

Naval history. Naval history is the area of military history concerning war at sea and the subject is also a sub-discipline of the broad field of maritime history.
Traditionally, the focus has been on direct combat between ships at sea, rather than the use of ships to transport armies or military supplies, although frequently naval strategy hinges on the need to protect transport shipping. Recent writing in naval history has expanded the scope of the subject to include the full range of issues associated with navies, including matters of technology, finance, bureaucracy, social history, shipbuilding, supply, and logistics. See also[edit] External links[edit] 1795–1820 in fashion. Painting of a family game of checkers ("jeu des dames") by French artist Louis-Léopold Boilly, c. 1803.
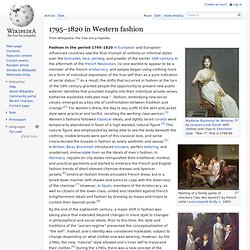
In the early 1800s, women wore thin gauzy outer dresses while men adopted trousers and overcoats. Rutger Jan Schimmelpenninck and his family, 1801–02. A well-to-do family edge cautiously along a plank to avoid the filthy streets of Paris, by Boilly, 1803 By the end of the eighteenth century, a major shift in fashion was taking place that extended beyond changes in mere style to changes in philosophical and social ideals. Prior to this time, the style and traditions of the “ancien-regime” prevented the conceptualization of “the self”. Changes in fashion[edit] 1790s: 1800s: 1810s: 1820s: Women: dress waist lines began to drop; elaborate hem and neckline decoration; cone-shaped skirts; sleeves pinchedMen: overcoats/greatcoats w. fur of velvet collars; the Garrick coat;[17] Wellington boots; jockey boots.
Coat of arms. Sometimes the term coat of arms is used to refer to the full achievement, but this usage is wrong in a strict sense of heraldic terminology.[1][2] The ancient Romans used similar insignias on their shields, but these identified military units rather than individuals.
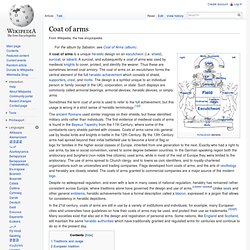
The first evidence of medieval coats of arms is found in the Bayeux Tapestry from the 11th Century, where some of the combatants carry shields painted with crosses. Coats of arms came into general use by feudal lords and knights in battle in the 12th Century. By the 13th Century arms had spread beyond their initial battlefield use to become a kind of flag or logo for families in the higher social classes of Europe, inherited from one generation to the next. Exactly who had a right to use arms, by law or social convention, varied to some degree between countries. Traditions and usage[edit]
Simo Häyhä. Simo Häyhä (Finnish pronunciation: [ˈsimɔ ˈhæy̯hæ]; December 17, 1905 – April 1, 2002), nicknamed "White Death" (Russian: Белая смерть, Belaya Smert; Finnish: valkoinen kuolema; Swedish: den vita döden) by the Red Army, was a Finnish marksman.
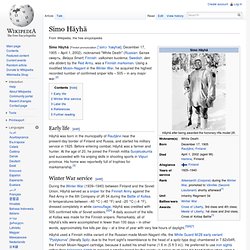
Using a modified Mosin–Nagant in the Winter War, he acquired the highest recorded number of confirmed sniper kills – 505 – in any major war.[2] Early life[edit] 5 Real Life Soldiers Who Make Rambo Look Like a Pussy. We all understand that action movies are cheesy escapism.
After all, could one commando really take out a whole compound full of bad guys? Actually, yes. It turns out the history books are full of stories of soldiers doing things so badass they'd hesitate to put them into a film for fear of killing the realism. Like these five, for example. #5. Who Was He? Simo Hayha had a fairly boring life in Finland. List of designated terrorist organizations. This is a list of designated terrorist organizations by national governments, former governments and inter-governmental organizations, where the proscription has a significant impact on the group's activities.
Many organizations that are accused of being a terrorist organization deny using terrorism as a military tactic to achieve their goals, and there is no international consensus on the legal definition of terrorism.[1][2] Organizations currently officially designated as terrorist by various governments[edit]
Europe. Middle East. Heraldry. Wars and Battles - Wars and Battles in History. Since the dawn of time, wars and battles have had a significant impact on the course of history.
From the earliest battles in ancient Mesopotamia to today's war in Iraq, conflicts have had the power to shape and change our world. Conflict Overviews Throughout history, conflicts have been solved by wars. Over the centuries combat has become increasingly more sophisticated, but war's ability to change the world has stayed the same. Military History Timelines Gain a quick overview of military history with these timelines that trace battles and wars through the ages. Great Battles.
JAPAN. GERMANY. Eagle (heraldry) One style of heraldic eagle, typical of German and Scandinavian heraldry In medieval and modern heraldry eagles are often said to indicate that the armiger (person bearing the arms) was courageous, a man of action and judicious.
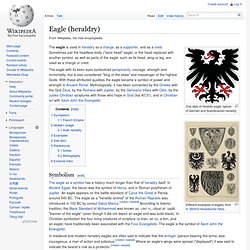
[citation needed] Where an eagle's wings were spread ("displayed") it was said to indicate the bearer's role as a protector. [citation needed] From the reign of Frederick Barbarossa in 1155 the single-headed eagle became a symbol of the Holy Roman Empire. The eagle was clearly derived from the Roman eagle and continues to be important in the heraldry of those areas once within the Holy Roman Empire. The French Imperial Eagle or Aigle de drapeau (lit. Heraldic eagles are enduring symbols of many countries, including the German Bundesadler.
Ancient Rome.