

The Philippines's alternative weekly magazine. Bilingual (Tagalog-English) version of Epics “Mga Epiko” Kundiman. Kundiman is a genre of traditional Filipino love songs.
Principalía. For the most part, the social privileges of the nobles were freely acknowledged as befitting their greater social responsibilities.
The gobernadorcillo during that period received a nominal salary and was not provided government funds for public services. In fact more often the gobernadorcillo had to maintain government of his municipality by looking after the post office and the jailhouse, and by managing public infrastructure.[1](p326)[9](p294) History and evolution[edit] Pre-colonial principalities[edit] Portrait of a pre‑conquest Visayan (Panay) noble couple depicted in Boxer Codex. Chavacano language. Chavacano or Chabacano [tʃaβaˈkano] is a Spanish-based creole language spoken in the Philippines.
The word Chabacano is derived from Spanish, meaning "poor taste", "vulgar", for the Chavacano language which was developed in Cavite City, Ternate, Zamboanga and Ermita. It also derived from the word chavano which was coined by the people of Zamboanga. Six different dialects have developed: Zamboangueño in Zamboanga City, Davaoeño Zamboangueño / Castellano Abakay in Davao City, Ternateño in Ternate, Cavite, Caviteño in Cavite City, Cotabateño in Cotabato City and Ermiteño in Ermita. Background information[edit] Linguistic significance[edit] Nick Joaquin. Nicomedes Márquez Joaquín (May 4, 1917 – April 29, 2004) was a Filipino writer, historian and journalist, best known for his short stories and novels in the English language.
He also wrote using the pen name Quijano de Manila. Joaquin was conferred the rank and title of National Artist of the Philippines for Literature. He is considered[by whom?] One of the most important Filipino writers in English, and the third most important overall, after José Rizal and Claro M. Recto. Biography[edit] Early life and education[edit] Filipino folk music. Bong Bong? A Filipina woman asks, Do we have the wackiest names? Vedic Empire - Indian Origins of Filipino Customs. Early Relations with India The early relations between the Philippines and the Indian empires of Sri-Vijaya and Majapahit were commercial and cultural, not political.
As a free and independent people, the early Filipinos carried on trade with Borneo, Celebes, Java, Sumatra, and other countries of Southeast Asia. And through Sri-Vijaya and Majapahit, they received India's cultural influences. ‘Aswang, Aswang!’ - INQUIRER.net, Philippine News for Filipinos. MANILA, Philippines - Halloween schmalloween, my more nationalistic friends complain, why are we celebrating this western concoction?
Yet, Filipinos do enjoy Halloween and I suspect that amid all those western-based witches and goblins, we do see, from our own culture, the aswang. The aswang has been reincarnated many times over. Ask a Metro Manila kid from the slums from which many modern-day sightings of the aswang have been reported, and they? Ll answer ? Bampira,? Animism and Christianity mixed among the Bukidnon of Panay. Advertisement After our introduction to the Ati people, the sellers in the Barter of Panay, we decided to trek through an area inhabited by the Bukidnon people, the alleged buyers.
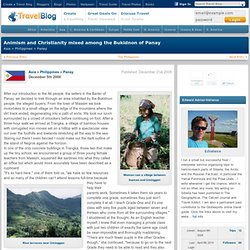
From the town of Maasim we took motorbikes to a small village on the edge of the mountains where the dirt track ended, degenerating into a path of sorts. We took our lunch surrounded by a crowd of onlookers before continuing on foot. After a three-hour walk we arrived at Trangka, a village of bamboo houses with corrugated iron rooves set on a hilltop with a spectacular view out over the foothills and lowlands stretching all the way to the sea. Religious Beliefs and Cosmology of the Filipinos, Indigenous beliefs. Check out Paul Kekai Manansala's book at lulu.com!
Philippines YogaMeditation SydneyMindfulness Indigenous Religious Beliefs and Cosmology of the Filipino Table of Contents Introduction. Digital Library - Hermano Pule. Apolinario de la Cruz (July 22, 1814 - November 4, 1841), known as Hermano Pule or Puli ("Brother Pule"), led a major revolt against Spanish rule of the Philippines based on a struggle for religious freedom and independence.
