

What is mw and what is gwh in electrical terms - Yahoo! Answers. Research and development. Cycle of research and development The research and development (R&D, also called research and technical development or research and technological development, RTD in Europe) is a specific group of activities within a business.
The activities that are classified as R&D differ from company to company, but there are two primary models. In one model, the primary function of an R&D group is to develop new products; in the other model, the primary function of an R&D group is to discover and create new knowledge about scientific and technological topics for the purpose of uncovering and enabling development of valuable new products, processes, and services. Under both models, R&D differs from the vast majority of a company's activities which are intended to yield nearly immediate profit or immediate improvements in operations and involve little uncertainty as to the return on investment (ROI). Background[edit] Heliostat. Heliostat by the Viennese instrument maker Ekling (ca. 1850) A heliostat (from helios, the Greek word for sun, and stat, as in stationary) is a device that includes a mirror, usually a plane mirror, which turns so as to keep reflecting sunlight toward a predetermined target, compensating for the sun's apparent motions in the sky.
Business process outsourcing. Business process outsourcing (BPO) is a subset of outsourcing that involves the contracting of the operations and responsibilities of specific business functions (or processes) to a third-party service provider.
Originally, this was associated with manufacturing firms, such as Coca Cola that outsourced large segments of its supply chain.[1] BPO that is contracted outside a company's country is called offshore outsourcing. BPO that is contracted to a company's neighboring (or nearby) country is called nearshore outsourcing. Often the business processes are information technology-based, and are referred to as ITES-BPO, where ITES stands for Information Technology Enabled Service.[2] Knowledge process outsourcing (KPO) and legal process outsourcing (LPO) are some of the sub-segments of business process outsourcing industry.
What is Energy? Energy is the capacity of a system to do work.
That system may be a jet, carrying hundreds of passengers across the ocean. A baby’s body, growing bone cells. Energy. All of the many forms of energy are convertible to other kinds of energy, and obey the conservation of energy.
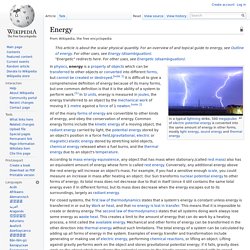
Common energy forms include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the radiant energy carried by light, the potential energy stored by an object's position in a force field,(gravitational, electric or magnetic) elastic energy stored by stretching solid objects, chemical energy released when a fuel burns, and the thermal energy due to an object's temperature. According to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass when stationary,(called rest mass) also has an equivalent amount of energy whose form is called rest energy. Conversely, any additional energy above the rest energy will increase an object's mass. For example, if you had a sensitive enough scale, you could measure an increase in mass after heating an object.
Living organisms require available energy to stay alive, such as the energy humans get from food. Barrel (unit) Since medieval times the term barrel as a unit of measure has had various meanings throughout Europe, ranging from about 100 litres to 1000 litres, or more in special cases.
The name was derived in medieval times from the French baril, of unknown origin, but still in use, both in French and as derivations in many other languages such as Italian, Polish and Spanish. In most countries such usage is obsolescent, increasingly superseded by SI units. As a result the meaning of corresponding words and related concepts (vat, cask, keg etc.) in other languages often refers to a physical container rather than a known measure.
International System of Units. For a topical guide to this subject, see Outline of the metric system.
The standards, published in 1960 as the result of an initiative started in 1948, are based on the metre–kilogram–second (MKS) system, rather than the centimetre–gram–second (CGS) system, which, in turn, had several variants. The SI has been declared to be an evolving system; thus prefixes and units are created and unit definitions are modified through international agreement as the technology of measurement progresses, and as the precision of measurements improves. The system has been adopted by most countries in the developed (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) world, though within English-speaking countries, the adoption has not been universal. In the United States metric units are not commonly used outside of science, medicine and the government; however, United States customary units are officially defined in terms of SI units. History[edit] Uncoordinated development[edit] Thomson Maxwell. British thermal unit. Calorie. The name calorie is used for two units of energy.
The small calorie or gram calorie (symbol: cal) is the approximate amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius.[1]The large calorie, kilogram calorie, dietary calorie, nutritionist's calorie, nutritional calorie, Calorie (capital C)[citation needed] or food calorie (symbol: Cal, equiv: kcal) is approximately the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of one kilogram of water by one degree Celsius. The large calorie is thus equal to 1000 small calories or one kilocalorie (symbol: kcal).[1] Although these units are part of the metric system, they have been superseded in the International System of Units by the joule.
