

What are the 5 Ps of prayer? Host: What are the 5 Ps of prayer? Rev. Joseph McCloskey: The five Ps of prayer are, if I am going to do it properly it is how do I get myself into the presence of God? So the first P is called Presence. Falling for God. Safed the sage. The Attributes of God. Asperger - PubMed Results. A Christian Perspective of Myers-Briggs Personality Types. 3D Facial Expression Database - Binghamton University.
Analyzing Facial Expressions in Three Dimensional Space Introduction Traditionally, human facial expressions have been studied using either 2D static images or 2D video sequences.

The 2D-based analysis is difficult to handle large pose variations and subtle facial behavior. This exploratory research targets the facial expression analysis and recognition in a 3D space. The analysis of 3D facial expressions will facilitate the examination of the fine structural changes inherent in the spontaneous expressions. Project Progress I. 3D facial models have been extensively used for 3D face recognition and 3D face animation, the usefulness of such data for 3D facial expression recognition is unknown. The database presently contains 100 subjects (56% female, 44% male), ranging age from 18 years to 70 years old, with a variety of ethnic/racial ancestries, including White, Black, East-Asian, Middle-east Asian, Indian, and Hispanic Latino. Human Intelligence: The APA 1996 Intelligence Task Force Report. The American Psychological Association (APA) Task Force on Intelligence was created in response to the debate surrounding the publication of The Bell Curve in 1994.
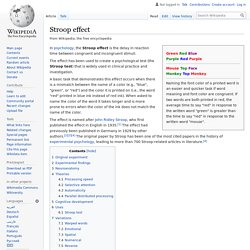
The task force issued its report in 1995 and published a revised version in the February 1996 issue of American Psychologist. The report and article have been influential and are highly cited. In this Hot Topic, we refer to the group as the 1996 task force because the 1996 article drew the most attention to the group's work. Why an APA Task Force? Stroop effect. Green Red BluePurple Blue Purple Blue Purple RedGreen Purple Green.
Simons Lab. Most of the videos on this site are also available on Prof.

Simons's personal website and are also viewable on his YouTube channel. Adoption History: Harry Harlow, Monkey Love Experiments. The Gifts of the Holy Spirit. By Ron R.

Ritchie. Peter Salovey, University leadership. President Peter Salovey A.B., A.M., Ph.D.

Peter Salovey is the 23rd president of Yale University, and the Chris Argyris Professor of Psychology. His presidential term began in July 2013. Prior to becoming president, Salovey served as the provost of Yale University from 2008 to 2013. 4 Scales of Personality Type Preferences. Big Five personality traits. In psychology, the Big Five personality traits are five broad domains or dimensions of personality that are used to describe human personality.

The theory based on the Big Five factors is called the five-factor model (FFM).[1] The five factors are openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism. Acronyms commonly used to refer to the five traits collectively are OCEAN, NEOAC, or CANOE. Beneath each global factor, a cluster of correlated and more specific primary factors are found; for example, extraversion includes such related qualities as gregariousness, assertiveness, excitement seeking, warmth, activity, and positive emotions.[2]:24 The Big Five model is able to account for different traits in personality without overlapping. Empirical research has shown that the Big Five personality traits show consistency in interviews, self-descriptions and observations.
§Five factors[edit] Intelligence. Harry Harlow. Harry Frederick Harlow (October 31, 1905 – December 6, 1981) was an American psychologist best known for his maternal-separation, dependency needs, and social isolation experiments on rhesus monkeys, which demonstrated the importance of care-giving and companionship in social and cognitive development.
He conducted most of his research at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, where humanistic psychologist Abraham Maslow worked for a time with him. Harlow's experiments were controversial; they included rearing infant macaques in isolation chambers for up to 24 months, from which they emerged severely disturbed.[1] Some researchers cite the experiments as a factor in the rise of the animal liberation movement in the United States.[2] Biography[edit] Ultimatum game. Extensive form representation of a two proposal ultimatum game.
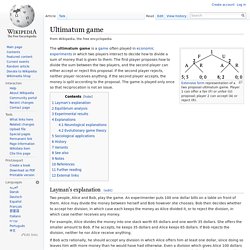
Player 1 can offer a fair (F) or unfair (U) proposal; player 2 can accept (A) or reject (R). The ultimatum game is a game often played in economic experiments in which two players interact to decide how to divide a sum of money that is given to them. The first player proposes how to divide the sum between the two players, and the second player can either accept or reject this proposal. If the second player rejects, neither player receives anything. Robert Axelrod - The Complexity of Cooperation. Robert Axelrod's recent Complexity of Cooperation is a sequel to his celebrated Evolution of Cooperation (1984).

In the new book, updated versions of his papers on the subject since 1984 are reprinted together with a commentary that places them in context. PsycARTICLES - Insult, Aggression, and the Southern Culture of Honor: An “Experimental Ethnography†Rorschach test. The Rorschach test (/ˈrɔrʃɑːk/ or /ˈrɔərʃɑːk/,[3] German pronunciation: [ˈʁoːɐʃax]; also known as the Rorschach inkblot test, the Rorschach technique, or simply the inkblot test) is a psychological test in which subjects' perceptions of inkblots are recorded and then analyzed using psychological interpretation, complex algorithms, or both. Some psychologists use this test to examine a person's personality characteristics and emotional functioning. It has been employed to detect underlying thought disorder, especially in cases where patients are reluctant to describe their thinking processes openly.[4] The test is named after its creator, Swiss psychologist Hermann Rorschach. Although the Exner Scoring System (developed since the 1960s) claims to have addressed and often refuted many criticisms of the original testing system with an extensive body of research,[10] some researchers continue to raise questions.
History Method. Anatol Rapoport. Anatol Rapoport Anatol Rapoport (Russian: Анато́лий Бори́сович Рапопо́рт; May 22, 1911 – January 20, 2007) was a Russian-born American mathematical psychologist. He contributed to general systems theory, mathematical biology and to the mathematical modeling of social interaction and stochastic models of contagion. Biography[edit] Raymond Cattell. 16 Personality Factors. Change detection database. John Maxwell’s Formula For Raising Your Level of Leadership - Knowledge@Emory. Best-selling author and leadership guru John C. The Shepard Tabletop Illusion. F.A.C.E. Training. Eight Personality Type Preferences Working Together. Felix S. Cohen. Felix Solomon Cohen (July 3, 1907 – October 19, 1953) was an American lawyer and scholar who made a lasting mark on legal philosophy and fundamentally shaped federal Indian law and policy. Biography[edit] J. Kevin O'Regan. J. Kevin O'Regan jkevin.oregan@gmail.comOnline calendar last updated 16 Oct 2013.