

Meat-eating dinosaur caught turning veggie - life - 04 May 2005. Palaeontologists have caught a cousin of the carnivorous Velociraptor in the process of turning vegetarian.
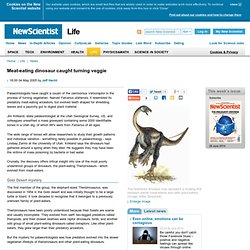
Named Falcarius utahensis, it resembled its predatory meat-eating ancestors, but evolved teeth shaped for shredding leaves and a paunchy gut to digest plant material. Jim Kirkland, state palaeontologist at the Utah Geological Survey, US, and colleagues unearthed a mass graveyard containing some 2000 identifiable bones in a Utah dig, of which 99% were from Falcarius of all ages. The wide range of bones will allow researchers to study their growth patterns and individual variation - something rarely possible in palaeontology - says Lindsay Zanno at the University of Utah. Kirkland says the dinosaurs had gathered around a spring when they died.
He suggests they may have been the victims of mass poisoning by bacteria or bad water. Gobi Desert mystery Therizinosaurs have been poorly understood because their fossils are scarce and usually incomplete. Research finds dinosaurs classified as ‘mesotherms’ with metabolism similar to tuna and sharks. Research has uncovered the answer to an age-old dinosaur question.
Pictured, a still from the movie Walking with Dinosaurs. Source: Supplied DINOSAURS weren't cold-blooded like modern reptiles or warm-blooded like mammals and birds, according to a study aiming to answer a question that has intrigued palaeontologists for decades. Instead, the prehistoric creatures' metabolic rates were somewhere in between, says the report published in the US journal Science on Friday. The results suggest the practice of splitting species into two distinct groups depending on whether animals regulate their body temperature externally or internally is not accurate. Did climate change turn all dinosaurs male? Discovery of 1.4 million-year-old fossil human hand bone closes human evolution gap. Humans have a distinctive hand anatomy that allows them to make and use tools.
Apes and other nonhuman primates do not have these distinctive anatomical features in their hands, and the point in time at which these features first appeared in human evolution is unknown. Now, a University of Missouri researcher and her international team of colleagues have found a new hand bone from a human ancestor who roamed the earth in East Africa approximately 1.42 million years ago. They suspect the bone belonged to the early human species, Homo erectus. The discovery of this bone is the earliest evidence of a modern human-like hand, indicating that this anatomical feature existed more than half a million years earlier than previously known.
Meat-eating dinosaurs not so carnivorous after all. Tyrannosaurus rex may have been a flesh-eating terror but many of his closest relatives were more content with vegetarian fare, a new analysis by Field Museum scientists has found.
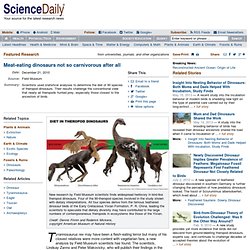
The scientists, Lindsay Zanno and Peter Makovicky, who will publish their findings in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, used statistical analyses to determine the diet of 90 species of theropod dinosaurs. Their results challenge the conventional view that nearly all theropods hunted prey, especially those closest to the ancestors of birds. Rather, Zanno and Makovicky show that among the most bird-like dinosaurs -- known as coelurosaurs -- plant eating was a common way of life. "Most theropods are clearly adapted to a predatory lifestyle, but somewhere on the line to birds, predatory dinosaurs went soft," Zanno says. A Dino With Just One Finger. Dino With Huge Nose and Horns Unearthed in Utah. Earth's earliest dinosaur may have been discovered. A wonky beast about the size of a Labrador retriever with a long neck and lengthy tail may be the world's earliest known dinosaur, say researchers who analyzed fossilized bones discovered in Tanzania in the 1930s.
Now named Nyasasaurus parringtoni, the dinosaur would've walked a different Earth from today. It lived between 240 million and 245 million years ago when the planet's continents were still stitched together to form the landmass Pangaea. Tanzania would've been part of the southern end of Pangaea that also included Africa, South America, Antarctica and Australia. It likely stood upright, measuring 7 to 10 feet (2 to 3 meters) in length, 3 feet (1 m) at the hip, and may have weighed between 45 and 135 pounds (20 to 60 kilograms).
Creationists and dinosaurs: Answers in Genesis teams with dissident scientists to deny feathered dino fossil record. Illustration by Cheung Chungtat The dinosaurs of our childhood aren’t around anymore.
The sluggish, swamp-bound pea-brains that haunted museum halls and trundled through picture books have been eviscerated by agile, hot-blooded, and, often, feathery dinosaurs that more accurately reflect what Tyrannosaurus rex and kin were actually like. Dog stumbles upon 300 million-year-old fossil - Technology & Science. A family and their dog named Kitty have stumbled upon one of the most significant fossil finds ever in Nova Scotia.

Previously, scientists had discovered fossilized footprints in Colchester County and a few scattered bones on P.E.I., but Superstar is the most complete specimen to date. (Nova Scotia Museum) The reptile fossil, affectionately nicknamed "Superstar," is the first of its kind to be found in the province. While out walking along Nova Scotia's fossil-rich Northumberland shore, Patrick Keating, his family, and their dog, Kitty, found a fossilized rib cage, backbone and partial sail. When they went back to the same area a week later, they found the creature's fossilized skull. Dinosaur Debate Gets Cooking. Earth's time bombs may have killed the dinosaurs - environment - 27 July 2011. THE fate of the dinosaurs may have been sealed half a billion years before life even appeared, by two geological time bombs that still lurk near our planet's core.
A controversial new hypothesis links massive eruptions of lava that coincided with many of Earth's largest extinctions to two unusually hot blobs of mantle 2800 kilometres beneath the crust. The blobs formed just after the Earth itself, 4.5 billion years ago. Dinosaur Reproduction & Dinosaur Family Behaviors. Tiny prints from baby dinosaurs dot the oldest dino nesting site found to date, a 190-million-year-old nursery in South Africa, researchers said.
The hatchery and the baby footprints uncovered there are significant clues about the evolution of complex family behaviors in early dinosaurs, providing the oldest-known evidence that dinosaur hatchlings remained at nests long enough to at least double in size. 10 Unbelievable Dinos That Really Existed. Oldest Dinosaur Embryos Discovered in China, Organic Remains Found inside Embryonic Bones. An international team of paleontologists has unearthed the earliest collection of fossilized dinosaur embryos to date, and discovered organic material inside the embryonic bones.

Semitransparent flesh reconstruction of embryonic dinosaur inside egg, with skeleton (D.