

VIDS: re-enactment. Braddock's defeat Battle of Monongahela river. Battle : Braddock’s defeat on the Monongahela River War : The French and Indian War also known as the Seven Year War (1757 to 1762) Date : 9th July 1755 The French & Indians launch their attack on the British & American troops; Braddock falls shot while George Washington attempts to assist him.
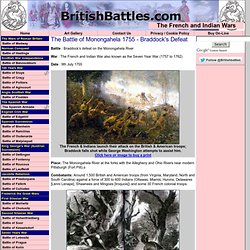
Click here or image to buy a print Place: The Monongahela River at the forks with the Allegheny and Ohio Rivers near modern Pittsburgh (Fort Pitt).s Combatants: Around 1,500 British and American troops (from Virginia, Maryland, North and South Carolina) against a force of 300 to 600 Indians (Ottawas, Miamis, Hurons, Delawares [Lenni Lenape], Shawnees and Mingoes [Iroquois]) and some 30 French colonial troops. The Battle of Ticonderoga 1758. The Battle of Louisburg 1758. Battle: LOUISBURG War: The French and Indian War also known as the Seven Year War (1757 to 1762) Date: 27th July 1758 Place: On the North East coast of Nova Scotia on the eastern seaboard of Canada.

Combatants: British and Americans against the French and Canadians. Generals: General Amherst commanded the British and American force with Brigadier James Wolfe as one of his subordinate commanders. Battle of the Plains of Abraham. The Battle of the Plains of Abraham, also known as the Battle of Quebec, (Bataille des Plaines d'Abraham or Première bataille de Québec in French) was a pivotal battle in the Seven Years' War (referred to as the French and Indian War in the United States).
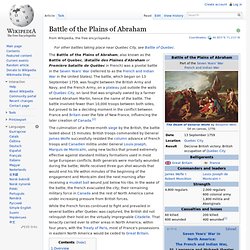
The battle, which began on 13 September 1759, was fought between the British Army and Navy, and the French Army, on a plateau just outside the walls of Quebec City, on land that was originally owned by a farmer named Abraham Martin, hence the name of the battle. The battle involved fewer than 10,000 troops between both sides, but proved to be a deciding moment in the conflict between France and Britain over the fate of New France, influencing the later creation of Canada.[2] Overview[edit] A portrait of Wolfe printed circa 1776 In preparation for the fleet's approach to Quebec, James Cook surveyed a large portion of the river, including a dangerous channel known as The Traverse. Preparations[edit] Death of General Wolfe (by Benjamin West, 1770) Death of General Montcalm (by Charles Jefferys)
Louis-Joseph de Montcalm. Montcalm was born near Nîmes in France to a noble family, and entered military service early in life.
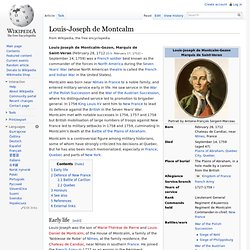
He saw service in the War of the Polish Succession and the War of the Austrian Succession, where his distinguished service led to promotion to brigadier general. In 1756 King Louis XV sent him to New France to lead its defence against the British in the Seven Years' War. Montcalm met with notable successes in 1756, 1757 and 1758 but British mobilisation of large numbers of troops against New France led to military setbacks in 1758 and 1759, culminating in Montcalm's death at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham.
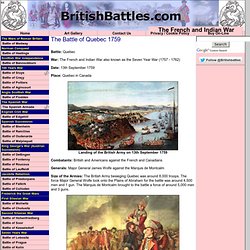
Montcalm is a controversial figure among military historians, some of whom have strongly criticized his decisions at Quebec. But he has also been much memorialized, especially in France, Quebec and parts of New York. Early life[edit] Defence of New France[edit] Montcalm trying to stop Native Americans from attacking British soldiers and civilians as they leave Fort William Henry. The Battle of Quebec 1759. Battle: Quebec War: The French and Indian War also known as the Seven Year War (1757 - 1762) Date: 13th September 1759 Place: Quebec in Canada.
French Empire in America, 1753. 1763: North America following Treaty of Paris. French and Indian Wars (1688-1763) Not to be confused with French and Indian War, the name given to the fourth conflict of the following wars The French and Indian Wars is a name used in the United States for a series of intermittent conflicts between the years 1689 and 1763 in North America that represented colonial events related to the European dynastic wars.
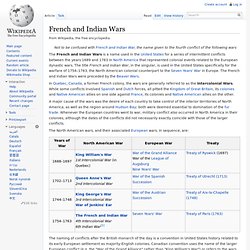
The title French and Indian War, in the singular, is used in the United States specifically for the warfare of 1754–1763, the North American colonial counterpart to the Seven Years' War in Europe. The French and Indian Wars were preceded by the Beaver Wars. In Quebec, Canada, a former French colony, the wars are generally referred to as the Intercolonial Wars. While some conflicts involved Spanish and Dutch forces, all pitted the Kingdom of Great Britain, its colonies and Native American allies on one side against France, its colonies and Native American allies on the other.
VID: The Seven Years War. The Seven Years War and the Great Awakening: Crash Course US History #5. VID: French & Indian Wars. Last revised: March, 2014 Acceptance of Terms Please read this Terms of Service Agreement ("Terms of Service", "Terms of Use") carefully.
These terms apply to Education Portal and its related websites owned and operated by Remilon, LLC ("Education Portal,", "Site", "Sites", "our", "us"). Education Portal provides the Services, which are defined below, to you subject to the following Terms of Service, which may be updated by us from time to time without notice to you. BY ACCESSING, BROWSING OR USING THE SITE AND THE SERVICES PROVIDED THROUGH OR IN CONNECTION WITH EDUCATION PORTAL, YOU SIGNIFY AND ACKNOWLEDGE THAT YOU HAVE READ THE TERMS OF SERVICE AND AGREE THAT THE TERMS OF SERVICE CONSTITUTES A BINDING LEGAL AGREEMENT BETWEEN YOU AND EDUCATION PORTAL, AND THAT YOU AGREE TO BE BOUND BY AND COMPLY WITH THE TERMS OF SERVICE.
Privacy Policy Education Portal respects your privacy and permits you to control the treatment of your personal information. Terms Applicable to All Services a. I. B. French and Indian War. Not to be confused with the French and Indian Wars, the name given to a series of conflicts, which includes the following war.
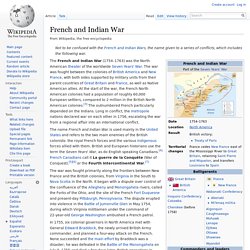
The name French and Indian War is used mainly in the United States and refers to the two main enemies of the British colonists: the royal French forces and the various indigenous forces allied with them. British and European historians use the term the Seven Years' War, as do English speaking Canadians.[4] French Canadians call it La guerre de la Conquête (War of Conquest).[5][6] or the Fourth Intercontinental War.[7]