

After Success in Florida, The Use Of Virtual Reality To Treat PTSD Is Expanding. The University of Central Florida is using virtual reality to treat post-traumatic stress disorder.
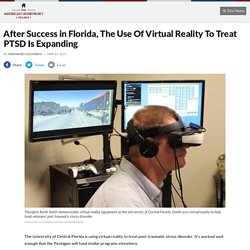
It's worked well enough that the Pentagon will fund similar programs elsewhere. Stephanie Colombini reports that veterans are using virtual reality to treat their PTSD. Imagine walking through a village in a war zone in Iraq. Suddenly a bomb explodes. Guns are firing. It's all very disturbing. Except this isn't an Iraqi village. A program called "UCF RESTORES" has been using virtual reality since 2010 as part of an exposure therapy program to treat post-traumatic stress disorder in combat veterans. Clinic Director Deborah Beidel said many of the program's patients struggle with everyday tasks like shopping or going to the gas station. "We never think people's traumatic memories are going to go away," Beidel said. Army National Guard veteran Kevin Tergliafera, 38, served in Afghanistan and for years battled anger and manic depression. Tergliafera said he was shocked to see himself open up.
How Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy (VRET) Treats PTSD. Virtual reality exposure therapy (VRET) is being examined as another way to help people recover from PTSD.1 VRET is a type of exposure therapy that has increasingly been used to treat a variety of anxiety disorders, including specific phobias2 .
Before learning how VRET treats PTSD symptoms, however, it's important to have a handle on what exposure therapy is. Exposure Therapy Exposure therapy is considered to be a behavioral treatment for PTSD. Exposure therapy targets behaviors that people engage in (most often avoidance) in response to situations or thoughts and memories that are viewed as frightening or anxiety-provoking.3 For example, a rape survivor may begin to avoid relationships or going out on dates for fear that she will be attacked again. If not addressed, avoidance behavior can become more extreme and interfere with a person's quality of life. This is done by actively confronting the things that a person fears most. Augmented Reality in Healthcare. Augmented reality (AR) is one of the latest innovations taking route into various markets which include gaming, medicine, automotive, retail amongst others.
AR technology has been in development since the 1960’s. According to a recent forecast, the AR device market is expected to reach $659.98 million by the end of 2018. AR technology lets users see the real world and projects digital information onto the existing environment. In many ways, AR is a mixture of VR, imposed into real life. These virtual contents are typically in the form of digital imagery or sound, usually applied in 3D models or videos. AR Opportunities in Healthcare The application of augmented reality technology is opening up new opportunities in the healthcare industry.
Augmented Surgery As data access technologies are already very advanced, the next step is to provide real-time, life-saving patient information to surgeons which they can use during simple or complex procedures. Augmented Surgery Startups to Watch. How Leading Hospitals Are Using Mobile Apps for Training and Better Patient Care. Skip to content.
Going Mobile: A review of mobile learning in medical education — mcdreeamie-musings. Teachers’ attitudes toward and ability with mobile resources are a major influence on students deciding to use them.
It’s been suggested that Web 2.0 offers opportunities for educator innovation. However, it has been shown that teachers may be less engaged than their students in utilising Web 2.0 resources especially in accessing materials outside of the classroom. I’ve not been able to find any research in the literature looking at the perceptions of UK medical educators toward mobile learning. However, a recent online survey of 284 medical educators in Germany did show some interesting findings. Respondents valued interactive patient cases, podcasts and subject-specific apps as the more constructive teaching tools while Facebook and Twitter were considered unsuitable as platforms for medical education.
Virtual and Augmented Reality in Medical Education. 1.

Introduction Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are the current trends in medical education. VR is the virtual construction of an artificial world. The key element of VR is the high level of user’s immersion over the virtual environment, namely, the high level of structures’ fidelity, as well as the interaction of the user with them in a realistic manner. This has become recently available, as it requires high standards of certain technologies, including advanced haptic devices with force-feedback capabilities (bidirectional stimuli), high-resolution audio-visual effects, motion detection technology, and high-performance processing power to transmit, and processes all this information with near-zero latency.
Extended Reality in Medical Education: Driving Adoption through Provider-Centered Design - FullText - Digital Biomarkers 2019, Vol. 3, No. 1. Zweifach S.M.a · Triola M.M.b Author affiliations aNYU School of Medicine, NYU Langone Health, New York, NY, USAbNYU School of Medicine, Institute for Innovations in Medical Education, NYU Langone Health, New York, NY, USA Corresponding Author.

A New Reality in Clinical Care: How XR Could Transform Healthcare. While they have not hit the mainstream yet, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are clearly not just for gaming anymore.

They are serious business and hold real promise for the future of medicine. Known collectively as XR, this technological movement in immersive computing is quietly gaining momentum and could transform healthcare in ways many never thought possible. According to an Accenture report, more than one-third of healthcare organizations have already adopted extended reality (XR) across one or more business units. Already, these technologies are impacting key areas of patient care in dozens of innovative applications, from medical and skill-based training to the assisted delivery of high-precision robotic surgery and much more. AccuVein Vein Visualization-Improves IV 1-Stick Success 3.5x.