

The Battle of Cable Street. Battle of Cable Street: Lessons from Fascism Fight of 1936. (17) Putting Edward VIII’s Sympathies Towards Nazi Germany in Context. British Union of Fascists. Far-right political party.
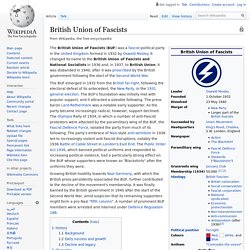
US History: The Great Depression. History >> US History 1900 to Present Migrant MotherPhoto by Dorothea Lange Farm Security Administration The Great Depression was a time of great economic crisis during the 1930s.
It began in the United States, but quickly spread throughout much of the world. Spanish Civil War Facts for Kids. The Spanish Civil War (18 July 1936 – 1 April 1939) was a war in which the Spanish General Francisco Franco and his troops successfully took control of Spain.

A lot of different groups worked together with the Spanish Republic (the government of the time) to stop him, including socialists, communists, anarchists, and other leftist groups. The fascist governments of Germany and Italy provided troops and supplies for Franco, while the communist Soviet Union sold the Republican forces weapons. Lots of people from other countries volunteered to fight against Franco (sometimes against the orders of their own countries), including people from the United States, Britain, France, Belgium, Germany, Italy, and many other countries.
These groups were known as the International Brigades. The Treaty of Versailles, 1919. The Interwar Years 1919 to 1939 - The Super Summary of World History Revised. The “war to end all wars” was finally over in 1919 with the execution of the Treaty of Versailles.
Europe was at peace. It would remain at peace for twenty years. It turned out the “war to end all wars” only set up Europe for the next conflict which was even greater. World War II would officially start in 1939 with Germany, led by Adolph Hitler, invading Poland. The Interwar Years (1919-1938): Britain During the Inter-War Years (1919-1938) Summary The British government had a great deal of difficulty in adjusting to post-war politics.
David Lloyd George, the talentedd Liberal prime minister, was permitted to retain his office by the Conservative majority. At first he continued to run the government as he had during the war, using only his closest advisors to discuss and execute policy decisions. He often worked behind closed doors. Though he had returned from the Paris Peace Conference to general approval, things gradually began to look less rosy. Immediately after World War I, workers in many key industries began to strike, demanding higher wages, better working conditions, and shorter hours now that the war was ended. However, political stability could not be maintained. Cable Street: 'Solidarity stopped Mosley's fascists' Seventy-five years ago east London Jews and Irish labourers stood up to fascists who wanted to march through their streets.
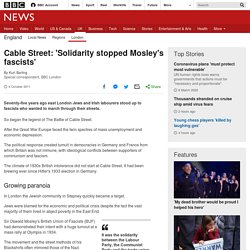
Facism in the UK during the 1930s. They shall not pass: Fighting fascism in 1930s Britain. "The Battle of Cable Street" - a mural in London's East End depicts another anti-Mosley demonstration from 1936. | Trades Union Congress When I was growing up on a dairy farm near Sequim, Wash. back in the 1950s, my father would regale us with stories of his exploits as a Rhodes Scholar at Oxford University in the 1930s.

Soon after he arrived in Oxford in 1936, the British Union of Fascists (BUF) announced that Sir Oswald Mosley, führer of the BUF, would come to speak at a rally in Oxford. He would be accompanied by more than 100 of his Blackshirt thugs. British Fascism in the 1930s in Life and Literature. Culture - The psychological tricks used to help win World War Two. Secrets and spies The word ‘propaganda’ might suggest some form of misinformation – yet in boosting morale during World War Two, the British government had to maintain a careful balancing act.
While employing a range of psychological tricks, they had to be seen to be as truthful as possible. Enemy within: The network of Britons who spied for Hitler during Second World War. To his circle of fervent recruits, he was “Jack King” – the Gestapo’s man in England.
While Britons rallied to war against Hitler in 1940, the masterful Nazi agent toured the country signing up those who could be trusted to show their loyalty to the Fatherland when the time came. For five years, King evaded detection as he built up a coterie of committed and ruthless British Nazis ranging from provincial engineers, to an astrologer, to a Catholic priest. National Government in 1930s Britain - 1939 Register. Skip to content This site uses cookies.
By continuing to use this website you agree to our cookie policy. Interwar Britain. Politics of 1920s[edit] Enlarging democracy[edit] The Representation of the People Act 1918 finally gave Britain universal manhood suffrage at age 21, with no property qualifications. Even more dramatically it opened up woman suffrage for most women over the age of 30. In 1928, all women were covered on the same terms as men.[3] With the emergence of revolutionary forces, most notably in Bolshevik Russia and Socialist Germany, but also in Hungary, Italy and elsewhere, revolution to overthrow established elites and aristocracies was in the air.
The Labour Party largely controlled working-class politics, and it strongly supported the government in London and opposed violent revolution. Nevertheless, there were concerns about republicanism. Ireland[edit] An armed insurrection by Irish republicans known as the Easter Rising took place in Dublin during Easter Week, 1916. A brief history of the British Royals and their alleged Nazi connections. The British Royal Family have never been able to escape the spectre of their unsavoury historical Nazi connections – Nazi sympathisers the Duke and Duchess of Windsor (whose relationship is explored in SBS documentary Spying on the Royals), alleged WWII plots to install a pro-Nazi government and that controversial footage of Queen Elizabeth apparently making the Nazi salute as a child. Now the question remains: just how far reaching were their Nazi connections? With the Royal Family refusing to release historical documents that would bring greater clarity to the issue, alternate evidence has come to light and theories abate.
The Nazi sympathisers: the Duke and Duchess of Windsor The Windsors – former monarch Edward VIII and his American love, Wallis Simpson, for whom he abdicated the throne – were a pesky thorn in the Royals’ side, not least because they were thought to be Nazi sympathisers. British Fascism. British fascism is the form of fascism promoted by some political parties and movements in the UK.[1] It was based on British ultranationalism with aspects of Italian Fascism and Nazism before and after World War II.[2] Ideological origins[edit] Tenets[edit] A flowchart showing the history of the early British fascist movement Nationalism and racialism[edit] On racial issues, the various British Fascist movements held different policies.
There were small, short-lived Fascist groups at several universities including Oxford, Cambridge, Birmingham, Liverpool and Reading. Foreign policies[edit] Fascism, abdication and war: the story of a turbulent era. 24 February 1920 The German Workers party (DAP) becomes the Nazi party (NSDAP). Adolf Hitler becomes its leader in 1921. 18 July 1925 Volume one of Hitler’s autobiographical manifesto, Mein Kampf, is published, outlining his ideology. Peaky Blinders: What led to downfall of Oswald Mosley and the British Union of Fascists? Oswald Mosley (played by Sam Claflin) went head-to-head with Tommy Shelby (Cillian Murphy) in the latest series of Peaky Blinders. Battle of Cable Street. Background[edit] Operation Sea Lion. Mitford family. The Mitford family is an aristocratic English family, whose principal line had its seats at Mitford, Northumberland.
Oswald Mosley. British fascist politician.