

Sound Waves To Control Brain Cells Through Sonogenetics Discovered. Salk scientists have developed a new way to selectively activate brain, heart, muscle and other cells using ultrasonic waves.
The new technique, dubbed sonogenetics, has some similarities to the burgeoning use of light to activate cells in order to better understand the brain. This new method--which uses the same type of waves used in medical sonograms--may have advantages over the light-based approach--known as optogenetics--particularly when it comes to adapting the technology to human therapeutics. It was described September 15, 2015 in the journal Nature Communications. "Light-based techniques are great for some uses and I think we're going to continue to see developments on that front," says Sreekanth Chalasani, an assistant professor in Salk's Molecular Neurobiology Laboratory and senior author of the study.
"But this is a new, additional tool to manipulate neurons and other cells in the body. " Video: Sonogenetics So far, sonogenetics has only been applied to C. elegans neurons. Stem Cells Help In Identifying New Treatments for Dementia. Researchers in Belgium are using induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technology to create neurons that are targeted by dementia.
By studying these neurons, the scientists have found a defect that prevents normal neurodevelopment. Stem cells were taken from patients who has an inheritable type of dementia that is responsible for 50% of dementia cases for people below the age of 60. Dementia is a neurological disorder that causes loss of brain function. Memory, language, behavior, judgement and how the patient thinks are affected by dementia. It is a serious loss of global cognitive ability in a previously unimpaired or normal person, beyond what might be expected from normal aging. The most common type of dementia is Alzheimer's disease. Usually associated with elderly patients, there are cases of dementia occurring to patients below the ages of 60/65. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Found To Improve Memory. A study by the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine find that stimulating a part of the brain with electromagnetic pulses in a process called Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation can improve memory.
The non-invasive process uses electrical current using magnetic pulses to target a region of the brain. This is the first time that memory functions of a brain can be manipulated without the use of surgery or of drugs. By targeting a specific area of the brain in the hippocampus, they observed that TMS can be used to improve memory for events at least 24 hours after the stimulation is given. The study, published in Science, used 16 healthy adults ages 21 to 40 (see video below). They received brain stimulation through Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) twenty minutes a day for five consecutive days. Nintendo Game Console Improves Multiple Sclerosis Rehabilitation.
Working Memory - Studying How The Brain Performs Tasks Based On Memory. Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), researchers at Brown University released a study on how the brain, using working memory, chooses and plans a course of action or task or a series of task.
Similar to short term memory, working memory is a form of memory that keeps and uses information to complete a task or course of action. Working memory is stored in the brain for a limited amount of time; enough time to organize, plan, and execute the task. The researchers at Brown measured the reaction time of 22 adult volunteers on how the receive, process, and execute a task using working memory. Working Memory - Studying How The Brain Performs Tasks Based On Memory. Brain Rewrites and Edits Memory To Suit Current Situation. A Northwestern Medicine study shows that memory is not as accurate as people might think.
The study revealed that the brain rewrites stored memory infusing it with things from the present. By conducting memory experiments on 17 men and women, the team used computers and an MRI scanner to observe how the brain worked during the experiment. Brain Response Time Not Dependent on Number of Neurons in Neural Network. Neuroscientists using a supercomputer to run a simulation of a neural network, have noted that the response time of the brain is the same regardless if the number of neurons in the network is 50 or 1,000.
The constructed computer simulation of the neural network showed that the simulated neurons responded with the same speed on both models. Neurons are responsible for transmitting information and signals to and from the brain. These cells are the main component of the nervous system which includes the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral ganglia (relay points and intermediary connections between different neurological structures in the body). DDT Pesticide Linked To Alzheimer's Disease. A study on Alzheimer's disease on 86 Alzheimer's patients and 79 healthy elderly controls show that the Alzheimer's patients have four times higher levels of DDE in their blood compared to the healthy controls.
DDE is a metabolite (substance produced during metabolism) of DDT. Although the cause of late-onset Alzheimer's disease (AD) is not yet clear, researchers believe that factors such as genetic, environmental and lifestyle can influence the development of the disease. The latest finding linking DDT to AD reinforces the link between the environment and AD. Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) is a pesticide used in agriculture and mosquito control.
New Process Developed To Image How The Brain Forms Memories. Researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University have imaged the brain while forming memories on the molecular level.
This was achieved by tagging fluorescent beta-actin mRNA molecules using a mouse model. The tagged molecules were observed by the scientists in real time while brain cells were forming memories. See embedded video. They note that the stimulated individual hippocampal neurons caused a rapid transcription of the beta-actin gene within 10 to 15 minutes. The hippocampus is the region of the brain where where memories are made and stored. The neurons connect to each other through spines of dendrites where long-lasting synaptic connections form between neurons in contact with each other.
Ankyrin-G and Kinesin-1 Protein Responsible For Movement Mechanics of Neuron's Sodium Ion Channel to Axon. Scientists have discovered how sodium ion channels travel from the neuron to the axon to initiate central nervous communications to and from the brain.
