

Earth Day from Space. There are many ways to celebrate Earth Day, from sustainability efforts (and check out our new blog, Guilty Planet) to simply appreciating nature.
And while this is a beautiful shot of Forest Park right here in Portland, it doesn’t compare — in my eyes — to the perfection of Earth as seen from so far away. In October of 1946, a V-2 missile was launched from New Mexico, straight up into the air. And at its maximum height of 65 miles (just barely into what was then considered outer space), it snapped the first photographs of the Earth from Space. (And you can click every image on this page to enlarge it.) It wasn’t until Apollo 8, 22 years later, that the first color photograph of Earth was taken. Fake Landslides May Help Understand Natural Ones. Using artificial landslides created in a giant outdoor laboratory, scientists have uncovered key details on how these disasters happen — research that could help them improve forecasts of landslides' size and impact.
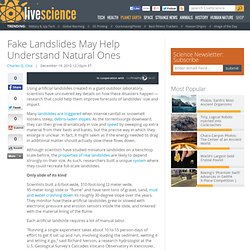
Many landslides are triggered when intense rainfall or snowmelt loosens steep, debris-laden slopes. As the torrentssurge downward, they can then grow dramatically in size and speed by sweeping up extra material from their beds and banks, but the precise way in which they enlarge is unclear. In fact, it might seem as if the energy needed to drag in additional matter should actually slow these flows down. Although scientists have studied miniature landslides on a benchtop scale before, the properties of real landslides are likely to depend strongly on their size. As such, researchers built a unique system where they could recreate full-scale landslides.
Only slide of its kind Each artificial landslide requires a lot of manual labor. Wet vs. dry. Forest Service National Avalanche Center. How Fast does the Earth Move? Feeling the Motion of the Earth. The Question (Submitted October 28, 1997) How fast does the Earth move around the Sun?

Why, when the Earth moves at such a high rate of speed, don't we feel it? The Answer Earth's average distance to the Sun is 150,000,000 km (93 million miles), therefore the distance it travels as it circles the Sun in one year is that radius x 2 x pi, or 942,000,000 million kilometers in a year of 24 hours/day x 365 1/4 = 8,766 hours so you divide to get 107,000 km/h or about 67,000 mph. You could also say the Earth moves around the Sun at 30 km/s. As to why you can't feel this speed: it's because you have no 'speed organs' which can sense absolute speed, you can only tell how fast you are going relative to something else, and you can sense changes in velocity (accelerations).
Suppose you are in a car traveling down the road. OK, now, how fast are you going? Now scrape off the paint off your windows before you run into a tree (or a tree runs into you). David Palmer for Ask an Astrophysicist. At what speed does the earth move around the sun? Let's calculate that.

How Fast Are You Moving When You Are Sitting Still? Www.astrosociety.org/uitc No. 71 - Spring 2007 © 2007, Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 390 Ashton Avenue, San Francisco, CA 94112.
How Fast Are You Moving When You Are Sitting Still? By Andrew Fraknoi Foothill College & the Astronomical Society of the Pacific Download this issue as a PDF file | Subscribe to The Universe in the Classroom | Send the URL for this issue to a friend | UITC Home. How fast is the earth moving through space as it travels around the sun. How fast is the earth moving while going around the sun. How Fast Does Earth Move? As passengers on Earth we are all carried around the sun at a mean velocity of 66,600 mph.
Add to that dizzying notion the fact that we are spinning (at the equator) at a 1,000 miles-per-hour clip (an action that cause the planet to bulge outward). Of course, these velocities are relative (to the sun and to the poles, respectively). The reason we don't feel the rush is the same reason we aren't pinned to our seats while in an airplane moving at constant speed. Velocity can only be measured with reference to another object moving at a different velocity, and we cannot feel velocity while in a constant frame of reference. This is why it might be news to you that our entire solar system is whizzing around the center of our galaxy at a fairly inconceivable 560,000 mph. Earth Speeds. You can't measure the speed of an object by itself, it has to be measured relative to something else (this was one of Einstein's realizations).

If we ask the question, "How fast the Earth is moving? " we have to specify that we want the speed with respect to another object. Motion cannot be measured without a reference point.