

One of America's most famous highways is about to become an awesome science experiment. There's a highway in America that's so famous, it has its own rock song which goes like this: "Well if you ever plan to motor West, just take my way, that’s the highway, that’s the best…” (That's the Chuck Berry version, obviously.)
Image by Vincente Villamon/Flickr Designated in 1926, Route 66 traversed almost 2,500 miles, starting in Chicago, Illinois, and ending in Santa Monica, California. Historic Route 66 could be the solar-powered road of the future. Route 66 could be set for a seriously high-tech upgrade, turning the "Main Street of America" into a solar-powered, glowing superhighway.
The Missouri Department of Transportation (MoDOT) has announced plans to upgrade a small stretch of the historic roadway, which originally ran from Chicago through America's Midwest to California. The project is in partnership with Solar Roadways, who creates specially-engineered, solar-powered panels which can support the weight of cars. The panels feature built-in LEDs to create light-up road markings and can be used to generate electricity to donate back to the grid.
While Solar Roadways has won a number of contracts with the US Department of Transport, don't expect glowing arteries criss-crossing the country just yet. Will We Soon Be Riding on Solar Roads? The Idea Gains Traction. Solar is popping up just about everywhere, even landfills and parka pockets.

So why not roads? Indeed, solar road projects are gaining interest around the world, and some promise to even charge electric cars while moving. The Netherlands built the first solar road, a bike path, in 2014. France announced a bolder move in January—over the next five years, it plans to install 1,000 kilometers (621 miles) of solar roads, designed to supply power to five million people. That's not all. The Netherlands Gets The World's First Solar-Powered Bike Lane. This story was originally published by City Lab and is reproduced here as part of the Climate Desk collaboration.

It’s tough to make cycling any greener, but the Dutch have done just that with a bike lane that powers street lights and even houses. What’s being billed as the world’s first solar-powered bike path will officially open on November 12 in Krommenie, a town northwest of Amsterdam. Riders will be able to hop on at one end and then, after a few seconds of pedaling, dismount at the other. Being a pilot project, the lane is only 230 feet long (though it’ll stretch to 328 feet when finished).
The so-called SolaRoad is the result of a collaboration among the private sector, government, and academia. Do-it-yourself CRISPR genome editing kits bring genetic engineering to your kitchen bench. Biology Loz Blain November 11, 2015 CRISPR genome editing is one of the most significant, world-changing technologies of our era, allowing scientists to make incredibly precise cut n' paste edits to the DNA of living organisms.
Now, one synthetic biologist from NASA plans to make it as accessible as a home science kit, so you can bio-hack yeast and bacteria on your kitchen bench. If you're not up to date with how CRISPR gene editing works, take a quick look at this excellent MIT video. In short, CRISPR/Cas9 is a radically fast and easy way to precisely cut and replace DNA sections in a living organism. A Quarter Of The World's Power Now Comes From Renewables. In Brief Renewable energy now accounts for a quarter of the world's power, according to a new global report by REN21.

The Rise of Renewables The days of fossil fuels may finally be numbered. A new report states that renewable energy now accounts for a quarter of the world’s power. REN21 published a global status report for renewables, highlighting that renewable energy was already supplying about 23.7% of global electricity by the end of 2015. Royal Canadian Mint sells Mintchip digital payments platform to Toronto's nanoPay. The Royal Canadian Mint is ending its experiment with digital payments, selling off its MintChip platform to Toronto-based financial startup nanoPay.
The government agency developed MintChip as a secure way to send and spend money online, launching the project in April 2012 and showing off its first implementation in 2014. Consumers could use MintChip with a mobile device at a cash register or send money with a text message, email or potentially a social media message. NanoPay CEO Laurence Cooke says the goal is for MintChip to replace cash as a go-to source for what he calls frictionless transactions, without the hassle and fees of payments linked to credit cards or bank accounts.
The system works much like a pre-loaded credit card, with consumers able to deposit value on their MintChip wallet from their bank account or credit card. Artificial intelligence: What is deep learning? Scientists have fed an artificially intelligent system with Daily Mail articles so it can learn how natural language works.
While it’s not quite HAL 9000, it’s a worrying thought for any left wing tecchies. This process, called deep learning, is old news. Researchers have been attempting to train algorithms since the 1970s but computational and data limitations slowed progress in the 1980s. Now deep learning is enjoying a renaissance. DNA nanobots deliver drugs in living cockroaches - health - 08 April 2014. It's a computer – inside a cockroach.
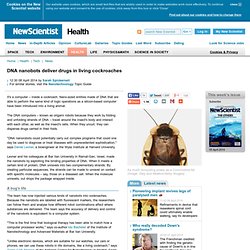
Nano-sized entities made of DNA that are able to perform the same kind of logic operations as a silicon-based computer have been introduced into a living animal. The DNA computers – known as origami robots because they work by folding and unfolding strands of DNA – travel around the insect's body and interact with each other, as well as the insect's cells. When they uncurl, they can dispense drugs carried in their folds. "DNA nanorobots could potentially carry out complex programs that could one day be used to diagnose or treat diseases with unprecedented sophistication," says Daniel Levner, a bioengineer at the Wyss Institute at Harvard University.
Levner and his colleagues at Bar Ilan University in Ramat-Gan, Israel, made the nanobots by exploiting the binding properties of DNA. Object moved. Artificial intelligence is not only around us but it is part of us Better, faster, more productive... these used to be words to describe what we wanted from our internet broadband connection.

Now they describe what we expect not only from all our products and services but also from each other. The expectations that we have from the world and the world has from us are dynamic, ever-changing and transforming at speed. Dental Fillings Heal Teeth With Stem Cells. New Alzheimer’s treatment fully restores memory function. Australian researchers have come up with a non-invasive ultrasound technology that clears the brain of neurotoxic amyloid plaques - structures that are responsible for memory loss and a decline in cognitive function in Alzheimer’s patients. If a person has Alzheimer’s disease, it’s usually the result of a build-up of two types of lesions - amyloid plaques, and neurofibrillary tangles. Amyloid plaques sit between the neurons and end up as dense clusters of beta-amyloid molecules, a sticky type of protein that clumps together and forms plaques.
Object moved.