Zoom
Trash

China in perspective. Marco Polo famously wrote the following in his Travels of Marco Polo - a book about his travels through Asia along the Silk Road - I did not write half of what I saw, for I knew I would not be believed.
It's impossible to capture the breadth and depth of Chinese history and culture in a single exhibition, or maybe even at all. It is however worth it to try to show how others have depicted and captured China in their own imaginations, how they've taken their impressions of China with them to Europe to tell stories about the Far East. The best way to get to know someone is to walk a mile in their shoes, but how can we try and get to know an entire culture - thousands of years of ideas, practices and people? In this exhibition, we set out for a journey of discovery through China exploring works of art, artefacts and photographs preserved in European heritage collections. A guide to ancient stargazing in China - BBC Sky at Night Magazine. Chinese astronomers have been studying the night sky for longer than any other culture.
The oldest star maps and the earliest records of sunspots have been unearthed by archaeologists in China, where a unique way of looking at the night sky developed about 1,200 BC. Chinese astronomers Gan De and Shi Shen are credited as the first to create star catalogues in the 4th century BC, and the Buddhist monk Yi Xing conducted an astronomical survey in the 8th century AD to help with the prediction of solar eclipses.
Discover more guides like this via our History of Astronomy webpage. Chinese or Lunar New Year starts on the day after the first new Moon that falls between 21 January and 20 February (in the Gregorian calendar) and ends with the next full Moon. You may also know about the ancient Chinese belief that a solar eclipse occurs when a dragon eats the Sun. China’s star lore divides the sky into four groups of 283 asterisms (‘xing guan’). It looks set to become a world-class facility. Hear an Ancient Chinese Historian Describe The Roman Empire (and Other Voices of the Past)
Those who see the world from only one narrow point of view get called a number of things–parochial, provincial, and worse–and are encouraged to seek out other perspectives and broaden their view.
Not everyone can travel the world, but the world comes to us through immigration and the internet, restaurants and recipes. Most of us, if we are inclined, can learn about and appreciate the cultures, cuisines, and histories of others. But can we see ourselves the way that others see us? This is a harder ask, I think, especially for Americans, who are used to the world coming to us and to defining the world on our terms, whether through soft power or military force.
When we read about history, we might diversify our sources, taking in perspectives from writers with different ideological commitments and beliefs. A great part of why we don’t read such histories is that we generally don’t even know they exist. Related Content: Ancient Chinese Historian Describes The Roman Empire // 3rd century AD "Weilüe" // Primary Source. The History of China – The Official Site of The History of China Podcast. How 3rd century Chinese saw the Romans. A country of “numerous minor kings” where fierce tigers and lions kill travelers.
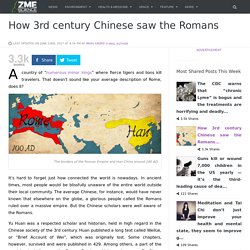
That doesn’t sound like your average description of Rome, does it? The borders of the Roman Empire and Han China around 100 AD. It’s hard to forget just how connected the world is nowadays. In ancient times, most people would be blissfully unaware of the entire world outside their local community. SilkRoad. The myth behind the Chinese zodiac - Megan Campisi and Pen-Pen Chen. 5 TED-Ed Lessons on Chinese history. Happy Chinese New Year!

Ancient Chinese Weapons Video - Great Wall of China. Ancient China Crossbow Facts, Ancient Chinese Crossbow History. Advert Ancient Chinese Crossbow: A crossbow is a weapon which is used to shoot the projectile, also referred to as bolts.
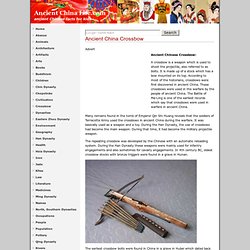
It is made up of a stock which has a bow mounted on its top. Military Technology. The Song period is a good point to take stock of China's military technology.

