

Cofactor Genomics Awarded NIH Grant to Develop a Circular RNA Enrichment Kit and Reference Profile. August 2014, Cofactor Genomics has been awarded a grant by the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), an institute of the NIH, to develop a standardized enrichment kit and define the normal reference profile for circular RNAs (circRNA) in the nervous system.
These types of products could prove critical in advancing studies focused on neuronal development, substance abuse, and psychiatric disorders. “This is truly an honor for our team, which has developed and refined many of the kits on the market for our industry clients. This is an opportunity to bring Cofactor’s expertise in kit and software development together with our team’s focus on RNA characterization solutions to develop a unique product that addresses a very specific need.” said Cofactor’s CEO Jarret Glasscock. Using galaxy-P to leverage RNA-Seq for the discovery of novel protein variations. Current practice in mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics is to identify peptides by comparison of experimental mass spectra with theoretical mass spectra derived from a reference protein database; however, this strategy necessarily fails to detect peptide and protein sequences that are absent from the database.
We and others have recently shown that customized proteomic databases derived from RNA-Seq data can be employed for MS-searching to both improve MS analysis and identify novel peptides. While this general strategy constitutes a significant advance for the discovery of novel protein variations, it has not been readily transferable to other laboratories due to the need for many specialized software tools. Researchers from the University of Wisconsin-Madison present three bioinformatic workflows that allow the user to upload raw RNA sequencing reads and convert the data into high-quality customized proteomic databases suitable for MS searching. Using next-generation RNA sequencing to identify imprinted genes. RNA Morphology. Roman Stocsits Interdisciplinary Centre for Bioinformatics University of Leipzig Peter F.

Stadler Bioinformatics Group Department of Computer Science University of Leipzig Functional non-coding RNA molecules can serve as a major source of data in molecular phylogenetics. But the peculiarities of RNA evolution, and in particular the long term conservation of their secondary structures, have been taken into account only recently.
Functional non-coding RNAs are e.g.: tRNA, rRNA, miRNAs, viral genomes, and transportation signals. Because the functions of non-coding RNA are mediated by their structures, selective pressure acts on these structures. Models: If selection acts to preserve a structural element in spite of sequence variation then it must carry some function. The workflow starts using a standard sequence alignment, RNAalifold extracts a consensus structure out of an sequence alignment, a set of basic structural features that are represented in all sequences.
Db. Events. EBI. Bioinfojournal. Tools. TRAC 45: Bioinformatic Analysis of Next Generation Sequencing Data. Biotechnology Training Courses at the National Institutes of Health This course will introduce students to bioinformatic analysis of next generation sequencing data, particularly for DNA-seq, RNA-seq, CHIP-seq, and epigenomics.
The course will be comprised of lectures and hand-on sessions. Lectures will cover background knowledge and survey various software programs. For hand-on sessions, command line tools will be presented and the galaxy web based platform will be used to analyze primary data. Cloud computing, genomic databases, and de novo assembly will be surveyed. Topics: Overview on Bioinformatics Tools: Galaxy (Pre-processing, Format Conversion, etc.), Databases and Tools, SNP Callers, Cloud; RNA-seq; CHIP-seq; Epigenomics; Cloud Computing; 10k Genomes; Data Visualization; Comparative Genomics and Genome Alignment (biology + software); Tutorial & Laboratory for de novo Assembly; RNA-seq, DNA-sequencing.
OSA: a fast and accurate alignment tool for R... [Bioinformatics. 2012. Bioinformatics postdoctoral research fellowship available. Description: The Greengard laboratory (Rockefeller University, New York, USA) is accepting applications from outstanding individuals for a 2-3 year postdoctoral research fellowship in the field of bio-informatics and/or applied mathematics.
The position is available immediately. The candidate should have a PhD in the field of bio-informatics or applied mathematics, ideally with some experience in biology related questions. The candidate should already be familiar with gene expression data analysis, preferably with RNA-Seq data analysis. Proficiency in Linux scripting, in a major programming language and in handling large datasets are a must. Greengard.bioinfo@gmail.com Employer: Rockefeller University has a long history of outstanding scientific research. Project: Our laboratory is now applying this technology to study various disorders and neurodegenerative diseases.
Biostar. Mybiosoftware. Bioinfo. Tip of the Week: SNPexp, correlation between SNPs & gene expression. SNPexp is a nice simple tool that uses PLINK to calculate the correlation (p-value) between SNPs in a given range of locations in the genome, or alternatively a list of specific SNP rsIDs, and the expression of a gene of interest.
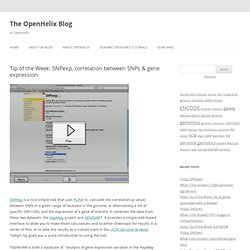
It combines the data from these two datasets: the HapMap project and GENEVAR*. It provides a simple web-based interface to allow you to make those calculations and to either download the results in a series of files, or to view the results as a custom track in the UCSC Genome Browser. Today’s tip gives you a quick introduction to using the tool.