

Ancient Greece : Athenian Democracy. Greek Archeologist Discovers Odysseus’s Palace In Ithaca. Ancient Greece - Information on Ancient Greece. Theater in Ancient Greece. Our interest in the theater connects us intimately with the ancient Greeks and Romans.
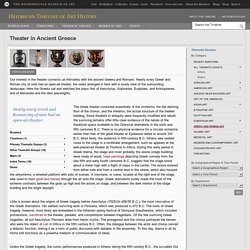
Nearly every Greek and Roman city of note had an open-air theater, the seats arranged in tiers with a lovely view of the surrounding landscape. Here the Greeks sat and watched the plays first of Aeschylus, Sophokles, Euripides, and Aristophanes, and of Menander and the later playwrights. The Greek theater consisted essentially of the orchestra, the flat dancing floor of the chorus, and the theatron, the actual structure of the theater building.
Since theaters in antiquity were frequently modified and rebuilt, the surviving remains offer little clear evidence of the nature of the theatrical space available to the Classical dramatists in the sixth and fifth centuries B.C. There is no physical evidence for a circular orchestra earlier than that of the great theater at Epidauros dated to around 330 B.C. Greek Pottery. Early Bronze Age Greek Pottery (c.3,000 - 2,000 BCE) From around 3,000 BCE, Aegean art in the Peloponnese and eastern Mediterranean took over from Thessaly as the leading centre of pottery, as shapes and styles began to be strongly influenced by the parallel art of metalworking.
Meanwhile, in the Cyclades (southern Greek islands) new forms of pottery included Sesklo ware, which incorporated geometric decoration with incised spirals and maritime motifs. Cretan pottery also had geometric designs: first, in dark paint over a light clay background; then in white over dark paint. Early Minoan shapes included high-spouted jugs and long-spouted drinking vessels, not unlike tea-pots. Middle Bronze Age Greek Pottery (c.2,000 - 1600 BCE) The Greek Chorus in Greek Dramas. Individual Sporting Events or Games of the Ancient Olympics.
About the Greek Philosopher. Name: Aristocles [don't confuse the name with Aristotle], but known as PlatoPlace of Birth: AthensDates 428/427 - 347 B.C.Occupation: Philosopher Who Was Plato?
He was one of the most famous, respected, and influential philosophers of all time. A type of love (Platonic) is named for him. Everyday Life in Ancient Greece, 4th Century BC. Everyday Life in Ancient Greece Centered within a loose collection of city-states (often at war with one another), ancient Greek culture reached its pinnacle during the fourth century BC - an era described as its "Golden Age.
" Art, theater, music, poetry, philosophy, and political experiments such as democracy flourished. Greek influence stretched along the northern rim of the Mediterranean from the shores of Asia Minor to the Italian peninsula. In Athens, society was male-dominated - only men could be citizens and only upper-class males enjoyed a formal education. Most homes were modest, windowless and wrapped around a courtyard. Xenophon was a pupil of Socrates. "Why, then, Socrates, my habit is to rise from bed betimes, when I may still expect to find at home this, that, or the other friend whom I may wish to see. After this, usually I mount my horse and take a canter. Pericles (Leader of Athens) Biography. Who Was Pericles?
: Pericles was a leader of Athens who was responsible for rebuilding Athens following the Persian Wars. He was also leader of Athens during the Peloponnesian War, but he died of the plague that ravaged the city. He was so important that the era in which he lived (during the 5th Century B.C.) is known as the Age of Pericles. Occupation: Leader. Architecture in Ancient Greece. Geography of Ancient Greece. Ancient Greece. Primary History - Ancient Greeks. Who were the ancient Greeks?
Who were the ancient Greeks? Discover different ancient Greek cities and find out how they were ruled. How did the Olympic Games begin? Learn how the Olympic Games began over 2,700 years ago! Find out what events were at the ancient Olympics. What was it like to live in an ancient Greek family? What was everyday life like in ancient Greece? Death, Burial, and the Afterlife in Ancient Greece. Profile of the Greek God Apollo. Pictures | Fast Facts | Profile Apollo is a many-talented Greek god of prophecy, music, intellectual pursuits, healing, plague, and sometimes, the sun.
