


Tom Hayden Thomas Emmet Hayden, known as Tom Hayden (born December 11, 1939), is an American social and political activist, author, and politician, who is director of the Peace and Justice Resource Center in Culver City, California. Known best for his major role as an anti-war, civil rights, and radical intellectual counterculture activist, Hayden is the former husband of actress Jane Fonda and the father of their son, actor Troy Garity. Early life[edit] Radical activism[edit] Hayden drafted SDS's manifesto, the Port Huron Statement. From 1964 to 1968, Hayden lived in Newark, New Jersey, where he worked with impoverished inner-city residents as part of the Newark Community Union Project. In 1965, Hayden, along with CPUSA member Herbert Aptheker and Quaker peace activist Staughton Lynd undertook a controversial visit to North Vietnam and Hanoi. In 1968, Hayden played a major role in the protests outside the Democratic National Convention in Chicago, Illinois. Political career[edit] Bibliography[edit]
Terence McKenna rotten > Library > Biographies > Mad Science > Terence McKenna Terence McKenna was the Magellan of psychedelic head space, and humanity's first ambassador to the hyperdimensional machine elves of the Eschaton. McKenna was a true child of the '60s, graduating from UC Berkeley with one of those majors you could only get in Berkeley in the '60s — Ecology, Resource Conservation and Shamanism. When he got out of school, he set off for the Amazon, where he "studied" the native hallucinogenic drugs used in various South American shamanic traditions. McKenna studied these drugs repeatedly and in large doses, along with his brother, Dennis. While pursuing these scientific studies, McKenna experienced some interesting effects on his consciousness, not surprisingly. His work has influenced a generation of writers and philosophers, and his writings have been as influential as that of better-known contemporaries like Timothy Leary and Abbie Hoffman. Refined sugar was a particular target of his ire.
Tom Wolfe Thomas Kennerly "Tom" Wolfe, Jr. (born March 2, 1931)[1] is an American author and journalist, best known for his association and influence over the New Journalism literary movement in which literary techniques are used in objective, even-handed journalism. Beginning his career as a reporter he soon became one of the most culturally significant figures of the sixties after the publication of books such as The Electric Kool-Aid Acid Test, a highly experimental account of Ken Kesey and the Merry Pranksters, and his collections of articles and essays, Radical Chic & Mau-Mauing the Flak Catchers and The Kandy-Kolored Tangerine-Flake Streamline Baby. He is also known, in recent years, for his spats and public disputes with other writers, including John Updike, Norman Mailer, and John Irving. Early life and education[edit] Wolfe was born in Richmond, Virginia, the son of Louise (née Agnew), a landscape designer, and Thomas Kennerly Wolfe, Sr., an agronomist.[2][3] Non-fiction books[edit]
Psychedelic '60s: Home Page THE SUMMER OF 1967, with its "Love-Ins," "Be-ins," and "Flower Power," came to be known as "The Summer of Love," and was one of the seminal moments of our generation. Over thirty years later, we who came of age during the turbulent decade of the sixties are dismayed to realize that, to the young adults of today, those years are now ancient history. The "Psychedelic Sixties" broke the rules in every conceivable way from music to fashion (or lack of it), to manners and mores. Boundaries were challenged and crossed in literature and art; the government was confronted head-on for its policies in Vietnam; the cause of civil rights was embraced by the young; and mind-expanding drugs were doing just that. Were the sixties the best of times or the worst of times? Did America evolve as a nation and we as individuals?
tomhayden.com - Peace Exchange Bulletin Why Terence McKenna Matters If anyone ever wanted to get to know me (i.e., what makes Daniel tick) the first thing I would have to tell them is, "Read Terence McKenna." In online forums and real life scenarios alike, I quote McKenna like Jules Winnfield quotes Ezekiel in Pulp Fiction. Passionate. With conviction. A few weeks ago my friend Michelle suggested I write a "Terence for Dummies" piece. The Background Terence Kemp McKenna (November 16, 1946 -- April 3, 2000) was born under the auspices of a conventional upbringing. Settling on the outskirts of the Mission at La Chorrera, it was the events that transpired during this crusade that became the catalyst of McKenna's ideas. The Experiment It was here that Terence and his party became acquainted with Stropharia cubensis fungi (now known as Psilocybe cubensis). In essence, you can change reality while tripping on shrooms. The bread crumbs leading the McKenna brothers to this perspective was in fact the shamanic method. The Result Time stopped, became tangible. 1.