Rizal Park monument Early life[edit] Hermano Pule was born on July 22, 1814 in Barrio Pandác in the town of Lucban in Tayabas province (now Quezon). Tamblot Uprising. The Tamblot Uprising of 1621, also known as the Tamblot Revolution or Tamblot Revolt, was led by Tamblot, a babaylan or native priest from the island of Bohol in the Philippines.
It was basically a religious conflict.[1] Tamblot exhorted his people to return to the faith of their forefathers and free themselves from Spanish oppression.[2] Tamblot[edit] Tamblot was a tumanan or hermit. He was also a biki or high priest of the local organized religion in Bohol dedicated to the god Ay Sono. Filipino History. * Ancient and pre-Spanish Era * Pre-Spanish influence, modern day * Magellan and the Spanish influence * Americas first entanglement * The Japanese and WWII years * Americas final rule * Early Independence Period * The Marcos Era * The Aquino Years and Beyond Ancient and pre-Spanish Era: It is believed that the first inhabitants of the Philippines arrived over many thousands of years ago. It is commonly thought that they migrated over a land bridge, which existed at that time, from the Asian mainland. List of Filipino Saints, Blesseds, and Servants of God. This is a list of Filipino Saints, Blesseds, and Servants of God recognized by the Roman Catholic Church.
Catholicism existed many years ago. It was brought by the Spanish explorers, with some priest and layperson companions, beginning with Ferdinand Magellan. Roman Catholicism in the Philippines. The Roman Catholic Church in the Philippines is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, with its head being the Pope. It is also one of two nations in Asia with a predominantly Roman Catholic population (the other being East Timor), and is the third largest Catholic country in the world (after Brazil and Mexico).[1] History[edit] Spanish Era[edit] Islam in the Philippines. Islam is the oldest recorded monotheistic religion in the Philippines. Islam reached the Philippines in the 14th century with the arrival of Muslim traders from the Persian Gulf, Southern India, and their followers from several sultanate governments in the Malay Archipelago. According to the U.S. Department of State International Religious Freedom Report for 2010, the Muslim population of the Philippines is between 5% to 9%,[1] majority are Sunnites with Shiite minority.
While the majority of the population are Roman Catholic, some ethnic groups are Protestant, non-religious, Hindu, Buddhist and Animist.[2] History[edit] Hinduism in the Philippines. OM, a sacred syllable and a quintessential symbol of Hinduism. Its meanings are many. Hinduism has been a major cultural, economic, political and religious influence in the archipelago that now comprise the Philippines. At present, however, it is limited to a small recent immigrant Indian community, though traditional religious beliefs in most parts of the country have strong Hindu and Buddhist influences. Hinduism arrived from the Javanese empire of Majapahit.[1] History[edit] Pre-contact period[edit]
Buddhism in the Philippines (pre-colonial period) There is little evidence remaining of the nature of religion in pre-colonial Philippines. The possibilities include animism, Philippine mythologies such as Anito, and influences from Hinduism or Buddhism. The earliest pieces of evidence that exist are archaeological finds including Hinduist or Buddhist gold statues. Buddhism in the Philippines. Arts of the Philippines: The Manunggul Jar as a Vessel of History. THE MANUNGGUL JAR AS A VESSEL OF HISTORYby: Michael Charleston B. Chua "…the work of an artist and master potter. "--Robert Fox 27th April 1995—I was 11 years old when I visited the National Museum -- the repository of our cultural, natural and historical heritage.
Manunggul Jar - WikiPilipinas: The Hip 'n Free Philippine Encyclopedia. Museum of the Filipino People. Proa. Plan of a Micronesian proa, from a 1742 sketch by Lt. Peircy Brett, an officer on Lord Anson's round-the-world voyage. University of Santo Tomas. University of San Carlos. For the similarly named university in Guatemala, see Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala. The University of San Carlos (USC) is a private Catholic university in Cebu City which is administered and managed by the Society of the Divine Word since 1935. It offers a Montessori preparatory academy, Basic Education, 80 Undergraduate, and 85 Graduate programs, with a broad spectrum of academic disciplines through its 8 colleges and 27 departments. Maragtas. Quezon Bridge.