

What have the Romans done for us? Rome. The History of Rome. The Roman Empire - Rise and Fall 1. The Roman Empire - Rise and Fall 2. How the Romans Buried (or Cremated) Their Dead. Aqueducts, Water Supply and Sewers in Ancient Rome. What We Think We Know About the Roman Water Supply: Ann Olga Koloski-Ostrow, a Brandeis classicist who has studied the Roman latrine, says, "There are no ancient sources where you can really learn about daily life....
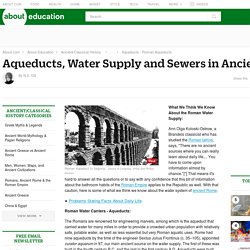
You have to come upon information almost by chance. "[*] That means it's hard to answer all the questions or to say with any confidence that this bit of information about the bathroom habits of the Roman Empire applies to the Republic as well. With that caution, here is some of what we think we know about the water system of ancient Rome. Problems Stating Facts About Daily Life Roman Water Carriers - Aqueducts: The Romans are renowned for engineering marvels, among which is the aqueduct that carried water for many miles in order to provide a crowded urban population with relatively safe, potable water, as well as less essential but very Roman aquatic uses.
Tiber River Aqueducts Listed by Frontinus: In 312 B.C., the Appia Aqueduct was built 16,445 meters long. Sewer: Roman Army - Recruitment, Legions, Siege Warfare & More. Weapons of the Roman Gladiators - Arms and Armor. Roman Republic Government's Three Branches. 3 Branches of Government in Republican Rome - Introduction:

Why Did Rome Fall? It's not entirely arbitrary that Medieval/Renaissance History at About.com begins and Ancient/Classical History ends in A.D. 476.
Edward Gibbon's 476 date for the Fall of Rome is conventionally acceptable because that's when the Germanic Odoacer deposed the last Roman emperor to rule the western part of the Roman Empire. However, the people who lived through the takeover would probably be surprised by the importance we place on this event. And there are other, reasonably momentous dates for the Fall of the Roman Empire. When Did Rome Fall? Some say the split into an eastern and western empire governed by separate emperors caused Rome to fall. Why did Rome Fall? What the Ancients Knew: Coliseum's Elevators. Huge ancient Roman shipyard unearthed - Technology & science - Science - LiveScience. A large Roman shipyard has been uncovered an ancient port in Rome called Portus, researchers reported.
Military Technology: Using a Cloud of Dust in Ancient Warfare. In the present age of technology, imagining the role that such a simple element as dust played in ancient warfare can be difficult.
But what we regard as a mere nuisance often helped decide victory or defeat on the battlefields and during the military campaigns of the classical era. Ancient Rome's greatest defeat arrived in a cloud of dust. Nearly half a millennium after the 216 b.c. Battle of Cannae, historian Lucius Annaeus Florus wrote: 'The crafty general [Hannibal] in his observation of the open plain of that region, because of the severe sun there, and very much dust, and the wind always blowing from the east, prepared his battle line so that the Romans would have dust, sun and wind…directed against their faces while the battle raged. With the aid of the elements, Hannibal's forces crushed their enemy. Such a costly lesson was not to be forgotten. Ancient literature contains many examples in which clouds of dust played a role. Rome's Ancient Catacombs. A cross inlaid in the floor of a library marks the spot where Indiana Jones has to dig to access the ancient catacombs of Venice in the film Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade.
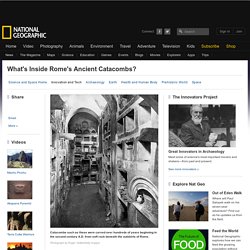
The catacombs, a network of dark and narrow underground tunnels and tombs, hold the secret that eventually leads Indy to the hideout of the Holy Grail. Unfortunately, the dramatic scene is a narrative license. "There are no catacombs in Venice, as the town rises on wood piles in the middle of the saltwater Venetian Lagoon. There is no room for underground chambers or passages, and only a few buildings have a basement," says Luigi Fozzati, head of the Archaeological Superintendence of Veneto. In fact, Venice's cemetery is located on a small island outside the town, and the oldest tombs of nobles and heads of state lie aboveground in churches. Ancient Rome - Ancient Rome from the Earliest Times Down to 476 A.D.
Ancient Rome.

Chapter XLVI. Houses, Customs, Institutions, Etc. The private houses of the Romans were poor affairs until after the conquest of the East, when money began to pour into the city. Many houses of immense size were then erected, adorned with columns, paintings, statues, and costly works of art. Some of these houses are said to have cost as much as two million dollars. Aqueducts, Water Supply and Sewers in Ancient Rome. Julius Caesar and His Rise to Power in the Roman Republic. By the time of the First Triumvirate, the republican form of government in Rome was already on its way to monarchy.
Before you get to the three men involved in the triumvirate, you need to know about some of the events and people that led to it: During the era of the late Republic, Rome suffered through a reign of terror. Terror's tool was a new one, the proscription list, by which large numbers of important, wealthy people, and often senators, were killed; their property, confiscated. Sulla, Roman dictator at the time, instigated this carnage: "Sulla now busied himself with slaughter, and murders without number or limit filled the city.
Although when we think of dictators we think of men and women who want enduring power, a Roman dictator was: a legal official duly nominated by the Senate to handle a major problem, with a fixed, limited term. Economic Reasons for the Fall of Rome. Whether you prefer to say Rome fell (in A.D. 410 when Rome was sacked or in 476 when Odoacer deposed Romulus Augustulus) or simply morphed into the Byzantine Empire and medieval feudalism, economic policies of the emperors had a heavy impact on the lives of the citizens of Rome.
Primary Source Bias Although they say history is written by the victors, sometimes it's just written by the elites. This is the case with Tacitus (c. A.D.56-c.120) and Suetonius (c.71-c.135), our primary literary sources on the first dozen emperors. Historian Cassius Dio, a contemporary of Emperor Commodus (180-192), was also from a senatorial (which, then as now, meant elite) family. Inflation Nero and other emperors debased the currency in order to supply a demand for more coins. Land Rome's wealth was originally in land, but this gave way to wealth through taxation. History - Ancient History in depth: The Fall of Rome.
History - The Colosseum: Emblem of Rome. Why Did Rome Fall?