The Last Outlaw: Pun Plamondon‘s Radical Odyssey These days, it’s common for musicians, rappers and would-be tough guys to pose as “outlaws” in hopes of dazzling the public. But in the revolutionary ‘60s, Pun Plamondon was the real deal. A native son of Traverse City, Pun was on the FBI’s “10 Most Wanted” list, living on the run in Algiers and the American underground on charges of bombing a CIA office in Ann Arbor. As Minister of Defense for the radical White Panther Party, Plamondon risked life in prison for his freewheeling hippie lifestyle, not to mention a political platform that touted a life of rock & roll, drugs, and sex in the streets. Every parent’s nightmare, he was a folk hero to thousands of dissaffected youth throughout the Midwest who rallied to the music and radical standard of the MC5 rock band. “It’s the old Jesse James syndrome,” he says during a phone interview from his home in southern Michigan. THE WHITE PANTHERS It was a tempestuous time. Did Pun bring down Richard Nixon?
Terence McKenna Vault Terence McKenna was a psychedelic author, explorer, and showman. He was born in 1946 and grew up in Paonia, Colorado. In high school he moved to Los Altos, California, and from there attended U.C. In 1975, Terence graduated from Berkeley with a degree in ecology, resource conservation, and shamanism. In 1985, Terence co-founded the non-profit Botanical Dimensions, with Kathleen Harrison-McKenna, to collect and propagate medicinal and shamanic plants from around the world. He spent the last few years of his life living in Hawaii, and died of brain cancer at the age of 53.
UC Berkeley Library Social Activism Sound Recording Project: Anti-Vietnam War Protests - San Francisco Bay Area April 15, 1967 Spring Mobilization to End the War, San Francisco (API) Year: 1960 | 1961 | 1962 | 1963 | 1964 | 1965 | 1966 | 1967 | 1968 | 1969 1970 | 1971 |1972 |1973 |1974 | 1975 | After the War About This Project Sources Cited Bibliography of Materials in the UC Berkeley Library Copyright Information The War | Anti-War/Political Activism The War In the early 60s, during the Kennedy administration, there are repeated insurgent attempts to overthrow this US-backed South Vietnamese government by the newly formed, largely Communist National Liberation Front (NLF). By December 31st, US forces in Vietnam number 900 [Bowman, p. 20] Political Activism February 1: In Greensboro, North Carolina, four black students from North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University begin a sit-in at a segregated Woolworth's lunch counter. May 13, 1960: Several hundred Berkeley students protest the hearings of the House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) in San Francisco. January 20, 1961: John F.
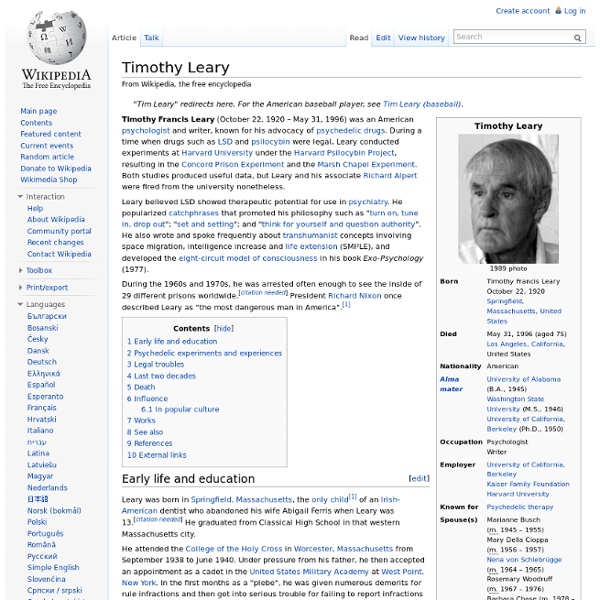
Timothy Leary Vault Timothy Francis Leary was born is Springfield, Massachusetts in 1920. He attended West Point in the early '40s (where he didn't exactly fit in) and then served in the military during WWII. He earned his PhD in psychology from U.C. Berkeley and taught there briefly but moved to Harvard after his first wife's death. He first took psilocybin mushrooms in 1960 during a trip to Mexico. In 1962 Leary was introduced to LSD for the first time by Michael Hollingshead. In 1965, while crossing into the U.S. from Mexico, Leary's daughter was caught with marijuana. In 1970, Leary was convicted once again of marijuana possession and sentenced to 10 years in prison. Leary became interested in virtual reality and cyberculture and spent the last twenty years of his life writing and lecturing.
