

Ww2 lesson plans. What was life really like for children and adults in World War Two?

To have to cope not only with the rationing and evacuee programmes, but also the Blitz, the Battle of Britain and the threat of invasion? To live in a time when sticking together and standing strong was not only expected but essential? Find out now in our exciting, interactive WW2 workshop delivered direct to your school and tailored perfectly to both the current creative curriculum and also the new 2014 National Curriculum for History.
Planned and delivered by an experienced QTS teacher, our workshop takes pupils back in time to the age of the 'Blitz spirit' in the form of a fun simulated Air Raid Warden training day, planned from the ground up with two main aims in mind. One, to bring your Second World War topic to life in a totally new way and two, to teach towards and to expand upon the topic objectives, so that your pupils will learn above and beyond all your expectations. History: World War Two. 1L KOKODA WW2. Australians in World War II. Nazi Propaganda (1933-1945) Adolf Hitler. Adolf Hitler was born on 20th April, 1889, in the small Austrian town of Braunau near the German border.
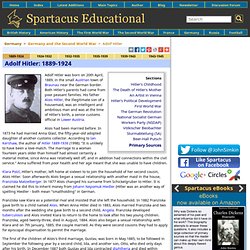
Both Hitler's parents had come from poor peasant families. Hitler Youth Materials. Kurt Gruber formed the first group of young members of the National Socialist German Workers Party (NSDAP) in 1926.
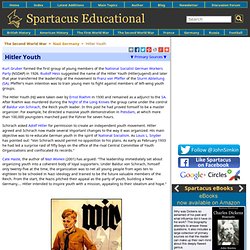
Rudolf Hess suggested the name of the Hitler Youth (Hitlerjugend) and later that year transferred the leadership of the movement to Franz von Pfeffer of the Sturm Abteilung (SA). Pfeffer's main intention was to train young men to fight against members of left-wing youth groups. Hitler and Nazi Germany. Dunkirk. Dunkirk, and the evacuation associated with the troops trapped on Dunkirk, was called a "miracle" by Winston Churchill.
The Battle for Stalingrad. Indigenous servicemen: their contribution. Military history of Australia during World War II - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Australia entered World War II shortly after the invasion of Poland, declaring war on Germany on 3 September 1939.
By the end of the war, almost a million Australians had served in the armed forces, whose military units fought primarily in the European theatre, North African campaign, and the South West Pacific theatre. In addition, Australia came under direct attack for the first time in its post-colonial history. Anzac Org.
The U-boat war 1940. U-boats were to play an important part in World War Two.
Winston Churchill claimed that the U-boat war was the only time that he felt that Britain might have to contemplate surrender. Submarines had made their mark in World War One – now, just twenty years later, the impact of the U-boats was devastating. Germany’s U-boat fleet operated out of their north German bases before the fall of France. After June 1940, they primarily used bases on the west coast of France to get to the Atlantic.
Battle of the Atlantic. The Battle of the Atlantic, which lasted from September 1939 until the defeat of Germany in 1945, was the war’s longest continuous military campaign.

