

Extracranial-intracranial bypass. Overview Cerebral bypass surgery is performed to restore, or "revascularize," blood flow to the brain.
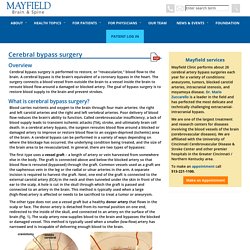
A cerebral bypass is the brain's equivalent of a coronary bypass in the heart. The surgery connects a blood vessel from outside the brain to a vessel inside the brain to reroute blood flow around a damaged or blocked artery. The goal of bypass surgery is to restore blood supply to the brain and prevent strokes. What is cerebral bypass surgery? Blood carries nutrients and oxygen to the brain through four main arteries: the right and left carotid arteries and the right and left vertebral arteries.
The first type uses a vessel graft – a length of artery or vein harvested from somewhere else in the body. The other type does not use a vessel graft but a healthy donor artery that flows in the scalp or face. The most common type of bypass is the STA-MCA (superficial temporal artery to middle cerebral artery) bypass. Heterotopic heart transplantation: experimental development and clinical experience. Skip to Main Content Sign In Register Advanced Search Journals Career Network Online ISSN 1873-734X Print ISSN 1010-7940 Copyright © 2017 European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery.

Craniotomy (brain surgery) Double-barrel bypass for cerebral ischemia: technique, rationale, and preliminary experience with 10 consecutive cases. St. Jude Medical Nanostim Leadless Pacemaker Receives CE Mark. 8inShare St.
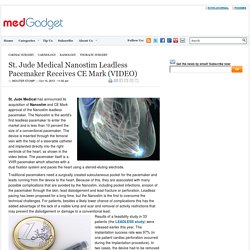
Jude Medical has announced its acquisition of Nanostim and CE Mark approval of the Nanostim leadless pacemaker. The Nanostim is the world’s first leadless pacemaker to enter the market and is less than 10 percent the size of a conventional pacemaker. The device is inserted through the femoral vein with the help of a steerable catheter and implanted directly into the right ventricle of the heart, as shown in the video below. The pacemaker itself is a VVIR pacemaker which attaches with a dual fixation system and paces the heart using a steroid-eluting electrode. Traditional pacemakers need a surgically created subcutaneous pocket for the pacemaker and leads running from the device to the heart. Brachytherapy - Information and support. Internal radiotherapy (brachytherapy) is often given after external radiotherapy.

Tubes are placed into your vagina through your cervix and into your womb. A radioactive capsule is placed in the tubes. If you’ve not had a hysterectomy, you’ll have intrauterine brachytherapy. Your doctor will place tubes into your vagina, through your cervix and into your womb while you’re sedated or under a general anaesthetic. If you’ve had a hysterectomy you’ll have intravaginal brachytherapy. The tubes will be connected to a machine that delivers a radioactive capsule into them. The most common way to give brachytherapy to the cervix is as a high-dose treatment. Image-guided brachytherapy (IGBT) uses MRI or CT scans to make radiotherapy very accurate. Epidural anaesthesia. An epidural is an injection in the back to stop you feeling pain in part of your body.