First, warfare was central to the history of the period. The confrontation between the Song and the three successive non-Chinese states to the north (Liao, Jin, and Yuan) made warfare not only a major preoccupation for those in government service, but also a stimulus to rethinking major intellectual issues. Second, we have illustrated sources for the military arts of the period, in particular, The Essentials of the Military Arts, published in the eleventh century. Most of the illustrations in this section have been drawn from this book. Ancient History Encyclopedia. The Qin dynasty was brief in duration (221-206 BCE) but very important in Chinese history.
It followed the Zhou dynasty (1046-256 BCE) and it ended when Liu Bang became the king of Han in 206 BCE (the formal beginning of the Han dynasty). Despite its brevity, the Qin dynasty left important marks on Chinese culture. Qin Dynasty, Qin Dynasty History, History of Ancient China. Era Information Time: 221 B.C.-207B.C.Location of Capital: Xianyang City in Shanxi Province, not far from Xian Emperors: Ying Zheng, Fushu, Zi Ying Replaced by:Han Dynasty In 221 B.C.

,Chinese were unified for the first time to construct a great country that ended the long era of disunity and warring. In that year the western frontier state of Qin, the most aggressive of the Warring States, subjugated the last of its rival state.Centralization and autarchy were achieved by ruthless methods and focused on standardizing legal codes, bureaucratic procedures, the forms of writing and coinage, and the pattern of thought and scholarship. To silence criticism of imperial rule, the kings banished or put to death many dissenting Confucian scholars and confiscated and burned their books. Qin expansionism was aided by frequent military expeditions pushing forward the frontiers in the north and south. A number of public works projects were also undertaken to consolidate and strengthen imperial rule.
Ancient Chinese Religion - Ancient China for Kids! Ancient China Religions, Ancient Chinese Religious Beliefs. Advert Ancient China Religion: History has witnessed that religion has always evolved with the evolution of different civilizations and various beliefs have come and disappeared along with the disappearance of a particular civilization.
Ancient China has also witnessed many religious practices. Ancient Tombs. Infobase. What is the Mandate of Heaven in China? Answer: The "Mandate of Heaven" is an ancient Chinese philosophical concept, which originated during the Zhou Dynasty (1046-256 BCE). The Mandate determines whether an emperor of China is sufficiently virtuous to rule; if he does not fulfill his obligations as emperor, then he loses the Mandate and thus the right to be emperor. There are four principles to the Mandate:1) Heaven grants the emperor the right to rule,2) Since there is only one Heaven, there can only be one emperor at any given time,3) The emperor's virtue determines his right to rule, and,4) No one dynasty has a permanent right to rule. Signs that a particular ruler had lost the Mandate of Heaven included peasant uprisings, invasions by foreign troops, drought, famine, floods and earthquakes. Of course, drought or floods often led to famine, which in turn caused peasant uprisings, so these factors were often interrelated.
Zhou Dynasty, Zhou Dynasty History, History of Ancient China, China's dynasties. Era Information Time: 1027 B.C.-221B.C.Location of Capital:Hao, near the city of Xian, Shannxi ProvinceEmperors: Twelve kings for eleven dynasties Replaced by:Spring and Autumn Period According to Chinese accounts, Zhou was built by a chieftain of a tribe called Zhou. The chieftain overthrew Shang’s last ruler and build the Zhou dynasty. He settled down in Hao, a city near today’s Xi’an city in Shannxi province. Take a Xian Tours to experience the historical site. Zhou dynasty has lasted for a long time from 1027B.C. to 221B.C.
The Zhou Dynasty originated from the Zhou clan whose existence stretches back into history. At that time, the Shang Dynasty was under the rule of King Zhou. After Zhou Wenwang died, his son Ji Fa (Zhou Wuwang) succeeded him. Chinese History - Common Core. From at least 1766BCE to the twentieth century of the Common Era, China was ruled by dynasties. A dynasty is a family that passes control from one generation to the next. A dynasty does not have to last for a long time. One Chinese dynasty lasted more than 800 years while another lasted only fifteen years. Chinese Dynasty Guide - The Art of Asia - History and Maps. Chinese history, which dates back more than 5,000 years, is extraordinarily rich, complex-and potentially confusing. Understanding at least its basic chronology and some of its most notable events and developments is made somewhat easier by virtue of its ancient system of dynasties.
World History Timeline Civilization: Ancient China. Ancient China Life History Facts:Dynasties,Discoveries,Religions,Crossbow,Sports,Chopsticks. Search. Ancient China for Kids. Ancient China - The Ancient Chinese Civilization. Chinese Historical Accounts. Timelapses from the Silk Road. Ancient China for Kids.