

10 Transitional Ancestors of Human Evolution. Humans The evolution from our closest non-human ancestor to present day humans is one with many transitions.
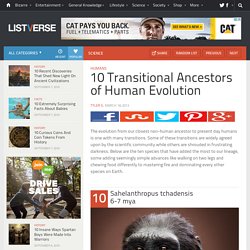
Some of these transitions are widely agreed upon by the scientific community while others are shrouded in frustrating darkness. Below are the ten species that have added the most to our lineage, some adding seemingly simple advances like walking on two legs and chewing food differently to mastering fire and dominating every other species on Earth.
14,000-year-old village unearthed on B.C. island by UVic student. CTV Vancouver Island Published Thursday, April 6, 2017 6:56PM PDT Last Updated Friday, April 7, 2017 1:07PM PDT An ancient village older than the pyramids has been unearthed by a University of Victoria student, and a B.C.
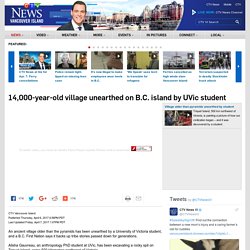
First Nation says it backs up tribe stories passed down for generations. Alisha Gauvreau, an anthropology PhD student at UVic, has been excavating a rocky spit on Triquet Island, some 500 kilometres northwest of Victoria. Oldest Human Fossil Discovered In Ethiopia. ShareTweetShareSendLink This 2.8 million-year-old jawbone may be the oldest human fossil in existence, according to two papers published simultaneously in Science.
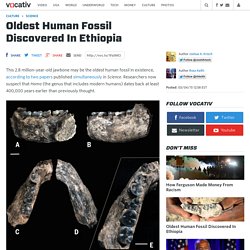
Researchers now suspect that Homo (the genus that includes modern humans) dates back at least 400,000 years earlier than previously thought. For decades scientists have been scouring Africa for ancient human remains. Human Ancestor May Put Twist in Origin Story. Known as the ancient human ancestor was discovered in the Malapa region of South Africa in 2008 and was described for the first time last April. (See "'Key' Human Ancestor Found: Fossils Link Apes, First Humans? " ) Now a suite of five studies, published in this week's issue of the journal is delving deeper into the species' unusual mix of human and apelike traits to help refine s place in the time line of human evolution . After examining s anatomy, for instance, scientists think they may have evidence that the species was capable of making and using tools. Meet 7 Celebrity Fossils and Find Out What Made Them Famous.
Research findings back up Aboriginal legend on origin of Central Australian palm trees. Updated The scientific world is stunned by research which backs an Aboriginal legend about how palm trees got to Central Australia.
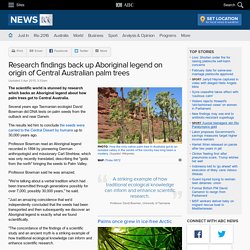
Several years ago Tasmanian ecologist David Bowman did DNA tests on palm seeds from the outback and near Darwin. A striking example of how traditional ecological knowledge can inform and enhance scientific research. Professor David Bowman, University of Tasmania The results led him to conclude the seeds were carried to the Central Desert by humans up to 30,000 years ago. Neanderthals Built Mystery Cave Rings 175,000 Years Ago. They painted magnificent cave paintings.
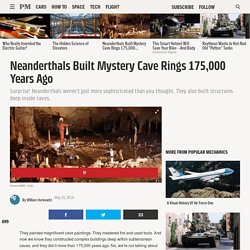
They mastered fire and used tools. And now we know they constructed complex buildings deep within subterranean caves, and they did it more than 175,000 years ago. No, we're not talking about early humans. Neanderthals did all this. Human Fossil Sites. Altamura Man. Altamura Man, surrounded by limestone deposits.
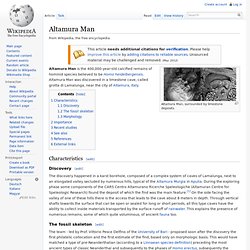
Altamura Man is the 400,000-year-old calcified remains of hominid species believed to be Homo heidelbergensis. Altamura Man was discovered in a limestone cave, called grotta di Lamalunga, near the city of Altamura, Italy. Characteristics[edit] Discovery[edit] Genetic Study Confirms Australian Aborigines Have Been Isolated For 50,000 Years. The indigenous aborigines of Australia have one of the oldest histories of any group of people living outside of Africa.
The general consensus is that modern humans reached the continent around 50,000 years ago, tens of thousands of years before humans even managed to populate Europe. The Iceman had a tummy bug. On the day that Ötzi the “Iceman” was murdered in the Tyrolean Alps of Italy about 5300 years ago, he had a full stomach—and a tummy bug.
