

Australian Democracy Part 1. Democratic rights and freedoms - About Australia. Australia’s approach to human rights and freedoms reflects its liberal democratic ideals and a belief in the inherent dignity and the equal and inalienable rights of all people, as set out in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
Australia played a leading role in the development of international human rights standards, and is party to six major UN human rights treaties. Australia also engages actively in UN human rights mechanisms and supports developing countries in improving human rights standards, particularly through providing significant support for the promotion of democratic institutions.
Promoting a strong, free democracy Australia’s federal structure, independent judiciary, robust representative parliamentary institutions and independent national human rights institution (the Human Rights and Equal Opportunity Commission) play an integral role in protecting human rights. They also provide a bulwark against abuses of power and denials of fundamental freedoms. Voting rights for Aboriginal people. Aboriginal ‘Vote’ poster.
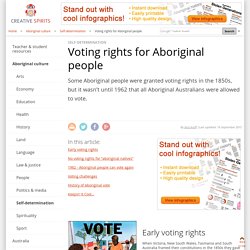
This poster is part of a series designed specifically for and in consultation with remote area communities by Aboriginal designers in the late 1980s to encourage Aboriginal citizens to become actively involved and to exercise their right to vote [1]. Early voting rights When Victoria, New South Wales, Tasmania and South Australia framed their constitutions in the 1850s they gave voting rights to all male British subjects over 21, which included Aboriginal men. In 1894 South Australia, which then included the Northern Territory, made laws which allowed all adults to vote, including all women and therefore all Aboriginal women [5]. Australian citizenship. The process of applying for Australian citizenship varies depending on your eligibility.
Based on your answers to a series of questions, the Citizenship Wizard will give you information about what to do and how to apply for Australian citizenship. /service/citizenship-wizard The process of applying for Australian citizenship varies depending on your eligibility. There are a number of different application options with different eligibility requirements. Documenting Democracy. Significance This document introduced the principle of citizenship for Australians as belonging to Australia, rather than to Britain.
Like the citizens of all the countries comprising the British Commonwealth, Australian citizens remained British subjects, but from the proclamation of the Act on 26 January 1949, were recognised also as citizens of their own country. The Act retained the concept of 'aliens', defining this as all those who are not British subjects, excepting Irish citizens and 'protected persons' within the British Commonwealth. History. Documenting Democracy. Photo of an Australian citizenship certificate. Citizenship Certificate. Aurtur caldwell. The Myth of Aboriginal Voting Rights. On 27 May 1967, campaigners for the rights and status of Indigenous Australians won the most decisive referendum victory in Australian history.
Over 90 per cent of Australian voters endorsed the constitutional amendments proposed. In no electorate was the affirmative vote less than 70 per cent; in some it exceeded 95 per cent. This was as close to consensus as can be expected in a democratic contest. The extraordinarily high affirmative vote, however, has promoted exaggerated assessments of the referendum's consequences. The 1967 referendum has been popularly memorialised as a turning point for Aboriginal rights: the moment when they won the vote, became citizens, gained legal equality and when Aboriginal affairs came under federal control.
Google Image Result for. AustralianCollaboration. Instagrok. Documenting Democracy. Coastal Waters (State Powers) Act 1980 (Cth) Significance This document transferred constitutional power over coastal waters, and title to seabed minerals within territorial limits, from the Commonwealth to the States and was passed with the consent of each State Parliament under Section 51.xxxviii of the Australian Constitution .

