

BU-311: Supplementary Battery Raw Materials. Battery University BU-311: Supplementary Battery Raw Materials The battery uses diverse elements that are harvested from the earth’s crust.
It is thought-provoking to realize that most of these materials are also shared by plants and living beings. We are made from stardust and anything that grows, moves and is produced comes from these resources. The substances are chosen carefully and in the right amount to achieve harmonious interaction. Last updated 2015-09-29 *** Please Read Regarding Comments *** Comments are intended for "commenting," an open discussion amongst site visitors. Previous Lesson Next Lesson Or Jump To A Different Article Basics You Should Know. BU-307: How does Electrolyte Work? Learn more about the catalyst that straddles the electrodes of a battery and makes electricity flow Electrolyte serves as catalyst to make a battery conductive by promoting the movement of ions from the cathode to the anode on charge and in reverse on discharge.

Ions are electrically charged atoms that have lost or gained electrons. The electrolyte of a battery consists of soluble salts, acids or other bases in liquid, gelled and dry formats as in polymer, as well as in solid ceramic and molten salts as in the Sodium-sulfur battery. BU-306: What do Separators Do? The building blocks of a battery are the cathode and anode, and these two electrodes are isolated by a separator.
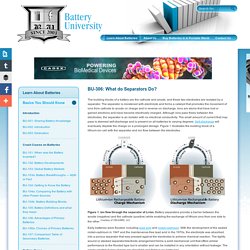
The separator is moistened with electrolyte and forms a catalyst that promotes the movement of ions from cathode to anode on charge and in reverse on discharge. Ions are atoms that have lost or gained electrons and have become electrically charged. Although ions pass freely between the electrodes, the separator is an isolator with no electrical conductivity. The small amount of current that may pass is deemed self-discharge and is present on all batteries to varying degrees. Self-discharge will eventually deplete the charge on a prolonged storage. Figure 1. Early batteries were flooded, including lead acid and nickel-cadmium. Early separators were made of rubber, glass fiber mat, cellulose and polyethylene plastic. Commercially available Li-ion cells use polyolefin as a separator.
Battery Safeguards; Protection Circuits. Battery University BU-304: Why are Protection Circuits Needed?
Learn how to make batteries safe with built-in protection circuits. Batteries can release high power, and most packs include protection to safeguard against malfunction. The most basic safety device in a battery is a fuse that opens on high current. Some fuses open permanently and render the battery useless; others are more forgiving and reset. Intrinsically Safe Batteries Intrinsically safe (IS) batteries contain protection circuits that prevent excessive currents that could lead to excess heat, sparks and explosion. Last Updated 2015-09-16 *** Please Read Regarding Comments *** Comments are intended for "commenting," an open discussion amongst site visitors. If you have a question, require further information, have a suggestion or would like to report an error, use the "contact us" form or email us at: answers@cadex.com. Previous Lesson Next Lesson. Confusion w/ Voltages (Battery Voltage Information) Battery University BU-303: Confusion with Voltages Explore why some battery packs pose odd voltages and how this affects the user.
A battery is an electrochemical device that produces a voltage potential when placing metals of different affinities into an acid solutions (electrolyte). The open circuit voltage (OCV) that develops as part of an electrochemical reaction varies according to the metals and electrolyte used. Applying a charge or discharge places the battery into the closed circuit voltage (CCV) condition. Lead Acid The nominal voltage of lead acid is 2.00 volts per cell, however when measuring the open circuit voltage; the voltage of a charged battery should be 2.10V/cell.
Serial and Parallel Battery Configurations and Information. BU-302: Configuraciones de Baterías en Serie y Paralelo (Español) Learn how to arrange batteries to increase voltage or gain higher capacity.

Batteries achieve the desired operating voltage by connecting several cells in series; each cell adds its voltage potential to derive at the total terminal voltage. Parallel connection attains higher capacity by adding up the total ampere-hour (Ah). Some packs may consist of a combination of series and parallel connections. Laptop batteries commonly have four 3.6V Li-ion cells in series to achieve a nominal voltage 14.4V and two in parallel to boost the capacity from 2,400mAh to 4,800mAh. Most battery chemistries lend themselves to series and parallel connection. A weak cell may not fail immediately but will get exhausted more quickly than the strong ones when on a load.
Single Cell Applications. Types of Battery Cells; Cylindrical Cell, Button Cell, Pouch Cell. Compare the pros and cons of the cylindrical cell, button cell, prismatic cell and pouch As batteries were beginning to be mass-produced, the jar design changed to the cylindrical format.
The large F cell for lanterns was introduced in 1896 and the D cell followed in 1898. A look at Old and New Battery Packaging. Discover familiar battery formats, some of which going back to the late 1800s.

Early batteries of the 1700s and 1800s developed in Europe were mostly encased in glass jars. As batteries grew in size, jars shifted to sealed wooden containers and composite materials. In the 1890s, battery manufacturing spread to the United States and in 1896 the National Carbon Company successfully produced a standard cell for widespread consumer use. It was the carbon-zinc Columbia Dry Cell Battery producing 1.5 volt and measuring six inches in length. With the move to portability, sealed cylindrical cells emerged that led to standards.