Zoom
Trash

CanadaInfo: Government in Canada. The Constitution of Canada divided the responsibilities of the Government into federal and provincial jurisdictions.

It also provided for the possibility of the provincial governments to delegate some of its responsibilities to one or more municipal governments. The Federal Government is seated in Ottawa and is headed by the Governor General of Canada on the advice of the Prime Minister. Its responsibilities include: defence, criminal law, employment insurance, postal service, census, copyrights, trade regulation, external relations, money and banking, transportation, citizenship, and Indian affairs. The Consitution also specified that every issue not mentioned as belonging to the provincial or territorial governments comes under the power of the Federal Government. The Provincial and Territorial Governments currently number ten and three, respectively. Property and civil rights, administration of justice, natural resources and the environment, education, health, and welfare. Primary History - Ancient Greeks. Who were the ancient Greeks?
Who were the ancient Greeks? Discover different ancient Greek cities and find out how they were ruled. How did the Olympic Games begin? Learn how the Olympic Games began over 2,700 years ago! Find out what events were at the ancient Olympics. What was it like to live in an ancient Greek family? What was everyday life like in ancient Greece? Who were the ancient Greek gods and heroes The Greeks believed in many gods and goddesses. The ancient Greeks at war Learn about ancient Greek soldiers, the Spartan soldier state and read about famous Greek battles.
What do we know about ancient Greek culture? Find out what ancient Greek theatre was like and learn about different ancient Greek festivals and art. Primary History - Ancient Greeks - The Greek world. Resources - Curious Curators. Virtual Wampum Belt. The Canadian Parliamentary System » J.J.'s Complete Guide to Canada. A legacy of the country’s colonial past, Canada’s government is based on the British parliamentary system, a democratic model of government adapted from centuries of English tradition.

Canada’s national Parliament, housed in an enormous neo-Gothic building in the capital city of Ottawa, is a bicameral legislature, meaning it’s split into two chambers: the House of Commons and the Senate. Here’s the quick summary: As we can see, the House of Commons consists of 308 elected politicians, while the Senate consists of 105 “qualified citizens” appointed by the prime minister. The Senate is fairly ceremonial and inconsequential (more on this later), so when most Canadians refer to “Parliament” they are usually referring to just the House. Members of the House of Commons are known as “Members of Parliament,” or more commonly, just “MPs.” Government in Canada - Grade 5: Social Studies - Learning Commons at Upper Canada Virtual Library.
ML_EnglishStudentHandbook.pdf. Legislative Assembly of Alberta - Student Zone. Welcome to the Zone!
Here you will discover some fun activities to help you learn about the Alberta Legislature! Step Inside the Alberta Legislature! Alberta Legislature Virtual Visit Did you know you could visit the Legislature Building without even leaving your room? Here's how: launch the 3-D Virtual Visit, create your own character and go exploring! You will even be able to enter some places that you can't visit on a regular tour. Trivia Challenge Test your knowledge of the Alberta Legislature and uncover the hidden picture. Take the Legislature Challenge! How does a bill become a law? Find out what would happen if someone decided that all Albertans should play the tuba! Something to think about:What would you do if you wanted to have a say on a proposed law? Where does tax money come from? Who decides where the money goes?
Something to think about:Why should citizens pay taxes? Guide to the Canadian House of Commons. Photo: Library of Parliament / Roy Grogan Our system of government is part of the reason why Canada is known around the world as a good place to live.
Canada's parliamentary system is open and democratic. Municipal Affairs. Learning about Municipal Governments When people hear the word community, many think of a neighbourhood, town, city or area.

A community can be a group of people who have something in common. This can include where they live, a common identity or a sense of belonging. Being part of a community can involve having a common history or common interests. Community members often share purposes or goals. What does community mean to you? Local governments work within communities to represent the interests and goals of community members.
What do you know about your local government? In Alberta, the areas that are served by local governments are called municipalities. What is Canada's political system? In Canada, there are 3 levels of government.
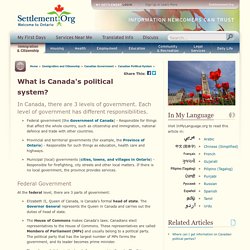
Each level of government has different responsibilities. Federal government (the Government of Canada) - Responsible for things that affect the whole country, such as citizenship and immigration, national defence and trade with other countries. Provincial and territorial governments (for example, the Province of Ontario) - Responsible for such things as education, health care and highways. Municipal (local) governments (cities, towns, and villages in Ontario) - Responsible for firefighting, city streets and other local matters. If there is no local government, the province provides services.