The Electric Kool-Aid Acid Test Plot[edit] Tom Wolfe chronicles the adventures of Ken Kesey and his group of followers. Throughout the work, Kesey is painted as a sort of Christ figure, someone starting a new religion. Due to the allure of the transcendent states achievable through drugs and because of Kesey's ability to preach and captivate listeners, he begins to form a band of close followers. They call themselves the "Merry Pranksters" and begin to participate in the drug-fueled lifestyle. Starting at Kesey's house in the woods of La Honda, California, the early predecessors of acid tests were performed. The Pranksters eventually leave the confines of Kesey’s estate. As an effort to broadcast their lifestyle, the Pranksters publicize their acid experiences and the term Acid Test comes to life. Kesey and some of the Pranksters returned to the United States. Cultural significance and reception[edit] The use of New Journalism yielded two primary reviews, amazement or disagreement. Film adaptation[edit] References[edit]
Timothy Leary rotten > Library > Biographies > Mad Science > Timothy Leary Timothy Leary (October 22, 1920 - May 31, 1996) "Six words: drop out, turn on, then come back and tune it in... and then drop out again, and turn on, and tune it back in... it's a rhythm... most of us think God made this universe in nature-subject object-predicate sentences... turn on, tune in, drop out... period, end of paragraph. Turn the page... it's all a rhythm... it's all a beat. Okay, so it's a little over six words, but it's the debut pop-culture rap delivered by counterculture guru Dr. The government was indeed alarmed by how quickly teenagers flocked to Leary in the sixties and seventies. Timothy Leary was a professor at Harvard University when he began experimenting with psilocybin, acid, and other hallucinogens. In 1944, while training in Pennsylvania, he met a woman named Marianne. Meanwhile, Marianne had been suffering from post partum depression, and she began to drink heavily. Leary promptly escaped. Dr.
United States v. U.S. District Court United States v. U.S. District Court, 407 U.S. 297 (1972), also known as the Keith case, was a landmark United States Supreme Court decision that upheld, in a unanimous 8-0 ruling, the requirements of the Fourth Amendment in cases of domestic surveillance targeting a domestic threat. After reading the briefs and hearing oral arguments by a then young Constitutional attorney, Hugh "Buck" Davis,[1] Judge Damon Keith[2] of the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Michigan disagreed and ordered the Government to disclose all of the illegally intercepted conversations to the defendants. The Government appealed, filing a petition for a writ of mandamus with the Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit to set aside the order. The decision[edit] The Supreme Court upheld the prior rulings in the case, holding that the wiretaps were an unconstitutional violation of the Fourth Amendment and as such must be disclosed to the defense. Quotations[edit] See also[edit] References[edit]
Albert Hofmann Vault Albert Hofmann was born in Baden, Switzerland in 1906. He graduated from the University of Zürich with a degree in chemistry in 1929 and went to work for Sandoz Pharmaceutical in Basel, Switzerland. With the laboratory goal of working towards isolation of the active principles of known medicinal plants, Hofmann worked with Mediterranean squill (Scilla maritima) for several years, before moving on to the study of Claviceps purpurea (ergot) and ergot alkaloids. Over the next few years, he worked his way through the lysergic acid derivatives, eventually synthesizing LSD-25 for the first time in 1938. After minimal testing, LSD-25 was set aside as he continued with other derivatives. In addition to his discovery of LSD, he was also the first to synthesize psilocybin (the active constituent of 'magic mushrooms') in 1958.