But it wasn’t just any gut microbe—this early farmer was infected with a particular ancient strain of Helicobacter pylori bacteria that is most similar to modern Asian strains. By sequencing the genome of this ancient pathogen, which can cause ulcers in people today, researchers have made a surprising discovery about Ötzi’s own history: His ancestors inherited bacteria from Asia rather than Africa, suggesting that the predecessors of early European farmers had intimate contact with Asians before they migrated to Europe. The World's Cities Over the Last 6,000 Years. Oldest Human Footprints in North America Discovered. The footprints tell the story of a hunter-gatherer who marched through a marshy basin in the Chihuahuan Desert long before the Mesoamerican civilizations like the Mayans dominated the Mexican landscape.
“To my knowledge the oldest human prints previously reported in North America are around 6,000 years old,” Nicholas Felstead, a geoarchaeologist at Durham University in the U.K., said in a statement, according to Western Digs. Felstead, who spearheaded the new study of the tracks, was able to date the footprints because they were preserved in travertine, a sedimentary rock containing small traces of uranium. Since scientists know the rate at which uranium decays, becoming thorium, researchers were able to determine the footprints’ age by measuring the ratios of the two elements. According to their study, published in the Feb. 2014 edition of the Journal of Archaeological Science, North America’s oldest footprints were made around 10,550 years ago.
All blue-eyed people related to single European ancestor. Every blue-eyed person on the planet is descended from a single European who lived around 6,000 to 10,000 years ago, and who first developed a specific mutation that accounts for the now widespread iris coloration.
Originally, all humans had brown eyes, although genetic variation relating to a gene called OCA2 resulted in changes to the amount of pigment produced by different individuals, resulting in the emergence of different shades of brown. Oldest Javelins Predate Modern Humans, Raise Questions on Evolution. Charles Q. Choi The oldest known stone-tipped projectiles have been discovered in Ethiopia. The Jarawa, Onge and Sentinelese of the Andaman islands. Picture by Salome. Two women from the Jarawa people. These near pygmy sized ‘Negrito’ people live on the Andaman and Nicobar islands south of Myanmar. there are thought to be less then 300 of them now, and possibly even fewer, as a recent measles epidemic devasted their population.
No-one has ever been able to get enough to the Sentinelese for a photo, as they tend to shoot at helicopters and careless fishermen with arrows, which is very sensible of them. Ancient Hunter-Gatherers Kept in Touch. Until about 8500 years ago, Europe was populated by nomadic hunter-gatherers who hunted, fished, and ate wild plants. Then, the farming way of life swept into the continent from its origins in the Near East, including modern-day Turkey. Within 3000 years most of the hunter-gatherers had disappeared. Little is known about these early Europeans. Endangered Species: Humans Might Have Faced Extinction 1 Million Years Ago. Sentinelese people. The Sentinelese (also Sentineli, Senteneli, Sentenelese, North Sentinel Islanders) are an indigenous people of the Andaman Islands, in the Bay of Bengal. They inhabit North Sentinel Island, which lies westward off the southern tip of the Great Andaman archipelago.
They are noted for resisting attempts at contact by outsiders. The Sentinelese maintain an essentially hunter-gatherer society subsisting through hunting, fishing, and collecting wild plants. There is no evidence of either agricultural practices or methods of producing fire.[1] Their language remains unknown. The Sentinelese are a designated Scheduled Tribe.[2] Population[edit] The precise population of the Sentinelese is not known. On previous visits, groups of some 20–40 individuals were encountered regularly. Characteristics[edit] No close contacts have been established, however, the author Heinrich Harrer described one man as being 1.6 m (5' 4") tall and apparently left handed.[6] Culture[edit] Present situation[edit] See a familiar face? Big brains, no fur, sinuses - were our ancestors 'aquatic apes'?
It is one of the most unusual evolutionary ideas ever proposed: humans are amphibious apes who lost their fur, started to walk upright and developed big brains because they took to living the good life by the water's edge. Human phylogenic map. Ishango bone. Morning Edition. Ötzi. Light skin mutation stems from one ancestor. All instances of a gene mutation that contributes to light skin color in Europeans came from the same chromosome of one person who most likely lived at least 10,000 years ago, according to researchers.
Paranthropus boisei: 1.34-Million-Year-Old Hominin Found in Tanzania. "The Crossed Bison" (understand 3D) Jimmy Nelson Photographs Vanishing Tribes in Before They Pass Away. Photographer Jimmy Nelson in Papua New Guinea I’ve been fascinated by tribal cultures for over 20 years, ever since I interviewed my grandfather about our family history and learned we had American Indian blood on both sides. The 5 Strangest Things Evolution Left in Your Body. Becoming Human. Ardi Continues to Shake the Human Family Tree. Why crying babies are so hard to ignore. Olduvai Gorge ("The Cradle of Mankind") Lucy Skeleton. Archaeologists discover the earliest complete example of a human with cancer.
(17 March 2014) Dance, Monkeys, Dance. Adam and Eve: Adam's rib count. Claim CB381: As related in Genesis 2, Eve was created from one of Adam's ribs. CRACKED: 6 Things Your Body Does Every Day That Science Can't Explain. Ape Skeletal Similarities [not to scale]