

Eye of Apophis. 99942 Apophis (Ateroid) 99942 Apophis (/əˈpɒfɪs/, previously known by its provisional designation 2004 MN4) is a near-Earth asteroid that caused a brief period of concern in December 2004 because initial observations indicated a probability of up to 2.7% that it would hit Earth in 2029.
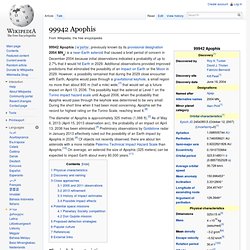
Additional observations provided improved predictions that eliminated the possibility of an impact on Earth or the Moon in 2029. However, a possibility remained that during the 2029 close encounter with Earth, Apophis would pass through a gravitational keyhole, a small region no more than about 800 m (half a mile) wide,[7] that would set up a future impact on April 13, 2036. This possibility kept the asteroid at Level 1 on the Torino impact hazard scale until August 2006, when the probability that Apophis would pass through the keyhole was determined to be very small.
The Infernal Trinity - Religious Education Forum. The Eye of Horus 2/6. Symbols of Satinism (Documentary) Information Awareness Office. The Information Awareness Office (IAO) was established by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) in January 2002 to bring together several DARPA projects focused on applying surveillance and information technology to track and monitor terrorists and other asymmetric threats to U.S. national security, by achieving "Total Information Awareness" (TIA).[4][5][6] This was achieved by creating enormous computer databases to gather and store the personal information of everyone in the United States, including personal e-mails, social networks, credit card records, phone calls, medical records, and numerous other sources, without any requirement for a search warrant.[7] This information was then analyzed to look for suspicious activities, connections between individuals, and "threats".[8] Additionally, the program included funding for biometric surveillance technologies that could identify and track individuals using surveillance cameras, and other methods.[8]
Sauron. Biography[edit] Before creation of the world[edit] The cosmological myth prefixed to The Silmarillion explains how the supreme being Eru initiated his creation by bringing into being innumerable spirits, "the offspring of his thought," who were with him before anything else had been made.
The being later known as Sauron thus originated as an "immortal (angelic) spirit. Thyrsus. Symbolism[edit] The thyrsus, associated with Dionysus (or Bacchus) and his followers, the Satyrs and Maenads, is a symbol of prosperity, fertility, hedonism, and pleasure/enjoyment in general.[1] It has been suggested that this was specifically a fertility phallus, with the fennel representing the shaft of the penis and the pine cone representing the "seed" issuing forth.
The thyrsus was tossed in the Bacchic dance: Pentheus: The thyrsus— in my right hand shall I hold it? Or thus am I more like a Bacchanal? Dionysus: In thy right hand, and with thy right foot raise it".[2] Thrace. The physical-geographical boundaries of Thrace: the Balkan Mountains, the Rhodope Mountains and the Bosporus.
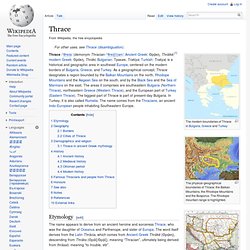
The Rhodope mountain range is highlighted. The Roman province of Thrace The Byzantine thema of Thrace Thrace and the Thracian Odrysian Kingdom under Sitalces c. 431-324 BC. Thrace /ˈθreɪs/ (demonym Thracian /ˈθreɪʃ(i)ən/; Ancient Greek: Θρᾴκη, Thrāikē;[1] modern Greek: Θράκη, Thráki; Bulgarian: Тракия, Trakiya; Turkish: Trakya) is a historical and geographic area in southeast Europe, centered on the modern borders of Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey. Staff of Dionysus ( thyrsus) Dionysus. The earliest cult images of Dionysus show a mature male, bearded and robed.
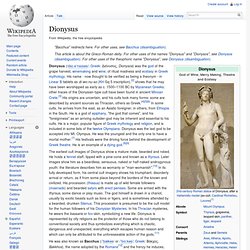
He holds a fennel staff, tipped with a pine-cone and known as a thyrsus. Later images show him as a beardless, sensuous, naked or half-naked androgynous youth: the literature describes him as womanly or "man-womanish".[10] In its fully developed form, his central cult imagery shows his triumphant, disorderly arrival or return, as if from some place beyond the borders of the known and civilized. His procession (thiasus) is made up of wild female followers (maenads) and bearded satyrs with erect penises.
Some are armed with the thyrsus, some dance or play music. Dionysian Mysteries. The Dionysian Mysteries were a ritual of ancient Greece and Rome which used intoxicants and other trance-inducing techniques (like dance and music) to remove inhibitions and social constraints, liberating the individual to return to a natural state.
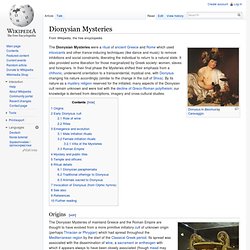
It also provided some liberation for those marginalized by Greek society: women, slaves and foreigners. Papal ferula. The Papal ferula (from Latin ferula, "rod") is the pastoral staff or crosier used by the Pope.
