

Culture of Syria. Orientation Identification.

Syria is the name that was given to the region by the Greeks and Romans and probably derives from the Babylonian suri. Arabs traditionally referred to Syria and a large, vaguely defined surrounding area as Sham, which translates as "the northern region," "the north," "Syria," or "Damascus. " Arabs continued to refer to the area as Sham up until the twentieth century.
That name still is used to refer to the entire area of Jordan, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, and the West Bank and has become a symbol of Arab unity. Location and Geography. Demography. Linguistic Affiliation. Symbolism. Syria History and Ethnic Relations Emergence of the Nation. Syria held its first parliamentary elections in 1932. Hafez al-Assad, the leader of a radical wing of the Arab Socialist party, the Baath, seized control in 1971. National Identity. Ethnic Relations. Syrian Food. Syria Flag - colors meaning history of Syria Flag.
Syria Flag - intorduction Today Syria is in crisis as a result of a civil war between forces favorable to the Mr.
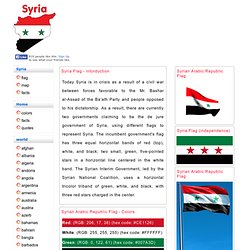
Bashar al-Assad of the Ba'ath Party and people opposed to his dictatorship. As a result, there are currently two governments claiming to be the de jure government of Syria, using different flags to represent Syria. The incumbent government's flag has three equal horizontal bands of red (top), white, and black; two small, green, five-pointed stars in a horizontal line centered in the white band. The Syrian Interim Government, led by the Syrian National Coalition, uses a horizontal tricolor triband of green, white, and black, with three red stars charged in the center. Syrian Arabic Republic Flag - Colors Red: (RGB: 206, 17, 38) (hex code: #CE1126) White: (RGB: 255, 255, 255) (hex code: #FFFFFF) Green: (RGB: 0, 122, 61) (hex code: #007A3D) Black: (RGB: 0, 0, 0) (hex code: #000000) Syrian Arabic Republic Flag - Colors meaning Red symbolizes bloody struggle for freedom.
Syria: Government. Due to the ongoing conflict in Syria, the information on these pages may not reflect current conditions in the country.

Chief of State: President Bashar al-AsadHead of Government: Prime Minister Wael Nader al-Halqi The Syrian constitution vests the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party with leadership functions in the state and society and provides broad powers to the president. The president, approved by referendum for a 7-year term, is also Secretary General of the Ba'ath Party and leader of the National Progressive Front, which is a coalition of 10 political parties authorized by the regime.
The president has the right to appoint ministers, to declare war and states of emergency, to issue laws (which, except in the case of emergency, require ratification by the People's Council), to declare amnesty, to amend the constitution, and to appoint civil servants and military personnel. The Syrian constitution of 1973 requires that the president be Muslim but does not make Islam the state religion. Location. Syria Economy: Population, GDP, Inflation, Business, Trade, FDI, Corruption. Numerical grading of Syria’s overall economic freedom remains suspended because of the ongoing political turmoil that has led to civil unrest and a significant deterioration in the quality of publicly available economic statistics.
Those facets of economic freedom for which data are still available have been individually scored. As a “mostly unfree” economy with a score of 51.2, Syria was ranked fourth lowest in the Middle East/North Africa region when it was last graded in the 2012 Index. Before grading was suspended, the fragility of the foundations of economic freedom in Syria had been documented in very low scores for property rights and freedom from corruption. The state has long dominated economic activity, and the repressive environment has marginalized the private sector and prevented any sustainable development. The Bashar al-Assad regime’s brutal actions to maintain its hold on power have destroyed the rule of law and destabilized the region. Close Background. Language.