One small calorie is approximately 4.2 joules (so one large calorie is about 4.2 kilojoules). Joule. In terms firstly of base SI units and then in terms of other SI units: One joule can also be defined as: Usage[edit] This SI unit is named after James Prescott Joule.
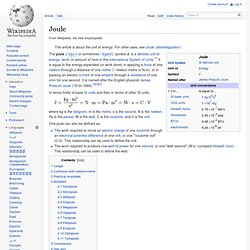
As with every International System of Units (SI) unit whose name is derived from the proper name of a person, the first letter of its symbol is upper case (J). However, when an SI unit is spelled out in English, it should always begin with a lower case letter (joule), except in a situation where any word in that position would be capitalized, such as at the beginning of a sentence or in capitalized material such as a title. Confusion with newton-metre[edit] Pascal (unit) Common multiple units of the pascal are the hectopascal (1 hPa ≡ 100 Pa), kilopascal (1 kPa ≡ 1000 Pa), megapascal (1 MPa ≡ 1,000,000 Pa), and gigapascal (1 GPa ≡ 1,000,000,000 Pa).
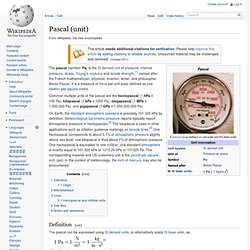
The pascal can be expressed using SI derived units, or alternatively solely SI base units, as: This SI unit is named after Blaise Pascal. Metre. The metre (International spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures), or meter (American spelling), (SI unit symbol: m), is the fundamental unit of length (SI dimension symbol: L) in the International System of Units (SI).[1] Originally intended to be one ten-millionth of the distance from the Earth's equator to the North Pole (at sea level), its definition has been periodically refined to reflect growing knowledge of metrology. Since 1983, it has been defined as "the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of 1/299,792,458 of a second.
"[2] History[edit] Metrology. Second. A light flashing approximately once per second The second (symbol: s) is the base unit of time in the International System of Units (SI)[1] and is also a unit of time in other systems of measurement (abbreviated s or sec[2]); it is the second division of the hour by sixty, the first division by 60 being the minute.[3] Between AD 1000 (when al-Biruni used seconds) and 1960 the second was defined as 1/86,400 of a mean solar day (that definition still applies in some astronomical and legal contexts).[4][5] Between 1960 and 1967, it was defined in terms of the period of the Earth's orbit around the Sun in 1900,[6] but it is now defined more precisely in atomic terms.
Seconds may be measured using mechanical, electric or atomic clocks. the duration of 9192631770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the caesium 133 atom.[1] International second[edit] Equivalence to other units of time[edit] History[edit] Kilogram. The gram was originally defined in 1795 as the mass of one cubic centimeter of water at 4 °C, making the kilogram equal to the mass of one liter of water. The prototype kilogram, manufactured in 1799 and from which the current kilogram is based, has a mass equal to the mass of 1.000025 liters of water. The kilogram is the only SI base unit with an SI prefix ("kilo", symbol "k") as part of its name.
It is also the only SI unit that is still directly defined by an artifact rather than a fundamental physical property that can be reproduced in different laboratories. Watt. Definition[edit] Newton (unit) International Financial Reporting Standards. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are designed as a common global language for business affairs so that company accounts are understandable and comparable across international boundaries.
They are a consequence of growing international shareholding and trade and are particularly important for companies that have dealings in several countries. They are progressively replacing the many different national accounting standards. The rules to be followed by accountants to maintain books of accounts which is comparable, understandable, reliable and relevant as per the users internal or external. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (United States) Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, US GAAP or GAAP stands for "generally accepted accounting principles". Although the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has stated that it intends to move from US GAAP to the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), they differ considerably from GAAP and progress has been slow and uncertain.[1][2]
Governmental Accounting Standards Board. Financial Accounting Standards Board. Mission statement[edit] Federal Accounting Standards Advisory Board. The Federal Accounting Standards Advisory Board (FASAB) is a United States federal advisory committee whose mission is to develop generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) for federal financial reporting entities. The Chief Financial Officers Act of 1990 required annual, audited financial statements for the United States Government and its component entities, referred to as federal reporting entities.