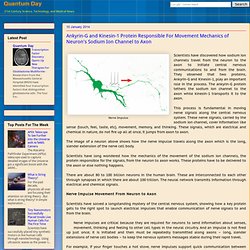
They observed that two proteins, Ankyrin-G and Kinesin-1, play an important role in the process. The ankyrin-G protein tethers the sodium ion channel to the axon while kinesin-1 transports it to the axon. This process is fundamental in moving nerve signals along the central nervous system. These nerve signals, carried by the sodium ion channel, cover information like sense (touch, feel, taste, etc), movement, memory, and thinking.
These signals, which are electrical and chemical in nature, do not fire up all at once, it jumps from axon to axon. AAN Study Suggests Concussions May Be Linked to Alzheimer's Disease. A study published in the American Academy of Neurology medical journal Neurology® suggest that there is a link between concussion and Alzheimer's Disease.
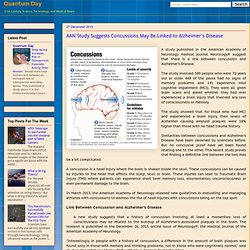
The study involved 589 people who were 70 years old or older. 448 of the peole had no signs of memory problems and 141 experience mild cognitive impairment (MCI). They were all given brain scans and asked whether they had ever experienced a brain injury that involved any loss of consciousness or memory. The study showed that for those who had MCI and experienced a brain injury, their levels of Alzheimer causing amyloid plaques were 18% higher than those with no head trauma history. Research Traces Link Between Beta Amyloid Protein, PirB/LilrB2 Protein And Alzheimer's Disease. Stanford University School of Medicine researchers suggest that a link between the beta-amyloid protein and the PirB/LilrB2 protein may be a strong factor in the development of Alzheimer's Disease.
The LilrB2 protein found in humans and its counterpart, the PiirB protein found in mice controls the visual system development in the brain. Running Improves Memory and Learning. Did you know that running can make you smarter? It’s true. It can also improve your memory and your test scores. That’s the latest news from assistant professor of psychology from the University of Illinois Justin Rhodes writing for Scientific American. “A growing body of evidence suggests we think and learn better when we walk or do another form of exercise,” writes Rhodes while citing a recent study that found “students who exercise perform better on tests than their less athletic peers.” Rather than worry about the legendary “freshman 15” trend whereby new college students typically gain 15 pounds in their first year, many students are lacing up their running shoes and signing up for a local 5K (3.1 mile) run.
How to get startedConsider your training a “course” subject. Commit to a race. Omega-3 Fish Oil Helps Protect Against Dementia. A Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine study suggests that Omega-3 fish oil helps protect the brain from alcohol related dementia. Researchers found that omega 3 helps protect the brain from against inflammation and cell death. Previous studies show that omega-3 fatty acids or polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are important for brain function, as well as normal growth and development. Omega-3 fatty acids include the nutrients called docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). They have also been found to reduce the risk of heart disease. Time and Brain Coordination Improves Memory Preservation.and Reduces Forgetfulness. Genetically Engineered Protein, ArcLight, Allows Direct Observation of Brain's Electrical Activity.
Scientists have genetically engineered a new protein called ArcLight to observe electrical activity in the neurons of the brain. The brain receives and transmits information by using electrical signals. These signals travel through synapses and neurons. By tracking neural activity in the body in real time, scientists get to understand how the brain works. Neurohormone Oxytocin Focusing Ability May Have Links To Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Brain Waves From 12,000 Brain Neurons Simulated In A Computer. Link Between Alzheimer's Disease and Glucose Intolerance (Pre-Diabetes) Georgetown University neurologist R. Scott Turner, MD, PhD, found that almost half (43%) of tested subjects nationwide who has mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease were also glucose intolerant (pre-diabetic) or are already diabetic. The study suggests a link between the two disorders and opens the subject up to further analysis.
Imaging Neurons While New Memories Are Formed Using mRNA Display and Microscopic FingRs Probes. Scientists have, for the first time, imaged neurons while new memories are being formed. This was done by using fluorescent markers on the synaptic proteins connected to the neurons. Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation (TRNS) Enhances Math Skills and Ability in Brain.
Scientists Study How Brain Stores Long Term Memory in the Brain. V5 Region of Visual Cortex Responsible For Tracking Fast Moving Object. In a study conducted by UC Berkeley scientists, research shows that for the brain to process fast moving objects, the V5 region of the visual cortex accurately predicts where and how these objects move. Protein Complex NF-κB In Brain's Hypothalamus May Have Effect In Aging. Clenching Fists Can Help Form Stronger Memories and Also In Recollecting Them. Berries Protect Brain From Toxins and Improve Behavior and Cognitive Functions. Cellular Reprogramming In Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis, Cerebral Palsy and other Myelin Disorders. New Neurostimulation Techniques in Spinal Cord Stimulation For Pain Management Developed. Controlling the Brain With Optogenetics Using Lasers and Magnets To Treat Substance Abuse. New AAN Guideline On Managing And Evaluating Athletes With Concussions Released.
