

What is cognitive health/ability? Systematic review of health behavioral risks and cognitive health in older adults. Crossref Citations This article has been cited by the following publications.
This list is generated based on data provided by CrossRef. 2010. Current awareness in geriatric psychiatry. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, Vol. 25, Issue. 9, p. i. Miksys, S L and Tyndale, R F 2010. Roberts, J Scott and Tersegno, Sarah M 2010. Molecule released during endurance exercise improves cognition. Molecule produced during exercise boosts brain health. Research has shown that exercise is good for the brain.

Now investigators have identified a molecule called irisin that is produced in the brain during endurance exercise and has neuroprotective effects. Researchers were able to artificially increase the levels of irisin in the blood to activate genes involved in learning and memory. The findings, published online October 10 in the Cell Press journal Cell Metabolism, may be useful for designing drugs that utilize this exercise-induced molecule to guard against neurodegenerative diseases and improve cognition in the aging population. While it's known that exercise can boost cognitive function and lessen symptoms of neurological diseases like depression, stroke, and Alzheimer's disease, the mechanisms underlying these effects are unclear.
One important player is thought to be a growth factor named brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Researchers have found further evidence that exercise may be beneficial for brain health and cognition. The findings suggest that certain hormones, which are increased during exercise, may help improve memory. Aerobic fitness, hormones predict recognition memory in young adults. Researchers at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) have found further evidence that exercise may be beneficial for brain health and cognition.
The findings, which are currently available online in Behavioural Brain Research, suggest that certain hormones, which are increased during exercise, may help improve memory. Hormones called growth factors are thought to mediate the relationship between exercise and brain health. The hippocampus, a region of the brain crucial for learning and memory, is thought to be uniquely affected by these hormones. The growth factors brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), have been implicated in the link between exercise and hippocampal function.
BDNF, for example, acts on the nervous system to help regulate communication between existing brain cells (neurons) and stimulate the growth and maturation of new hippocampal neurons and blood vessels. Exercising increases size of hippocampus and improves memory. Exercise training increases size of hippocampus and improves memory. - PubMed - NCBI. The Effectiveness of Exercise on Improving Cognitive Functio... : Journal of Nursing Research. Introduction Taiwan's population of adults aged 65 years or over accounted for 10.7% of the total population at the end of 2010 (Department of Statistics, Ministry of the Interior, 2011).
This population is expected to continue to grow through the next 30 years. Thus, aging is an increasingly important focus of Taiwan public health. Aging affects the functioning of central nervous, skeletomuscular, cardiopulmonary, and other organ systems. Particularly, as a person ages, brain weight decreases 10% to 20%, blood flow slows by 30%-40%, and the cranial nerve filament becomes entwined and develops plaque. As such, the well-documented physical benefits of exercise and the value of exercise for improving mental health have grown in importance (Hoffman et al., 2008). However, studies evaluating the effects of exercise on neurocognitive function have produced equivocal results. The Review Methods Search Strategy Inclusion Criteria Exclusion Criteria Search Outcome Quality Appraisal Results. Excessive daily TV at older age tied to poorer memory. Older people who want to preserve their faculties may wish to consider rationing their TV time.
A large new study of older adults found that those who spent at least 3.5 hours per day watching TV experienced a greater decline in verbal memory. Researchers at University College London in the United Kingdom analyzed data from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing (ELSA) on 3,662 adults aged 50 and older.
In 2008–2009, and again in 2014–2015, the ELSA participants had answered questions about the time they spent watching TV. At these times, they also completed tests of verbal memory and fluency. How can older adults stay active? Senior Exercise and Fitness Tips. No matter your age, it’s never too late to get fit.
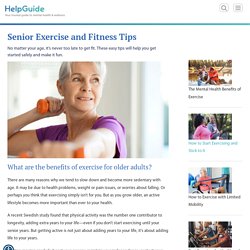
These easy tips will help you get started safely and make it fun. What are the benefits of exercise for older adults? There are many reasons why we tend to slow down and become more sedentary with age. It may be due to health problems, weight or pain issues, or worries about falling. Or perhaps you think that exercising simply isn’t for you. A recent Swedish study found that physical activity was the number one contributor to longevity, adding extra years to your life—even if you don’t start exercising until your senior years.
Getting moving can help boost your energy, maintain your independence, protect your heart, and manage symptoms of illness or pain as well as your weight. Physical health benefits. Physical Activity Is Key to Active Ageing. Physical activity helps older adults stay healthy and live more independently.
Aerobic, muscle and balance exercises are all suitable physical exercises for the elderly and promote healthy ageing. Types of Physical Activity There are three main types of physical activity: aerobic, muscle-strengthening and balance. Do all three types of activity to reap the health benefits which include chronic disease prevention and reduced risk of heart disease.
Aerobic Activity. Staying active mentally/cognitively. Cognitive-Training Can Result in Long-Term Improvement. There is a long-standing notion that playing brain games, such as puzzles and other mental undertakings, can help stave off the negative effects of aging.

But is the old "use it or lose it" adage really true? Do these cognitive games really have any sort of impact on mental functioning in the elderly? Study Points to Lasting Benefits of Cognitive-Training According to the results of a large-scale study, such mental training could help improve the cognitive function of older adults by as much as 38% by the year 2050.1.