

Mesopotamia - DK Find Out! Mesopotamia History for Kids. Assyrian Army The Assyrians were very able people with a range of achievements in science, technology and culture.

However, it was not these civilised qualities that allowed them to create an empire. The expansion was down to one of the cruellest and most merciless armies humanity has ever seen. Ancient Mesopotamia 101 - National Geographic. Art and artisans. Artisans were important people in ancient Mesopotamia as the objects they created were not only useful for the everyday lives of ordinary people and the upper classes, but they were often very beautiful and help us better understand our ancient history.In today’s society we make a distinction between artisans who make craft items usually with a practical purpose and artists whose work involves a much higher level of skill.
In Mesopotamia there was no such distinction. Sculpture Sculpture was an important form of art, especially in work done for the kings. Daily life. Daily life in Mesopotamia was, in some ways, not unlike our modern existence.
People were recognised by social rank, they lived in different forms of housing, the family was important, as was their leisure time. Social classes In the same way as our modern societies, Mesopotamians belonged to different social classes.The kings of city-states, regions or empires were at the very top of the social ladder. Religion and Gods. How did people worship?

In ancient Mesopotamia each city-state had its own god or goddess and their family. People believed that the gods were actually present in their cities, and they built temples called ziggurats for the gods to live in.The typical temple had three rooms with impressive decoration. The god could be found in the room closest to the centre of the building. The god was in the form of a statue. Sumerian writing and cuneiform. The first system of writing was invented by the Sumerians.
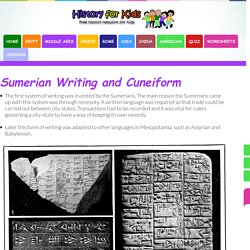
The main reason the Sumerians came up with this system was through necessity. A written language was required so that trade could be carried out between city-states. Transactions had to be recorded and it was vital for rulers governing a city-state to have a way of keeping its own records.Later this form of writing was adapted to other languages in Mesopotamia, such as Assyrian and Babylonian. Ancient civilisations for children: Ancient Mesopotamia. The time compass: Mesopotamia part 1. The time compass: Mesopotamia part 2. Mesopotamia: Crash Course World History #3 (0:45-11:10) Ancient Mesopotamia 5000 B.C. Populated with Physiology Driven Virtual Agents. Ancient Mesopotamia 5000 B.C. Virtual Guided Tour (click and drag to view 360 degrees))