

FOODS 26/10/21 New Trends in Photodynamic Inactivation (PDI) Combating Biofilms in the Food Industry—A Review. All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license.
No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. Feature Papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. Feature Papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and undergo peer review prior to publication. The Feature Paper can be either an original research article, a substantial novel research study that often involves several techniques or approaches, or a comprehensive review paper with concise and precise updates on the latest progress in the field that systematically reviews the most exciting advances in scientific literature.
FOODS 08/09/21 Bacterial Biofilms and Their Implications in Pathogenesis and Food Safety. All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license.
No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. Feature Papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. Feature Papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and undergo peer review prior to publication.
The Feature Paper can be either an original research article, a substantial novel research study that often involves several techniques or approaches, or a comprehensive review paper with concise and precise updates on the latest progress in the field that systematically reviews the most exciting advances in scientific literature. ANTIBIOTICS 03/02/20 Bacterial Biofilm and its Role in the Pathogenesis of Disease. Recognition of the fact that bacterial biofilm may play a role in the pathogenesis of disease has led to an increased focus on identifying diseases that may be biofilm-related.
Biofilm infections are typically chronic in nature, as biofilm-residing bacteria can be resilient to both the immune system, antibiotics, and other treatments. This is a comprehensive review describing biofilm diseases in the auditory, the cardiovascular, the digestive, the integumentary, the reproductive, the respiratory, and the urinary system. In most cases reviewed, the biofilms were identified through various imaging technics, in addition to other study approaches. FOOD SAFETY MAGAZINE - OCT/NOV 2020 - Addressing Biofilms through the Sanitation Process. Sanitation | October/November 2020 By Food Safety Magazine For years, food companies have struggled with biofilm prevention.

Its importance cannot be underestimated and should be addressed through effective sanitation programs. With proper implementation of the sanitation process, biofilms can be removed and prevented, and potential health risks reduced. Biofilms are a community of bacterial cells that adhere to each other and surfaces, protected by polysaccharides that act like glue.[1] These polysaccharides allow bacteria to attach themselves to surfaces and feed off the protein and soils that have not been removed. Eight Steps of Sanitation 1. 2. 3. . • Ensure proper foam application from bottom to top on all equipment. • Foam should be left on the equipment for 10–15 minutes, but do not let the foam dry. • Hand-scrubbing should be completed while the foam is on the equipment or with a separate scrub bucket of general-purpose cleaner and a scrub pad. 1. 2. 3. 4. 4. 5. 6. 7.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MICROBIOLOGY 25/08/20 The Role of Bacterial Biofilm in Antibiotic Resistance and Food Contamination. Biofilm is a microbial association or community attached to different biotic or abiotic surfaces or environments.

These surface-attached microbial communities can be found in food, medical, industrial, and natural environments. International Journal of Food Microbiology Available online 20 May 2020, Identification of biofilm hotspots in a meat processing environment: Detection of spoilage bacteria in multi-species biofilms. Biofilms are comprised of microorganisms embedded in a self-produced matrix that normally adhere to a surface.
In the food processing environment, they are suggested to be a source of contamination leading to food spoilage or the transmission of food-borne pathogens. To date, research has mainly focused on the presence of (biofilm-forming) bacteria within food processing environments, without measuring the associated biofilm matrix components. Here, we assess the presence of biofilms within a meat processing environment, processing pork, poultry and beef, by the detection of microorganisms and at least two biofilm matrix components.
Sampling included 47 food contact surfaces and 61 non-food contact surfaces from eleven rooms within an Austrian meat processing plant, either during operation or after cleaning and disinfection. The 108 samples were analysed for the presence of microorganisms by cultivation and targeted quantitative real-time PCR based on 16S rRNA. PENN STATE NEWS 21/08/19 Foodborne pathogen sheltered by harmless bacteria that support biofilm formation. UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Pathogenic bacteria that stubbornly lurk in some apple-packing facilities may be sheltered and protected by harmless bacteria that are known for their ability to form biofilms, according to Penn State researchers, who suggest the discovery could lead to development of alternative foodborne-pathogen-control strategies.
That was the key finding that emerged from a study of three tree-fruit-packing facilities in the Northeast where contamination with Listeria monocytogenes was a concern. The research, done in collaboration with the apple industry, was an effort to better understand the microbial ecology of food-processing facilities. FRONT. MICROBIOL 07/05/18 Biofilms in the Food Industry: Health Aspects and Control Methods. Biofilms in the Food Industry Biofilms are complex microbial ecosystems formed by one or more species immersed in an extracellular matrix of different compositions depending on the type of food manufacturing environment and the colonizing species.
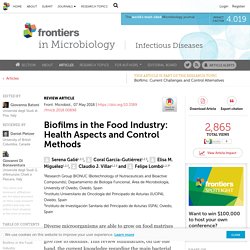
Examples of microorganisms that can comprise these biofilms include bacteria and fungi. The presence of more than one bacterial species in a biofilm has important ecological advantages because it can facilitate the biofilm’s attachment to a surface. For some species, this can even occur in the absence of specialized fimbriae. Mixed biofilms show higher resistance to disinfectants such as quaternary ammonium compounds and other biocides (Meyer, 2015). The extracellular matrix is mainly composed of polysaccharides, such as cellulose, proteins or exogenous DNA. Biofilms: Impact on the Food Industry. SANITATION | June/July 2012 By Michael Cramer Last month, I went to the dentist for my routine 6-month checkup.

Maintaining good oral health has always been important to me and was stressed in our family when I was growing up. As my father used to quip, “Be true to your teeth or your teeth will be false to you.” The dental hygienist cleaning my teeth asked if I brush my teeth manually or if I use an electric toothbrush. Biofilm.V1.ppt - Dév_et_éval_de_traitements_anti_biofilms_2.pdf. Biofilm-GB-FarbeLack.pdf. Influence of biofilms by... [Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1987. Folie 1 - biofilm_deutsch.pdf. Biofilms en industrie agro-alimentaire = Biofilms in food industry. Titre du document / Document title Auteur(s) / Author(s) Affiliation(s) du ou des auteurs / Author(s) Affiliation(s) (1) Afssa, (Agence française de sécurité sanitaire des aliments) Laboratoire d'études et de recherches pour l'alimentation collective, 94 Maisons-Alfort, FRANCE Résumé / Abstract Lorsqu'ils adhèrent et colonisent les surfaces, les micro-organismes acquièrent de nouvelles propriétés; ils sont notamment plus résistants aux désinfectants.
Revue / Journal Title Source / Source 2002, vol. 92, no NOV (28 p.) Biofilm ANSES. Biofilm. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre. Biofilm superficiel intertidal, en grande partie photosynthétique sur vaseestuarienne exondée, se formant à marée descendante. C'est une source de nourriture pour de nombreux invetégrés, mais aussi pour certains bécasseaux littoraux [1] qui trouvent là jusqu'à 50 % des ressources énergétiques dont ils ont besoin Autre exemple, essentiellement constitué d'algues couvrant une eau stagnante.