History. Women and Democracy. Australian democracy: an overview · Museum of Australian Democracy at Old Parliament House. Australian Citizenship History ‹ Australian Citizenship Test. Certificate of Naturalisation- Stanio Fancoff, Australia, 1935 - Museum Victoria. This Commonwealth of Australia Certificate of Naturalisation was awarded to Stanio Fancoff in 1935. Detailing the terms and conditions by which he become an Australian citizen, this document legally denounces Stanio's past allegiances to Bulgaria in favour of his committment to be an Australian subject, and thus entitles him to all rights and priviledges afforded to all Australian citizens. Stanio Ivanoff Fancoff was born in 1908 in Bojentsi, a small village in Bulgaria. At age 11, Stanio left home to learn the shoemaking trade. In 1929, he immigrated to Melbourne, settled in Fitzroy and began to work for the V.G. Zemancheff & Sons basket shoe factory in South Melbourne. Parliament of NSW - History of democracy in NSW.
The Parliament of New South Wales is Australia's first and oldest Parliament, and its complex of buildings includes the oldest building surviving in the Sydney Central Business District (CBD).
Sydney was founded as a convict colony by the British in 1788. Limited provision was made for infrastructure, convict labour being the main source of public building. When Governor Lachlan Macquarie (Governor of New South Wales from 1810-1821) arrived in the colony, he found there were no permanent hospital facilities. With no provision of funds from the distant British government, he managed to have Sydney's first permanent hospital, completed in 1816. To fund the building, he allowed the building contractors to import and sell 60,000 gallons of rum. History of Australia (1788–1850) The history of Australia from 1788–1850 covers the early colonies period of Australia's history, from the arrival of the First Fleet of British ships at Sydney to establish the penal colony of New South Wales in 1788 to the European exploration of the continent and establishment of other colonies and the beginnings of autonomous democratic government.
Colonisation and convictism [ edit ] Establishment of the first British Colony [ edit ] A proposal that Britain found a colony of banished convicts in the South Sea (or in Terra Australis) to enable the mother country to exploit the riches of those regions, had been put forward in 1766 by John Callander in Terra Australia Cognita . Following the loss of the American Colonies after the American Revolutionary War 1775-1783, Great Britain needed to find alternative land for a new British colony.
Australia was chosen for settlement, and colonisation began in 1788. A map of Sydney from 1789. Convicts and free settlers [ edit ] Exploration [ edit ] People fighting for democracy. A brief history of Australian democracy, Introduction to democracy, Potentials of democracy, SOSE Year 9. Documenting Democracy. For and against Federation, Federation, Australian democracy, HSIE Year 6, NSW. Australia before 1901 Today Australia is one country, or nation, which is divided into six separate states and two territories.

Whilst Australia's official head of state is the British monarch, Australia now has its own parliaments and is basically an independent nation. This has only been the case since Federation in 1901. Before Federation, Australia's six states were separate colonies, all of which were considered part of Britain. Each state operated independently and had its own defence forces, its own trade, postal and railway systems and its own immigration laws.
Documenting Democracy. Www.citizenship.gov.au/_pdf/cit_chron_policy_law.pdf. Documenting Democracy. Documenting Democracy. Significance This document put in place the law that was the cornerstone of Australia's 'White Australia' policy.
The Governor-General signed the document two days before Christmas Day 1901, a week after he had signed the Pacific Islander Labourers Act into law. Together with Section 15 of the 1901 Post and Telegraph Act (see below), these formed a powerful set of legal instruments shaping immigration policy at the foundation of the Commonwealth. They continued to guide thinking on immigration for half a century. History The Immigration Restriction Act was the key part of a package of legislation passed by the new Federal Parliament in 1901, aimed at excluding all non-European migrants.
The mechanism restricting immigration could not be overtly based on race as this was opposed by Britain and frowned upon by Britain's ally, Japan. May 1898 How to Vote. Australia History. Before the arrival of European settlers, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples inhabited most areas of the Australian continent.
Each people spoke one or more of hundreds of separate languages, with lifestyles and cultural traditions that differed according to the region in which they lived. Their complex social systems and highly developed traditions reflect a deep connection with the land and environment. Asian and Oceanic mariners and traders were in contact with Indigenous Australians for many centuries before the European expansion into the Eastern Hemisphere. Some formed substantial relationships with communities in northern Australia. The first recorded European contact with Australia was in March 1606, when Dutch explorer Willem Janszoon (c.1570 – 1630) charted the west coast of Cape York Peninsula, Queensland. Britain decided to use its new outpost as a penal colony; the First Fleet of 11 ships carried about 1500 people—half of them convicts.
A Nation is Born. Democracy. On this day: indigenous people get citizenship. Aboriginal people were recognised as Australian citizens only in 1967. (Credit: State Library of New South Wales) ON THIS DAY , 44 years ago, 90.77 per cent of Australians voted 'yes' in a constitutional referendum to improve indigenous rights and award citizenship to Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders. Until the referendum, every state had different laws for indigenous people, while the commonwealth constitution excluded them "in reckoning the numbers of the people of the Commonwealth".
Put simply, indigenous Australians were not citizens and had few, if any, rights. In 1965, Charles Perkins and a group of students from Sydney University led a bus tour through indigenous communities in NSW. At the same time, a petition for a referendum that had been circulating for nearly a decade surpassed a million signatures - a magic number for politics of the day, giving the parliament grounds to hold a referendum.
A referendum on indigenous rights was called for the 27 May, 1967. New Australian Citizenship Test - Most difficult questions. Welcome to Kidsview - Parliament in Focus, Parliamentary Education Office, Commonwealth Parliament of Australia. Photo of democracy in australia.