INFOGRAPHIC: Student plagiarism causes and solutions
New infographic includes a visual guide to current student forms of plagiarism and some helpful solutions Student plagiarism has become a lot more complex than simply quoting a famous author or a famous work without attribution. Thanks to the influx of internet resources and student and faculty reliance on these online sources, common examples of plagiarism are numerous. However, according to the University of Illinois at Chicago’s (UIC) Health Informatics Program, plagiarism is not necessarily simple laziness on a student’s part, leaving teachers to implement solutions to help students safegaurd against this increasingly common offense. Inspired by research done by professors from UIC Online, this new infographic explains the different kinds of plagiarism, why college students plagiarize, and how professors can educate their students on the correct citation writing.
Fair use
Exception to the exclusive right granted by copyright law to the author of a creative work Fair use is a doctrine in the law of the United States that permits limited use of copyrighted material without having to first acquire permission from the copyright holder. Fair use is one of the limitations to copyright intended to balance the interests of copyright holders with the public interest in the wider distribution and use of creative works by allowing as a defense to copyright infringement claims certain limited uses that might otherwise be considered infringement.[1] Like "fair dealing" rights that exist in most countries with a British legal history, the fair use right is a general exception that applies all different kinds of uses with all types of works and turns on a flexible proportionality test that examines the purpose of the use, the amount used, and the impact of the market on the original work. History[edit] U.S. fair use factors[edit]
Plagiarism Checker - Free Online Software by EduBirdie
Plagiarism is one’s deliberate copying of a content completed by another person and either presenting it as one’s own novel idea or simply not mentioning the name of its original author. Plagiarism may be intentional or unintentional when a person does not know that he or she uses someone else’s idea. What Is Plagiarised Content & Its Consequences? Students often think that some little paraphrasing will help them avoid this major issue if they do acknowledge a source.
Evolution of morality
The evolution of morality refers to the emergence of human moral behavior over the course of human evolution. Morality can be defined as a system of ideas about right and wrong conduct. In everyday life, morality is typically associated with human behavior and not much thought is given to the social conducts of other creatures. The emerging fields of evolutionary biology and in particular sociobiology have argued that, though human social behaviors are complex, the precursors of human morality can be traced to the behaviors of many other social animals. Sociobiological explanations of human behavior are still controversial.
WHAT IS PLAGIARISM AND HOW TO AVOID IT - Plagiarism - Otis College LibGuides at Otis College of Art and Design
What is a paraphrase? "A paraphrase is a detailed restatement in your own words of a written or sometimes spoken source material. Apart from the changes in organization, wording, and sentence structure, the paraphrase should be nearly identical in meaning to the original passage. It should also be near the same length as the original passage and present the details of the original." Paraphrasing is "your own rendition of essential information and ideas expressed by someone else, presented in a new form."
Ethics and Compliance Survey Results
Conflicts of interest and sexual harassment are the priority themes that Ethics and Compliance officers will be communicating in the coming months, according to our survey at SCCE’s Compliance & Ethics conference in Chicago last week (September 2016). Often regarded as two of the most difficult behaviors to effect change, it’s a positive sign that organizations remain determined to improve internal culture and not shy away from promoting good ethics, says SnapComms CEO, Sarah Perry, “In the past 12 months, we’ve experienced a threefold increase in enquiries from organizations looking for better ways to communicate these and other ethics-related topics. “Our experience reflects other external indicative factors*, which prove there is now greater value placed on promoting the right behavior within the workplace. There’s a noticeable shift taking place.” But this movement is not without its obstacles.
What is Plagiarism? - Plagiarism.org
Many people think of plagiarism as copying another's work or borrowing someone else's original ideas. But terms like "copying" and "borrowing" can disguise the seriousness of the offense: According to the Merriam-Webster online dictionary, to "plagiarize" means: to steal and pass off (the ideas or words of another) as one's own to use (another's production) without crediting the source to commit literary theft to present as new and original an idea or product derived from an existing source In other words, plagiarism is an act of fraud.
Does Your Compliance Program Contain the 5 Essential Elements?
The five elements are: LeadershipRisk AssessmentStandards and ControlsTraining and CommunicationsOversight Leadership
Social Media, Mobile Prove Too Much for Compliance Officers
Compliance professionals are struggling to keep up with the explosion of communications channels, including social media and mobile devices, according to the latest Electronic Communications Compliance Survey Report from Smarsh. The company’s sixth annual compliance survey reveals that gaps in enforcement, retention and policies remain very high, exposing firms to the risks of undetected fraud, errors and regulatory enforcement actions. The primary purpose of electronic message supervision is to fulfill regulatory requirements designed to protect investors, such as SEC rule 17a-4, which requires firms to archive electronic business communications in non-rewriteable and non-erasable (WORM) formats for at least three years. In addition to retention, firms are required to perform risk-based review of correspondence and internal communications.
What is Deforestation?
Deforestation refers to the cutting, clearing, and removal of rainforest or related ecosystems into less bio-diverse ecosystems such as pasture, cropland, or plantations (Kricher, 1997). What are the causes of deforestation? I. Logging II. Mining



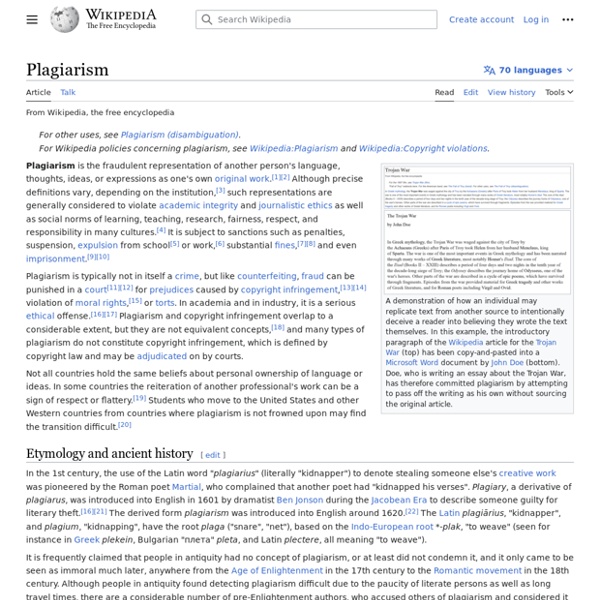
How can I make sure that I avoid plagiarism? It is important that you check your work to avoid plagiarism. ( Studying for a taught degree looks at what plagiarism is, and at a number of strategies you can use to make sure you do not commit this academic crime.) You should read that section again now. If you commit plagiarism unintentionally as part of an assignment you might be allowed to resubmit the work, or you may even pass the taught part of the course despite the fail mark you will get for that piece of work. Plagiarism in your thesis or dissertation, however, will almost certainly guarantee that you fail and are not awarded a degree. by raviii Sep 17
Plagiarism. To use someone else's ideas, words, sentences as if your own, without acknowledging their name. Found in Glossary: 2011 - (Jesson, et al.) Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques by raviii Apr 16