

Energy drinks: a trigger for heart attacks and stroke? When a 17-year-old girl, with a potentially life-threatening heart disorder, recently presented to me with an abnormally fast and irregular heart rhythm, I wondered how the natural history of her disease could so abruptly lead to a potentially fatal electrical rhythm disturbance.
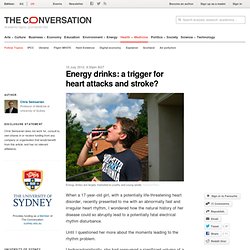
Until I questioned her more about the moments leading to the rhythm problem. Uncharacteristically, she had consumed a significant volume of a popular energy drink. Within an hour, she was in hospital receiving electrical shocks to her heart to bring it back to a normal rhythm. A mere coincidence, or did consuming an “energy drink” trigger her potentially fatal heart rhythm? Energy drink consumption has grown exponentially over the past five to ten years. The drinks are primarily targeted at the vulnerable youth and young adult market with aggressive advertising and marketing. So what is in energy drinks that could potentially trigger cardiac events? So what are the medical effects of energy drinks? Sports Medicine Female athletes. Home > PDHPE > Options > Option 3 - Sports Medicine > Sports Medicine Key Messages Eating disorders, iron deficiency and poor bone density are conditions that can affect female athletes and impede performance.

Female athletes need to be mindful of nutritional requirements, particularly in meeting the recommended dietary intake (RDI) of iron and calcium. Exercise during pregnancy is safe and beneficial as long as there is monitoring of basic guidelines. These guidelines relate to exercise intensity, type of exercise chosen and environment in which the exercise occurs. For females, participation in sport can achieve the same physiological, psychological and social benefits as for men. There are, however, a few factors that female athletes need to be aware of to ensure they are participating safely and efficiently. Eating disorders iron deficiency bone density pregnancy Eating disorders Eating disorders can impair performance. Iron deficiency Bone density Pregnancy whilst exercising. Back. Sports Medicine aged athletes. Sports Medicine young athletes.
Home > PDHPE > Options > Option 3 - Sports Medicine > Sports Medicine Key Messages Some children have special medical needs.

Coaches, managers and referees should have knowledge of conditions such as asthma, diabetes and epilepsy. To reduce the risk of overuse injuries children should stretch, wear correct footwear and undertake a conditioning program. Ankle Taping - Ankle Strapping. Health > Taping Techniques > Ankle Taping The following ankle taping techniques are designed to support the ankle and reduce stress on the ankle during activity.
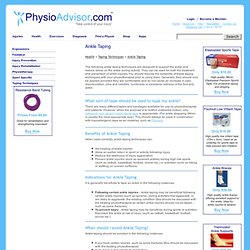
They can be used for both the treatment and prevention of ankle injuries.You should discuss the suitability of these taping techniques with your physiotherapist prior to using them. Generally, they should only be applied provided they are comfortable and do not cause an increase in pain, discolouration, pins and needles, numbness or excessive redness of the foot and ankle. Thumb Taping - Thumb Strapping - Strap Thumb. Health > Taping Techniques > Thumb Taping The following thumb taping techniques are designed to support the thumb and reduce stress on the thumb during activity.

They can be used for both the treatment and prevention of thumb injuries. You should discuss the suitability of these thumb taping techniques with your physiotherapist prior to using them. Generally, they should only be applied provided they are comfortable and do not cause an increase in pain, discolouration, pins and needles, numbness, swelling, itchiness or excessive redness of the hand, wrist, fingers or thumb.
Climate control: acclimatising to the heat. Author: Lisa Yates, Sports Dietitian, The Coaches Edge Issue:Volume 27 Number 1 Exercising in hot, humid conditions when the body is not accustomed to it can place the body under great stress.
The demand for circulation to working muscles, which are producing heat, overtakes the need for blood flow to the skin to transport heat away from the body. As a result, body temperature rises. Couple this with dehydration and the risks of heat illness, and poor performance increases. Athletes travelling overseas or to different climates should consider heat acclimatisation an important preparation strategy.
Is Fotu, 9 and 85kg, too big for his teammates' boots? - League - Sport. Are sports drinks better than water when exercising? - Health & Wellbeing. A: Sometimes, it depends on the individual situation Our expert: Profesor Louise Burke and Professor Clare Collins Published 21/07/2011 [Image source: iStockPhoto] Should you take a bottle of sports drink down to the gym when you do that hour's aerobics class?
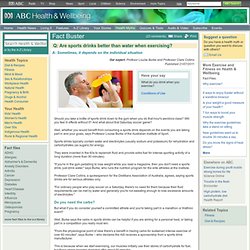
Will you feel ill effects without it? Well, whether you would benefit from consuming a sports drink depends on the events you are taking part in and your goals, says Professor Louise Burke of the Australian Institute of Sport. Sports drinks typically contain water and electrolytes (usually sodium and potassium) for rehydration and carbohydrates (as sugars) for energy. They were invented in the 60s to replenish fluid and provide extra fuel for intense sporting activity of a long duration (more than 90 minutes). "If you're in the gym pedalling to lose weight while you read a magazine, then you don't need a sports drink, just drink water," says Burke, who runs the nutrition program for the elite athletes at the institute.
PDHPE-Sports-Medicine-Notes. PDHPE CQ3: Sports Medicine - Sports policy and sports environment - HSC. Modified sports the safer option for kids. PDHPE CQ1: Ways to classify sports injuries - Sports Medicine - Classification and Management - HSC.