This page covers epidural anaesthesia, a type of epidural commonly given for pain relief in childbirth and in some types of surgery. Airways and Intubation. Oral intubation information. Patient. Endotracheal intubation is the placement of a tube into the trachea to maintain a patent airway in those who are unconscious or unable to maintain their airway for other reasons.
Compared to the use of pharyngeal airways (oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal), benefits of an endotracheal airway include: Protection against aspiration and gastric insufflationMore effective ventilation and oxygenationFacilitation of suctioningDelivery of anaesthetic and other drugs via the endotracheal tube (ETT) Intubation is a technique that requires training, experience and regular updating to maintain competence. Anyone attempting it should also be capable of managing any complications that arise. Kidney. Codeine Uses, Dosage, Side Effects & Warnings - Drugs.com. Generic Name: codeine (KOE deen)Brand Names: What is codeine?
Codeine is an opioid pain medication. An opioid is sometimes called a narcotic. Codeine is used to treat mild to moderately severe pain. Codeine may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide. Important information You should not use codeine if you are allergic to it, or if you have an uncontrolled breathing disorder, a bowel obstruction called paralytic ileus, or frequent asthma attacks or hyperventilation. Codeine can slow or stop your breathing. MISUSE OF NARCOTIC MEDICINE CAN CAUSE ADDICTION, OVERDOSE, OR DEATH, especially in a child or other person using the medicine without a prescription. Medicines that contain codeine should not be given to a child just after surgery to remove the tonsils or adenoids. Penicillin. Penicillin (PCN or pen) is a group of antibiotics which include penicillin G (intravenous use), penicillin V (oral use), procaine penicillin, and benzathine penicillin (intramuscular use).
Penicillin antibiotics were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. Penicillins are still widely used today, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use. About 10% of people report that they are allergic to penicillin; however, up to 90% of this group may not actually be allergic.[2] Serious allergies only occur in about 0.03%.[2] All penicillins are β-lactam antibiotics.
Medical uses[edit] Hydrochlorothiazide. Hydrochlorothiazide (abbreviated HCTZ, HCT, or HZT), is a diuretic medication often used to treat high blood pressure and swelling due to fluid build up.[2] Other uses include diabetes insipidus, renal tubular acidosis, and to decrease the risk of kidney stones in those with high calcium level in the urine.[2] For high blood pressure it is often recommended as a first line treatment.[2][3] HCTZ is taken by mouth and may be combined with other blood pressure medications as a single pill to increase the effectiveness.[2] Potential side effects include poor kidney function, electrolyte imbalances especially low blood potassium and less commonly low blood sodium, gout, high blood sugar, and feeling faint initially upon standing up.[2] While allergies to HCTZ are reported to occur more often in those with allergies to sulfa drugs this association is not well supported.[2] It may be used during pregnancy but is not a first line medication in this group.[2]
Metformin. Medication Metformin, marketed under the trade name Glucophage among others, is the first-line medication for the treatment of type 2 diabetes,[6][7] particularly in people who are overweight.[8] It is also used in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome.[6] It is not associated with weight gain.[9] It is taken by mouth.[6]
Amoxicillin. Amoxicillin (amox), also spelled amoxycillin, is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections.[1] It is the first line treatment for middle ear infections. It may also be used for strep throat, pneumonia, skin infections, and urinary tract infections among others. Azithromycin. Azithromycin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections.[2] This includes middle ear infections, strep throat, pneumonia, traveler's diarrhea, and certain other intestinal infections. It may also be used for a number of sexually transmitted infections including chlamydia and gonorrhea infections.
Along with other medications, it may also be used for malaria. It can be taken by mouth or intravenously with doses once per day.[2] Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and upset stomach. Omeprazole. Omeprazole, sold under the brand names Prilosec and Losec among others, is a medication used in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease, peptic ulcer disease, and Zollinger–Ellison syndrome.[1] It is also used to prevent upper gastrointestinal bleeding in people who are at high risk.[1] It can be taken by mouth or injected into a vein.[1][4] Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, headaches, and increased intestinal gas.
Serious side effects may include Clostridium difficile colitis, an increased risk of pneumonia, an increased risk of bone fractures, and the potential of masking stomach cancer. Amlodipine. Levothyroxine. Lisinopril. Lisinopril is a drug of the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor class used primarily in treatment of high blood pressure, heart failure, and after heart attacks. Statins. Statins are a group of medicines that can help lower the level of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in the blood. LDL cholesterol is often referred to as "bad cholesterol", and statins reduce the production of it inside the liver. Simvastatin. Simvastatin, marketed under the trade name Zocor among others, is a lipid-lowering medication.[1] It is used along with exercise, diet, and weight loss to decrease elevated lipid (fat) levels. Hydrocodone. Hydrocodone is a semi-synthetic opioid synthesized from codeine, one of the opioid alkaloids found in the opium poppy.
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) Corticosteroids. (Also Called 'Prednisone') What are corticosteroids? Corticosteroids are man-made drugs that closely resemble cortisol, a hormone that your adrenal glands produce naturally. Corticosteroids are often referred to by the shortened term "steroids. " Corticosteroids are different from the male hormone-related steroid compounds that some athletes abuse. Treatment of Vascular Malformations. Vascular Malformation Treatment Seminar Watch Sally Mitchell and Clifford Weiss discuss treatment of a Vascular Malformation at the Johns Hopkins Hospital. 10 Cutting Edge Medical Devices Recognized For Excellence In Design. The 2009 Medical Design Excellence Awards (MDEA) were announced this week by the Medical Device and Diagnostic Industry. There were 32 award winners and every one of the winners contributed a medical device that advances their industry and provides cutting edge technology to improve patient care.
Space and time don't allow me to introduce all of these devices to you, so I randomly selected 10 just to give you a sampling of medical inventions that may be significant to you some day. Linear Accelerator (LINAC) Nebulisers in General Practice. About nebuliser devices. Antibiotic awareness - The NHS in England. Sulfonamide (medicine) Scoliosis - Treatment for adults. This Guy Just Raised The Cost Of An HIV Drug By 5000% What is cyclophosphamide? CyclophosphamideActivation. 3D-Printed Hearts Help Surgeons Save Babies' Lives. ‘Ambulance Drone’ Could Drastically Increase Heart Attack Survival. Investigating Dimebon, a promising new drug for Alzheimer’s disease. Scientists Grow New Blood Vessels In Just 7 Days. Man With Severed Spinal Cord Walks Again After Cell Transplant.
Complete cardiac transplant. Endotracheal intubation: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia.