

Wyoming. Wyoming i/waɪˈoʊmɪŋ/ is a state in the mountain region of the Western United States.
Geography[edit] Location and size[edit] As specified in the designating legislation for the Territory of Wyoming, Wyoming's borders are lines of latitude, 41°N and 45°N, and longitude, 104°3'W and 111°3'W (27° W and 34° W of the Washington Meridian), making the shape of the state a latitude-longitude quadrangle.[5] Wyoming is one of only three states (along with Colorado and Utah) to have borders along only straight latitudinal and longitudinal lines, rather than being defined by natural landmarks. Utah. Utah (/ˈjuːtɔː/ or i/ˈjuːtɑː/; (Navajo: Áshįįh bi Tó Hahoodzo; Arapaho: Wo'tééneihí [7]) is a state in the western United States.
It became the 45th state admitted to the Union on January 4, 1896. Utah is the 13th-largest, the 33rd-most populous, and the 10th-least-densely populated of the 50 United States. Utah has a population of about 2.9 million, approximately 80% of whom live along the Wasatch Front, centering on Salt Lake City.[8] Utah is bordered by Colorado to the east, Wyoming to the northeast, Idaho to the north, Arizona to the south, and Nevada to the west. It also touches a corner of New Mexico in the southeast. The state is a center of transportation, education, information technology and research, government services, mining, and a major tourist destination for outdoor recreation. Etymology[edit] New Mexico. New Mexico (Spanish: Nuevo México [ˈnweβo ˈmexiko]; Navajo: Yootó Hahoodzo [jo:tó haho:dzo]) is a state located in the southwestern and western regions of the United States, admitted to the union as the 47th state on January 6, 1912.
It is usually considered one of the Mountain States. New Mexico is the fifth-most extensive, the 36th-most populous, and the sixth-least densely populated of the 50 United States. Inhabited by indigenous peoples of the Americas for many centuries before European exploration, New Mexico was subsequently part of the Imperial Spanish viceroyalty of New Spain. Later, it was part of Mexico before becoming a U.S. territory and eventually a U.S. state.
Among U.S. states, New Mexico has the highest percentage of Hispanics, including descendants of Spanish colonists who have lived in the area for over 400 years. New Mexico, or Nuevo México in Spanish, is often incorrectly believed to have taken its name from the nation of Mexico. Nevada. Nevada is a state in the Western, Mountain West, and Southwestern regions of the United States.
Nevada is the 7th most extensive, the 35th most populous, and the 9th least densely populated of the 50 United States. Nearly three-quarters of Nevada's people live in Clark County, which contains the Las Vegas–Paradise metropolitan area[5] where the state's three largest incorporated cities are located.[6] Nevada's capital is Carson City. Nevada is officially known as the "Silver State" due to the importance of silver to its history and economy. It is also known as the "Battle Born State", because it achieved statehood during the Civil War; as the "Sagebrush State", for the native plant of the same name; and as "Sage hen State".[7] Before European contact, Native Americans of the Paiute, Shoshone, and Washoe tribes inhabited the land that is now Nevada.
Nevada has a reputation for its libertarian laws. Etymology and pronunciation[edit] A topographic map of Nevada Geography[edit] Climate[edit] Montana. Montana i/mɒnˈtænə/ is a state in the Western region of the United States.
The state's name is derived from the Spanish word montaña (mountain). Montana has several nicknames, although none official, including "Big Sky Country" and "The Treasure State", and slogans that include "Land of the Shining Mountains" and more recently "The Last Best Place". Montana has a 545-mile (877 km) border with three Canadian provinces: British Columbia, Alberta, and Saskatchewan, the only state to do so. Idaho. Digitally colored elevation map of Idaho.
Reynolds Creek Experimental Watershed in the Owyhee Mountains, about 50 miles (80 km) southwest of Boise, Idaho Idaho ( Colorado. State of the United States of America State in the United States Colorado (, other variants)[8][9][10] is a state in the Mountain West region of the United States.
It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the Great Plains. Colorado is the eighth most extensive and 21st most populous U.S. state. The estimated population of Colorado is 5,758,736 as of 2019, an increase of 14.5% since the 2010 United States Census.[11] The region has been inhabited by Native Americans for more than 13,000 years, with the Lindenmeier Site containing artifacts dating from approximately 9200 BCE to 1000 BCE; the eastern edge of the Rocky Mountains was a major migration route for early peoples who spread throughout the Americas. Denver is the capital and most populous city in Colorado. Arizona. Saguaro cactus flowers and buds after a wet winter.
This is Arizona's official state flower. Arizona ( i/ɛrɪˈzoʊnə/; /ærɪˈzoʊnə/) (Navajo: Hoozdo Hahoodzo; O'odham: Alĭ ṣonak) is a state in the southwestern region of the United States. États des montagnes. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
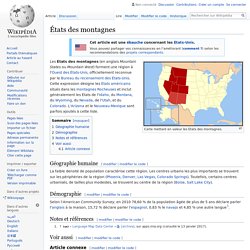
Carte mettant en valeur les États des montagnes. Les États des montagnes (en anglais Mountain States ou Mountain West) forment une région à l'Ouest des États-Unis, officiellement reconnue par le Bureau du recensement des États-Unis. Cette expression désigne les États américains situés dans les montagnes Rocheuses et inclut généralement les États de l'Idaho, du Montana, du Wyoming, du Nevada, de l'Utah, et du Colorado.
L'Arizona et le Nouveau-Mexique sont parfois ajoutés à cette liste. Géographie humaine[modifier | modifier le code] Démographie[modifier | modifier le code] Notes et références[modifier | modifier le code] Voir aussi[modifier | modifier le code] Article connexe[modifier | modifier le code] Montagnes Rocheuses.