During six years of naval warfare, German U-boats and warships – and later Italian submarines – were pitted against Allied convoys transporting military equipment and supplies across the Atlantic to Great Britain and the Soviet Union. This battle to control the Atlantic shipping lanes involved thousands of ships and stretched across thousands of perilous square miles of ocean. Early in the war German warships made a number of forays into the shipping lanes, aiming to catch and destroy Allied convoys. These had limited success, and led to the loss of major ships including Graf Spee and Bismarck. The Exploding Anti-Tank Dogs of World War II.
Today I found out about the use of exploding anti-tank dogs during World War II.
These dogs, usually Alsatians, were also called “Hundminen” or “dog mines.” They were trained to carry explosives on their bodies to enemy tanks, where they would then be detonated. No, it did not end very well for the dogs in question. This type of animal weaponry was first used by the Soviets. Following a decision in 1924 to allow dogs to aid the military, a dog training school was set up in Moscow. At first, dogs were trained to carry supplies, tracking mines, and rescuing people -tasks at which the dogs excelled.
There were several reasons that these methods didn’t work. The Soviets scrapped their initial plan, but unfortunately for Fido, they came up with a new one. How Churchill Led Britain To Victory In The Second World War. Winston Churchill became Britain's prime minister on 10 May 1940.
As he was later to write: 'I felt...that all my past life had been but a preparation for this hour and for this trial'. On the very day that Churchill fulfilled his life's ambition, Germany had, that morning, invaded France, Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg. Britain faced its supreme test. Winston Churchill: greatest British hero or a warmongering villain? Sir Winston Churchill, a journalist, a soldier, and a war-time leader, was a maverick who divided opinion throughout his lengthy political career.
As the 50th anniversary of his death approaches, historians and journalists appear no closer to agreeing on his legacy. We weigh up the leading arguments on both sides. Churchill as hero: Pearl Harbor Tour Reservations & Visitor Information. History - World Wars: Pearl Harbor: A Rude Awakening. The Battle of Stalingrad. The Battle of Stalingrad is considered by many historians to have been the turning point in World War Two in Europe. The battle at Stalingrad bled the German army dry in Russia and after this defeat, the Germany Army was in full retreat. One of the ironies of the war, is that the German Sixth Army need not have got entangled in Stanlingrad. Army Groups A and B were well on their way to the Caucasus in south-west Russia, when Hitler ordered an attack on Stalingrad. From a strategic point of view it would have been unwise to have left a major city unconquered in your rear as you advanced. The most brutal battle in history. Germans fighting for every inch of the road to Stalingrad, 1942 [] Four-and-a-half-million men deploying 600,000 vehicles, 3,700 tanks, 750,000 horses, 1,800 bombers and fighters and half a million guns streamed eastwards on a 1,800-mile-long front at 3.15am on the morning of June 22, 1941.
They were the bearers of a New World Order whose cruelty would beggar belief. This was the start of Operation Barbarossa, Hitler’s assault on the Soviet Union intended to wipe out communism, the Jewish race, and to give Germans the “living space” upon the vast Russian steppes that the Führer had promised his people in Mein Kampf. By the time the battle for the Eastern front was over at the end of 1944 an estimated seven million Russian soldiers had died in combat while a staggering 20 million civilians were murdered, killed in the fighting or in captivity, or starved to death. More than four million German troops died. Battle of Stalingrad - World War II. The Russians hailed it a “contemporary Cannae,” and the Germans condemned it as a Rattenkrieg (Rat War).
Both descriptions were fitting. In the Battle of Stalingrad, Soviet forces surrounded and crushed an entire German army under General Friedrich Paulus, emulating Hannibal’s encirclement and destruction of a Roman army under Aemilius Paulus in 216 B.C. For both sides, Stalingrad became a desperate ordeal of rodentlike scurrying from hole to hole. D-Day. D-Day At 3 am on 6 June 1944, a huge armada of 6,000 ships – including 864 converted merchant ships and 4126 landing craft – set sail for Normandy in 47 convoys. They carried 200,000 seamen, 185,000 soldiers and 20,000 vehicles.
The weather was still fairly bad. Many of the soldiers were so seasick that they joked that they would not mind going into battle, just to get off the ships! A few Royal Navy ships raced back and forth between Dover and Calais to make Nazi radar operators think that the invasion was going to take place at Calais. 20,000 men were dropped by parachute or landed in gliders behind enemy lines to disrupt communications and seize key points. 20 things Dday. D-Day - June 6, 1944: On the Beach.
By the end of the day, the Allies had achieved a tenuous toehold that would be laboriously expanded over the next weeks and would lead ultimately to the Nazi defeat in the West. Robert Edlin was a member of the 2nd Ranger Battalion that joined the first wave of the assault on Omaha Beach. We join his story as he his assault craft becomes mired on a sandbar: "Our assault boat hit a sandbar. Battle of Britain. The Battle of Britain was a struggle between the German Luftwaffe (commanded by Hermaan Göring) and the British Royal Air force (headed by Sir Hugh Dowding’s Fighter Command) which raged over Britain between July and October 1940.
8 Things You Need To Know About The Battle Of Britain. The Battle of Britain, as it happened on September 15, 1940. On September 16, the Germans moved to a new tactic: terror bombing. Daylight raids were abandoned in favour of what we now call the Blitz. The aim was still to break our spirit, but that was now harder than ever. Britain had won its first real victory of the war, and its value to public morale was incalulable. Japanese American internment. World War II: The Pacific. Objectives. Pacific War Sources and Lessons. Compiled August 2005. WWII extensive detail. Women in WW2. MV Wilhelm Gustloff. The MV Wilhelm Gustloff was a German military transport ship which was sunk on 30 January 1945 by Soviet submarine S-13 in the Baltic Sea while evacuating German civilians, Nazi officials and military personnel from Gdynia (Gotenhafen) as the Red Army advanced.
By one estimate,[3] 9,400 people died, which makes it the largest loss of life in a single ship sinking in history. Constructed as a cruise ship for the Nazi Kraft durch Freude (Strength Through Joy) organisation in 1937, she had been requisitioned by the Kriegsmarine (German navy) in 1939. She served as a hospital ship in 1939 and 1940. She was then assigned as a floating barracks for naval personnel in Gdynia before being put into service to transport evacuees in 1945. Construction[edit] Wilhelm Gustloff was constructed by the Blohm & Voss shipyards. Cruise liner[edit]