuropharmacology. 2002]










