

Google Creates Software That Tells You What It Sees in Images. Experimental software from Google can accurately describe scenes in photos, like the two on the left.
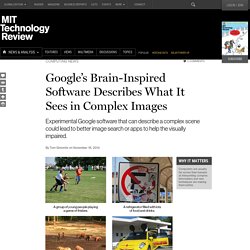
But it still makes mistakes, as seen with the two photos on the right. Google Search Will Be Your Next Brain — Backchannel. “I need to know a bit about your background,” says Geoffrey Hinton.
“Did you get a science degree?” Hinton, a sinewy, dry-witted Englishman by way of Canada, is standing at a white board in Mountain View, California, on the campus of Google, the company he joined in 2013 as a Distinguished Researcher. Hinton is perhaps the world’s premier expert on neural network systems, an artificial intelligence technique that he helped pioneer in the mid 1980s. Google Brain. Google Brain is a deep learning research project at Google.
History[edit] In June 2012, the New York Times reported that a cluster of 16,000 computers dedicated to mimicking some aspects of human brain activity had successfully trained itself to recognize a cat based on 10 million digital images taken from YouTube videos.[1] The story was also covered by National Public Radio[2] and SmartPlanet.[3] In March 2013, Google hired Geoffrey Hinton, a leading researcher in the deep learning field, and acquired the company DNNResearch Inc. headed by Hinton. Inside the Artificial Brain That's Remaking the Google Empire. Getty It was one of the most tedious jobs on the internet.
A team of Googlers would spend day after day staring at computer screens, scrutinizing tiny snippets of street photographs, asking themselves the same question over and over again: “Am I looking at an address or not?’ Click. Yes. Click. Google’s Artificial Brain Learns to Find Cat Videos. By Liat Clark, Wired UK When computer scientists at Google’s mysterious X lab built a neural network of 16,000 computer processors with one billion connections and let it browse YouTube, it did what many web users might do — it began to look for cats.
[partner id=”wireduk”] The “brain” simulation was exposed to 10 million randomly selected YouTube video thumbnails over the course of three days and, after being presented with a list of 20,000 different items, it began to recognize pictures of cats using a “deep learning” algorithm. This was despite being fed no information on distinguishing features that might help identify one. Picking up on the most commonly occurring images featured on YouTube, the system achieved 81.7 percent accuracy in detecting human faces, 76.7 percent accuracy when identifying human body parts and 74.8 percent accuracy when identifying cats. Google's New A.I. Ethics Board Might Save Humanity From Extinction. In 2011, the co-founder of DeepMind, the artificial intelligence company acquired this week by Google, made an ominous prediction more befitting a ranting survivalist than an award-winning computer scientist.
“Eventually, I think human extinction will probably occur, and technology will likely play a part in this,” DeepMind’s Shane Legg said in an interview with Alexander Kruel. Among all forms of technology that could wipe out the human species, he singled out artificial intelligence, or AI, as the “number 1 risk for this century.” Q&A with Shane Legg on risks from AI. Welcome to Forbes. Inside DeepMind. Google's Secretive DeepMind Startup Unveils a "Neural Turing Machine" One of the great challenges of neuroscience is to understand the short-term working memory in the human brain.

Google DeepMind. Google's DeepMind Builds Artificial Intelligence Computer That Mimics Human Brain. Google-owned artificial intelligence (AI) startup DeepMind has unveiled a computer prototype capable of mimicking properties of the human brain's short-term memory.
The Neural Turing Machine learns and stores algorithms and data as "memories", which it is then able to retrieve later to perform tasks it has not been previously programmed to do. "We have introduced the Neural Turing Machine, a neural network architecture that takes inspiration from both models of biological working memory and the design of digital computers," Alex Graves, Greg Wayne and Ivo Danihelka from DeepMind wrote in a recent research paper. "Our experiments demonstrate that it is capable of learning simple algorithms from example data and of using these algorithms to generalise well outside its training regime. " This new form of AI builds on the work of American cognitive psychologist George Miller, who first began research into the capacity and function of the short-term memory in the 1950s. Google's DeepMind AI project apes human memory and programming skills.
Military-Industrial-Googleplex Creating Artificial Intel. Tweet What could possibly go wrong with Google creating military-grade artificial intelligence (AI)?