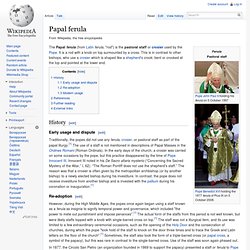
It is a rod with a knob on top surmounted by a cross. This is in contrast to other bishops, who use a crosier which is shaped like a shepherd's crook: bent or crooked at the top and pointed at the lower end. Papal regalia and insignia. Papal regalia and insignia are the official items of attire and decoration proper to the Pope in his capacity as the head of the Roman Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State.
Regalia[edit] The triregnum (a crown with three levels) is among the regalia of the papacy. It is also called the triple tiara[1] or triple crown. Crossed keys (Simon Peter) Saint Peter. Saint Peter (Latin: Petrus, Greek: Πέτρος Petros; died AD 64 or 67),[3] also known as Simon Peter, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus Christ, leaders of the early Christian Church, according to the New Testament.
He is venerated as a saint and considered to be the first bishop of Rome and first Pope by the Roman Catholic Church. According to Christian tradition, Peter was crucified in Rome under Emperor Nero Augustus Caesar. It is traditionally held that he was crucified upside down at his own request, since he saw himself unworthy to be crucified in the same way as Jesus Christ. Tradition holds that he was crucified at the site of the Clementine Chapel, while his mortal remains are contained in the underground Confessio of St. Peter's Basilica, where Pope Paul VI announced the excavated discovery of a first-century Roman cemetery in 1968. Names and etymologies[edit] New Testament account[edit] Peter was a fisherman in Bethsaida. "Rock" dialogue[edit] Papal Cross. A papal cross Rendition of the coat of arms of Pope Pius IX with supporters: two angels, each holding a papal cross. The papal cross is an emblem for the office of the Pope in ecclesiastical heraldry.
It is depicted as a staff with three horizontal bars near the top, in diminishing order of length as the top is approached. It is thus analogous to the two-barred archiepiscopal cross used in heraldry to indicate an archbishop, and seems to have been used precisely to indicate an ecclesiastical rank still higher than that of archbishop. Dionysus. Ferula. Ferula (from Latin ferula, "rod") is a genus of about 170 species of flowering plants in the family Apiaceae, native to the Mediterranean region east to central Asia, mostly growing in arid climates. They are herbaceous perennial plants growing to 1–4 m tall, with stout, hollow, somewhat succulent stems. The leaves are tripinnate or even more finely divided, with a stout basal sheath clasping the stem. The flowers are yellow, produced in large umbels. Many plants of this genus, especially F. communis are referred to as "giant fennel," although they are not fennel in the strict sense.
Ferula foetida Selected species[edit] Uses[edit] Religion and the Pine Cone. Pineal gland. The pineal gland, also known as the pineal body, conarium or epiphysis cerebri, is a small endocrine gland in the vertebrate brain. It produces melatonin, a serotonin derived hormone, which affects the modulation of sleep patterns in both seasonal and circadian rhythms.[1][2] Its shape resembles a tiny pine cone (hence its name), and it is located in the epithalamus, near the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres, tucked in a groove where the two halves of the thalamus join. Nearly all vertebrate species possess a pineal gland. Pineal_gland.brain_sections. Eye of Horus. Eye of Horus - Eygptian Symbols. Horus. Horus is one of the oldest and most significant deities in ancient Egyptian religion, who was worshipped from at least the late Predynastic period through to Greco-Roman times.
Different forms of Horus are recorded in history and these are treated as distinct gods by Egypt specialists.[1] These various forms may possibly be different perceptions of the same multi-layered deity in which certain attributes or syncretic relationships are emphasized, not necessarily in opposition but complementary to one another, consistent with how the Ancient Egyptians viewed the multiple facets of reality.[2] He was most often depicted as a falcon, most likely a lanner or peregrine, or as a man with a falcon head.[3] Etymology[edit] Horus was also known as Nekheny, meaning "falcon". Some have proposed that Nekheny may have been another falcon-god, worshipped at Nekhen (city of the hawk), with which Horus was identified from early on.
Osiris (God of Afterlife, Father of Horus, brother of set, killed by set) Hades. Isis (God of nature and magic,Ideal mother and wife as well as the patroness of )
Eyes-symbols-posts-s243a. Third eye. A Cambodian Shiva head showing a third eye. Third Eye - Pineal Gland. Pineal_gland.brain_sections. Eye of Providence. Religious use[edit] Many religions have used the image of an eye in their religious symbolism. Eye of Ra. Ra. Ra /rɑː/[1] or Re /reɪ/ (Egyptian: 𓂋ꜥ, rˤ) is the ancient Egyptian solar deity. By the Fifth Dynasty (2494 to 2345 BC) he had become a major god in ancient Egyptian religion, identified primarily with the midday sun. The meaning of the name is uncertain, but it is thought that if not a word for 'sun' it may be a variant of or linked to words meaning 'creative power' and 'creator'.[2] Ra and Ra-Horakhty. Set (mythology)
Sekhmet (Dauter of Ra) Wadjet (Another name for Sekhmet) Sekhmet (Sent by Ra to Push Non-believers) Destruction of Mankind in Sekhmet. Associated With Sekhmet. Pineal gland. Pineal_gland.brain_sections. Horus. The Eyes Have It (Eye of Horus and the Eye of Re (Ra)