The Effect of Serotonin on the Brain and In Central Fatigue. Treatment Window For Alzheimer's Disease and Related Conditions Identified. Brain Process In Encoding Sound Key In Study of Dyslexia. Update On Spinal Cord Injury Treatment Through Robotics, Neurorehabilitation, and Electrical-Chemical Stimulation. Visualizing Zebrafish Brain Activity - Seeing Fish Thoughts. Carotenoids In Fruits Prevent Or Delay Onset of ALS. Lightning May Induce The Onset of Headaches and Migraine. Neurobiologists Transform Projection Neuron To Motor Neuron Inside Brain Through Direct Lineage Reprogramming.
Amyloid beta (Aβ) And Its Role In Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. Aside From Chocolate, Milk Consuming Nations Have Higher Ratios Of Nobel Laureates Per Capita. Non-Surgical Treatment for Neurofibromatosis Type 2 Being Developed. Stem Cell Treatment For Lou Gehrig's Disease (ALS) Being Researched. How Nerve Cell Activity Between Neurons is Regulated Within the Brain's Hippocampus. Bilinguals Are Faster In Task Switching Than Single Language Speakers. Coffee Lowers Risk of Depression While Diet Drinks Increase Risk. Effective Screening for Alzheimer's Disease Through MRI of the Cerebrospinal Fluid.
Understanding How The Brain Spatially Represents Object and Action Categories Through fMRI. Research Into How Common Cat Parasite, Toxoplasma gondii, Enters The Human Brain. Scientists Discover Molecule Responsible For Converting Soundwaves To Brain Signals For Hearing. Neuroparasitology Studies Parasites That Turn Hosts Into Mindless Zombies. Diffusion Tensor Imaging Show Simple Mental Activities Can Maintain Healthy Brain In Old Age. Diabetes Medicine Rosiglitazone Shows Promise For Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease. Neuroprosthetic Algorithm Leads To Better Thought Controlled Objects Such As Bionic Arms and Legs. The Science of the Paranormal: Analyzing Brain Activity of Psychic Mediums. The Science of Rap: Studying fMRI Brain Activity While Freestyling. Exposure to Pesticide and Head Injury Resulting To Loss of Consciousness Increases Risk of Parkinson's Disease.
Coffee Improves Brain Performance In Implicit Recognition of Positive Words and Emotions. Repairing Spinal Cord Injuries Through Schwann Cell Transplantation and Inhibition of Scarring. High Level of Math Anxiety Linked To Brain Regions For Physical Pain and Threat Detection. Brain Neurons In The Lateral Intraparietal Area Discovered To Keep Track Of Time. Using fMRI To Examine Brain Activity In Forgetting Memories Through Suppression And Substitution. Motor Skills Interactions Affect How Brain Hemispheres Process Different Kinds of Sounds. MIT News: Astrocyte Brain Cells Plays Key Role In Processing Sensory Information. Studying Cell Senescence And Its Relation To The Aging Of the Brain. Quantum Day : Study Reiterates Position That Ginkgo Biloba Has No Significant Effect Against Alzheimer's Disease.
Quantum Day : Elite Group of Elderly "SuperAgers" Over 80 Have Younger Sharper Acting Brains. Brain Stem Cells Identified For Smarter and Bigger Brains. New Tool Developed To Monitor Patients Undergoing Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) Concussion Rate in College Athletes Increasing. Making The Brain Sharper and Overcoming Attentional Blink. Study Suggest Cats Can Cause Suicidal Behavior and Mental Illness In Women. Daily Exercise And Physical Activity May Reduce Risk of Alzheimer's Disease. Ursolic Acid In Apple Peels Reduces Obesity And Associated Health Problems. Mapping The Activity of Love And Desire In The Brain. Extent of Damage for Children With Brain Injury Difficult To Predict and Highly Variable. Research Into Facial Perception Reveals Brain Processes Information At A Deeper Level. Studies Show Pediatric Brain Tumors Are Diverse Enough To Require Different Treatments. Social Jetlag May Result In Obesity, Sleep Depravity, and Is A Health Risk.
Robotic Arm To Automate Whole Cell Patch Clamping For Studying Brain Cell. Eating Food Rich In Omega-3 Fatty Acids Such As Fish, Chicken, and Nuts Lowers Risk of Alzheimer's Disease. Spin Labeled Fluorene Compounds - Molecules That Can Aid In Prevention And Delay of Alzheimer's Disease. Bilingualism Improves Sensory and Cognitive Functions Such As Focus, Inhibitory Control, and Hearing. Behavioral Problems In Children May Be A Sign Of Mental Health Problems. Mental and Physical Stimulation During Old Age Show Better Cognitive Performance And A Younger Brain. Many Treatments Available To Help Prevent Migraine Unused. Studying 'Brain Freeze' Could Lead To New Treatments For Different Types of Headaches. When Head Injury or Trauma In Sports Leads To Memory Loss and Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
Study Suggest Trigger Protein Starts and Spreads Parkinson's Disease. New Drug Discovery May Lead to Faster Stroke Recovery. Discovery May Lead to New Therapy for Autoimmune Diseases. Research Data Reveals ADHD Is Overdiagnosed. Eating Flavonoids Can Help Protect Against Parkinson's Disease. Bilingual Persons Less Likely To Develop Dementia Symptoms.
Continuous Sleep Favorable In Long Term Memory Consolidation and Enhancement.