Stephen Hawking, a world-leading scientist, warned on the BBC that “the development of full artificial intelligence could spell the end of the human race” in part because it involves “developing weapons we cannot even understand.” Elon Musk, cofounder of Tesla Motors and Paypal, told The Guardian: “with artificial intelligence we are summoning the demon,” and that it’s “our biggest existential threat.” “This is not a case of crying wolf about something I don’t understand,” Musk said.
Google Chairman Eric Schmidt dismissed such fears at a Financial Times event: “These concerns are normal; they’re also to some degree misguided.” What Mr. Consider the evidence that Google already has the key component parts in place. A first look inside Google's futuristic quantum lab. In May, Google launched the Quantum Artificial Intelligence Lab with hardware from the Canadian quantum computing company D-Wave and technical expertise from NASA.
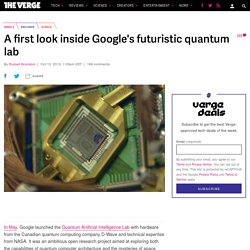
It was an ambitious open research project aimed at exploring both the capabilities of quantum computer architecture and the mysteries of space exploration — but in the months since, they've stayed quiet about exactly what kind of work they've been doing there. Operated at near-absolute-zero temperatures Tomorrow, they're breaking the silence with a brief short film, set to debut at the Imagine Science Films Festival at Google New York. The film takes a look at various researchers working on the project, as well as the computer itself, which has to be operated at near-absolute-zero temperatures.
Researchers hope the quantum architecture will eventually be used to optimize solutions across complex and interconnected sets of variables currently outside the capabilities of conventional computing. Quantum Artificial Intelligence Lab. The Quantum Artificial Intelligence Lab (also called the Quantum AI Lab or QuAIL) is a joint initiative of NASA, Universities Space Research Association, and Google (specifically, Google Research) whose goal is to pioneer research on how quantum computing might help with machine learning and other hard computer science problems. The lab is hosted at NASA's Ames Research Center.[1][2] History[edit] The Quantum AI Lab was announced by Google Research in a blog post on May 16, 2013.[1][3][4][5] At the time of launch, the Lab was using the most advanced commercially available quantum computer, D-Wave Two from D-Wave Systems.[1][3][4] On May 20, 2013, it was announced that people could apply to use time on the D-Wave Two at the Lab.[4] On October 10, 2013, Google released a short film describing the current state of the Quantum AI Lab.[6][7] On October 18, 2013, Google announced that it had incorporated quantum physics into Minecraft.[8][9][10] See also[edit] References[edit] External links[edit]
Quantum machine learning. Plus.google. Demis Hassabis: 15 facts about the DeepMind Technologies founder. • Now 37, Hassabis was born in London in July 1976 and quickly showed academic promise and skill with board games, especially chess. • At the ages of 13 Hassabis reached the rank of chess master, and was the second-highest-rated player in the world under 14 at the time – beaten only by the Hungarian chess grandmaster and strongest female chess player in history, Judit Polgár. • Accelerated through school, Hassabis completed his A-level exams two years early. • Released in 1994, Theme Park sold several million copies and won a Golden Joystick award.
The game set players the task of building a successful theme park in the UK with just a few thousand pounds and a small plot of land. . • Hassabis left Bullfrog to study Computer Science Tripos at Cambridge University, which in 1953 had the world's first undergraduate computer science course. . • After graduation, Hassabis rejoined Molyneux, who had now set up another games developer called Lionhead Studios, a breakaway from developer Bullfrog. Demis Hassabis of DeepMind, Google Shows AI Computer Playing Atari Games. Google’s artificial intelligence firm, DeepMind Technologies, has been making headlines with a computer that can program itself, a quest for “AI scientists” and software that can learn to play classic Atari games better than a human expert. Today, a video showing their famed software learning to play Breakout and mastering nine other Atari games including Enduro, Boxing and Demon Attack has resurfaced online.
Although it was uploaded to YouTube last April, it seems it’s finally receiving the attention it deserves. In the beginning of the video—taken at the 2014 First Day of Tomorrow conference— DeepMind founder Demis Hassabis narrates as footage of the software training to play Breakout shows behind him. Note that “training” just refers to time spent playing; the software was merely presented the game with no prior knowledge as to how it works or how to go about learning to play it. Prepare to be amazed.