

Alexander Fleming. Sir Alexander Fleming, FRSE, FRS,[1] FRCS(Eng) (6 August 1881 – 11 March 1955) was a Scottish biologist, pharmacologist and botanist.
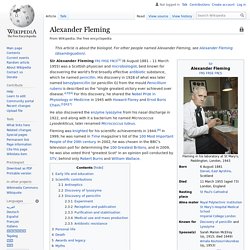
He wrote many articles on bacteriology, immunology, and chemotherapy. His best-known discoveries are the enzyme lysozyme in 1923 and the antibiotic substance penicillin from the mould Penicillium notatum in 1928, for which he shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945 with Howard Florey and Ernst Boris Chain.[2][3][4][5][6][7] Biography[edit] Early life and education[edit] Fleming was born on 6 August 1881 at Lochfield farm near Darvel, in Ayrshire, Scotland.
Fleming went to Loudoun Moor School and Darvel School, and earned a two-year scholarship to Kilmarnock Academy before moving to London, where he attended the Royal Polytechnic Institution.[8] After working in a shipping office for four years, the twenty-year-old Fleming inherited some money from an uncle, John Fleming. Sir Alexander Fleming. Alexander Fleming. Alexander Fleming (1881 - 1955) Born in Loudoun, Ayrshire, Fleming was educated at Kilmarnock Academy.
He began his working career as a shipping clerk in London, but after matriculation in 1902, he began a medical student-ship at St Mary's Hospital, London, and qualified as a physician and surgeon. Fleming joined Sir Almroth Wright's bacteriological laboratory and pioneered the use of anti-typhoid vaccines on humans. He continued his researches during a period as a medical officer in France during World War I. Alexander Fleming carried out most of his work at Queen Mary's Hospital, London, where he was professor of bacteriology from 1924 to 1948 (and where he made his most important discoveries). As early as 1922 Alexander Fleming discovered lysozyme, the antiseptic substance contained in tears. Fleming had been cultivating the bacteria responsible for boils (Staphylococcus) and had left the cultures for a number of days.
Back to Famous Scots. Inventor Alexander Fleming Biography. Alexander Fleming biography - Science Hall of Fame. Famous for: Discovering the antibiotic penicillin Researching the antiseptic properties of lysozyme.
Fleming played a key role in the development of modern antibiotics. His research and observations led to the development of penicillin – generally considered to be one of the most important advances in medical history. Humble beginnings Fleming was born on 6 August 1881 at Lochfield Farm, near Darvel in Ayrshire. He enjoyed a poor but happy childhood with a love of the outdoors. Alec attended primary school at Loudon Moor and Darvel before going on to Kilmarnock Academy. Medical degree in London When Fleming was 13, he moved to London to live with his brother who was a doctor. When he was 20 years old, Fleming inherited a small sum of money from an uncle. Fleming studied at St Mary's Medical School and was closely associated with this institution for the rest of his life. Almroth Wright's influence Head of the Inoculation Department at St Mary's was Almroth Wright.
Treating the war wounded. Alexander Fleming (1881-1955) - Online stuff. Penicillin: the first miracle drug. Home>Catalog>Penicillin Penicillin: the first miracle drug Many of you are here only because penicillin saved your life, or the life of one of your parents or grandparents.

Penicillin's ability to cure people of many once-fatal bacterial infections has saved so many lives that it is easy to understand why it was once called a "miracle drug". Antibiotics are chemicals, effective at very low concentrations, created as part of the life process of one organism, which can kill or stop the growth of a disease-causing microbe--a germ. In 1929, Alexander Fleming, a doctor and researcher at St.
World War II (1939-1945) had begun by the time their research was showing results. Creating the right environment for growth was the first step in producing enough penicillin to be used as a drug. Scientists were also determined to find another strain of Penicillium that might grow better in the huge deep fermentation tanks. Penicillin. Penicillin core structure, where "R" is the variable group.
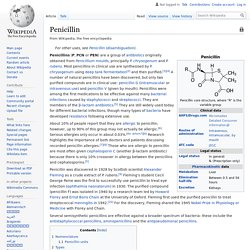
Penicillin (sometimes abbreviated PCN or pen) is a group of antibiotics derived from Penicillium fungi,[1] including penicillin G (IV use), penicillin V (oral use), procaine penicillin, and benzathine penicillin (intramuscular use). Penicillin antibiotics were among the first drugs to be effective against many previously serious diseases, such as syphilis and infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. Penicillins are still widely used today, though many types of bacteria have now become resistant. All penicillins are β-lactam antibiotics and are used in the treatment of bacterial infections caused by susceptible, usually Gram-positive, organisms. Several enhanced penicillin families also exist, effective against additional bacteria: these include the antistaphylococcal penicillins, aminopenicillins and the more-powerful antipseudomonal penicillins.
Medical uses[edit] Susceptibility[edit] Adverse effects[edit] History of Penicillin - Alexander Fleming - John Sheehan - Andrew Moyer. Penicillin is one of the earliest discovered and widely used antibiotic agents, derived from the Penicillium mold.
Antibiotics are natural substances that are released by bacteria and fungi into the their environment, as a means of inhibiting other organisms - it is chemical warfare on a microscopic scale. Alexander Fleming Biography - Alexander Fleming Childhood, Life & Timeline. Alexander Fleming Childhood Alexander Fleming was born on 6 August 1881 at Lochfield, a farm located near Darvel in Ayrshire, Scotland.
Fleming was third among 4 children born to father Hugh Fleming and Grace Stirling Morton. Alexander lost his father at the age of 7. Education. Penicillin Information from Drugs. Generic Name: penicillin V (pen i SILL in)Brand Names: PC Pen VK, Pen-V What is penicillin?

Penicillin V is an antibiotic in the penicillin group of drugs. It fights bacteria in your body. Penicillin V is used to treat many different types of infections caused by bacteria, such as ear infections,. Penicillin V may also be used for other purposes not listed in this medication guide. Important information Do not use this medication if you are allergic to penicillin V or to any other penicillin antibiotic, such as amoxicillin (Amoxil), ampicillin (Omnipen, Principen), carbenicillin (Geocillin), dicloxacillin (Dycill, Dynapen), or oxacillin (Bactocill).