Writers often contrast the cerebral, beardless young Apollo with his half-brother, the hedonistic Dionysus, god of wine. Leto (Latona) and Zeus (Jupiter) are the parents of the versatile god and his twin sister, the goddess Artemis (Diana), virgin hunter. There were 2 main sites to honor him: 1. Occupation. 3 Important Aspects About Daily Life in Ancient Greece.
Agriculture As with most agricultural societies, daily life in ancient Greece revolved in large part around the agricultural cycles of the seasons.
The rocky Greek soil made farming fairly difficult; common products included grapes, olives and grain. Grape harvest generally took place in the early fall, and the fruit was split into stores for eating and for conversion into wine, which involved stepping on the grapes and fermenting the juice. Olives grew in trees, and harvesters either picked them by hand or used sticks to knock them down. Some were saved for eating, while others were saved to make olive oil -- a vital product for Greeks that had applications for beauty products, lighting fuel, cooking, and even in the area of sports. Grain harvest generally arrived about a month after the grape harvest, and took place behind a plow pulled by oxen. Ancient Greece and You. Ancient Greek calculating device continues to reveal secrets. (PhysOrg.com) -- It's known as the Antikythera mechanism, a metal gear driven device found over a century ago on a sunken Roman ship, near the island of Antikythera, that for just as many years has had scientists analyzing, scratching their heads and offering suggestions as to its purpose.
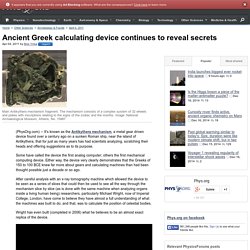
Some have called the device the first analog computer; others the first mechanical computing device. Either way, the device very clearly demonstrates that the Greeks of 150 to 100 BCE knew far more about gears and calculating machines than had been thought possible just a decade or so ago. Wright has even built (completed in 2006) what he believes to be an almost exact replica of the device. Error loading skin: Invalid XML. Unique Marvel of Ancient Greek Technology Gives Up New Secrets. The most sophisticated mechanical device of ancient Greece may finally be giving up its secrets.
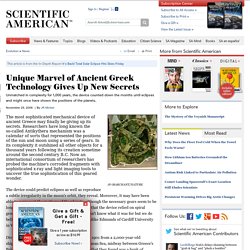
Researchers have long known the so-called Antikythera mechanism was a calendar of sorts that represented the positions of the sun and moon using a series of gears. In its complexity it outshined all other objects for a thousand years following its creation sometime around the second century B.C. Now an international consortium of researchers has probed the machine's corroded fragments with sophisticated x-ray and light imaging tools to uncover the true sophistication of this geared wonder. The device could predict eclipses as well as reproduce a subtle irregularity in the moon's orbit, they reveal. Ancient Greek ships traded more than just wine. (PhysOrg.com) -- While many historians have assumed that Greek sailors were using amphorae, or ancient storage containers, to transport and trade wine, new DNA testing is providing evidence that these containers were used for many different products. The research, published in the Journal of Archaeological Science, reveals the DNA results of vegetables, herbs and nuts in a sampling of jars tested.
Led by archaeologist Brendan Foley from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and geneticist Maria Hansson from Lund University in Sweden, the researchers retrieved DNA samples from nine amphorae that were obtained from sunken ships and dated back to the fifth and third centuries BC. Classics Technology Center: Connections between Ancient Greek Theater and Religion. Connections between Ancient Greek Theater and Religion by Peter Baiter, Betty Banks & John Burke This exercise is the basis for the study of the connections between ancient Greek theater and religion. Beginning with Step 1, read the brief explanation and click on the links to vases, sites, texts and images to learn more about the links between ancient Greek religion and theater.
Step 1: The Origin of Theater Link: Historical Overview, 4.12. Religion, Myth, and Community. Explanation: Greek theater grew out of a religious festival, and was often concerned with the deepest questions about morality and the relationship between mortals, the gods, and fate. Step 2: Hesiod's Theogony Link: Primary Text, Hesiod Theogony lines 1-100. Step 3: Tragedy Link: Historical Overview, 10.2. Step 4: Overview Link: Historical Overview, 10. Step 5: Sacrifice Link: Encyclopedia, Sacrifice.
Step 6: The practice of religious sacrifice Link: Vase Catalog, Harvard 1960.367. The Ancient Olympics.