

The Scale of the Universe. Celestial event. Cosmic Spider Swallows Starlight in Amazing Telescope View (Video, Photos) A dark, spider-shaped cloud of cosmic gas blocks out light from stars in a new image taken by a telescope in the Southern Hemisphere.
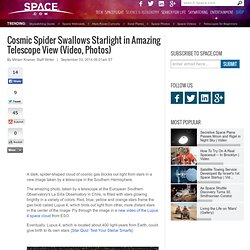
The amazing photo, taken by a telescope at the European Southern Observatory's La Silla Observatory in Chile, is filled with stars glowing brightly in a variety of colors. Red, blue, yellow and orange stars frame the gas blob called Lupus 4, which blots out light from other, more distant stars in the center of the image. Fly through the image in a new video of the Lupus 4 space cloud from ESO. Eventually, Lupus 4, which is located about 400 light-years from Earth, could give birth to its own stars. [Star Quiz: Test Your Stellar Smarts] A dark cloud of gas called Lupus 4 blocks out more-distant stars. "How many stars might eventually start to shine within Lupus 4? Welcome To Our New Galactic Supercluster Home: Laniakea. Your ultimate address just changed.
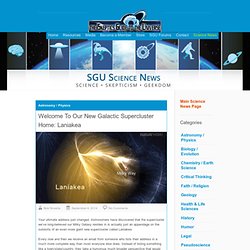
Astronomers have discovered that the supercluster we’ve long-believed our Milky Galaxy resides in is actually just an appendage on the outskirts of an even more giant new supercluster called Laniakea. Every now and then we receive an email from someone who lists their address in a much more complete way than most everyone else does. From Quark to Quasar: The Observable Universe. “That tiny dot that you can hardly make out in the screen is the Virgo Supercluster, where our galaxy, our local group and several others reside.
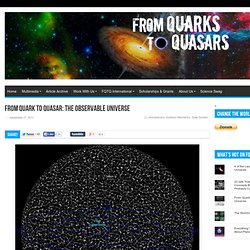
All of those other dots are superclusters, each containing perhaps trillions of stars. Via WikiMedia If you really want a headache (the good kind), take a long look at this “photo”. No, this is not a photo of the cosmic microwave background radiation (which you can actually see for yourself if you change your television channel to one of the “fuzzy” stations), neither is it a collection of graphs of a cell structure. So, instead of telling you what it isn’t, how about I tell you what it is? First Planck results: the Universe is still weird and interesting. Our current model of cosmology—the origin and structure of the whole Universe—has survived another major test, with the release of the first 15 months of data from the Planck mission.
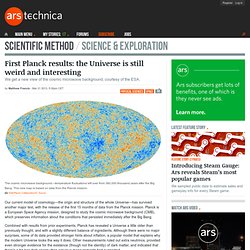
Planck is a European Space Agency mission, designed to study the cosmic microwave background (CMB), which preserves information about the conditions that persisted immediately after the Big Bang. Combined with results from prior experiments, Planck has revealed a Universe a little older than previously thought, and with a slightly different balance of ingredients.
Although there were no major surprises, some of its data provided stronger hints about inflation, a popular model that explains why the modern Universe looks the way it does. Astrometry. Better Not Avoid A Cosmic Void. (Inside Science) -- Sometimes nothingness can reveal a whole lot.
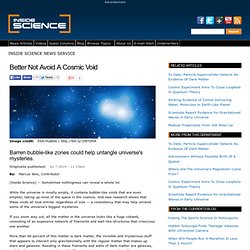
3D Galactic Map May Solve Interstellar Puzzle. Universal Formula for Cosmic Voids. +Enlarge image N.

Hamaus/Paris Inst. of Astrophys. & M. Warren/Los Alamos National Lab. Mystery of cosmic rays' origin finally solved - physics-math - 14 February 2013. Video: Stellar cataclysm The protons that constantly smack into Earth's atmosphere at near the speed of light get their huge energies from exploding stars.
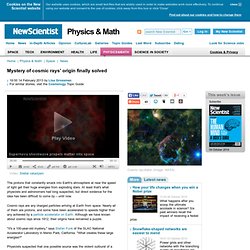
At least that's what physicists and astronomers had long suspected, but direct evidence for the idea has been difficult to come by – until now. Cosmic rays are any charged particles arriving at Earth from space. Nearly all of them are protons, and some have been accelerated to speeds higher than any achieved by a particle accelerator on Earth. Although we have known about cosmic rays since 1912, their origins have remained a puzzle. "It's a 100-year-old mystery," says Stefan Funk of the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in Menlo Park, California.
Physicists suspected that one possible source was the violent outburst of a supernova within the Milky Way. "Eventually their energy gets large enough that they can leave the shock region," Funk says. Total scramble Another approach to the problem was needed – and gamma rays provided it. CMB. Cosmic Background Radiation :
The-Observable-Universe.jpg (JPEG Image, 3850x1925 pixels) - Scaled (27%) Planetarium - Interactive star map and virtual sky. Interactive Star Charts, Planets, Meteors, Comets, Telescopes. 32 Nearby Stars. Chronology of Cosmic Microwave Background Astronomy. Chronology of Galaxies, Clusters of Galaxies, and Large Scale Structure.
Chronology of Astronomical Maps. Forensic astronomy. Forensic astronomy is the use of astronomy, the scientific study of celestial objects, to determine past celestial constellations.
This has been used, if relatively rarely, in forensic science (that is, for solving problems of relevance to the legal system) and for resolving historical problems more generally, notably issues in art history. Forensic science[edit] As a forensic science in the strict sense of the term, astronomical knowledge can help resolve certain legal questions.
In one reported instance, an astronomer testified in court as an expert witness as to whether a newly built house would cast a shadow on another house. Observable universe. The surface of last scattering is the collection of points in space at the exact distance that photons from the time of photon decoupling just reach us today.
These are the photons we detect today as cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR). However, with future technology, it may be possible to observe the still older neutrino background, or even more distant events via gravitational waves (which also should move at the speed of light).
What is the Universe Expanding Into?