How to organize your EndNote library
By Sarah Tanksalvala EndNote includes a number of functions to help organize your sources and find exactly what you want when you want it. Properly organizing a large number of sources can save you hours of work and frustration.
What Is Programme Management?
Traditional Project Management approaches tend to look at a project as a discrete entity having its own set of resources (the budget and project team) and producing its own set of deliverables that deliver benefit to the organisation. In a complex organisation such as a college or university rarely is any project completely self-contained. Even a relatively simple IT application is likely to require interfaces to other systems and most of our activities impact on a diverse range of stakeholder groups. Large organisations such as ours also tend to have hundreds of individual projects running at the same time and many find themselves at the mercy of inter-departmental competition for resources.
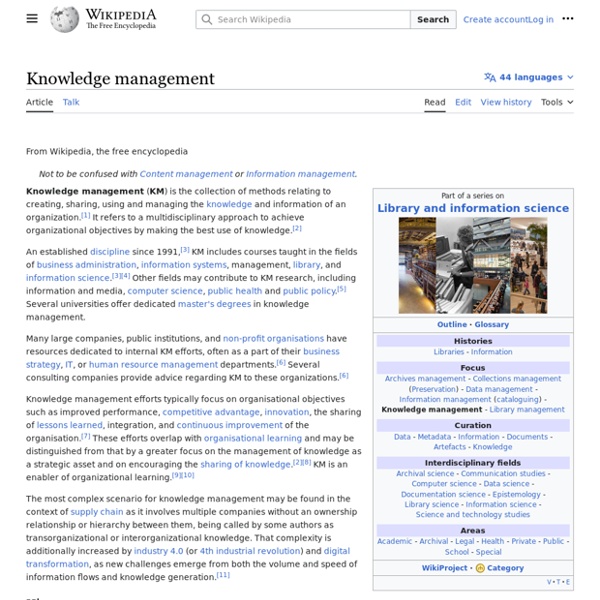
Organizational learning
Organizational learning is an area of knowledge within organizational theory that studies models and theories about the way an organization learns and adapts (Vasenska, 2013:615). In Organizational development (OD), learning is a characteristic of an adaptive organization, i.e., an organization that is able to sense changes in signals from its environment (both internal and external) and adapt accordingly. OD specialists endeavor to assist their clients to learn from experience and incorporate the learning as feedback into the planning process. Note a profound ambiguity in how the term adaptive system is used.
Tutorial 4: Introducing RDFS & OWL
Next: Querying Semantic Data Having introduced the advantages of modeling vocabulary and semantics in data models, let's introduce the actual technology used to attribute RDF data models with semantics. RDF data can be encoded with semantic metadata using two syntaxes: RDFS and OWL. After this tutorial, you should be able to: Understand how RDF data models are semantically encoded using RDFS and OWLUnderstand that OWL ontologies are RDF documentsUnderstand OWL classes, subclasses and individualsUnderstand OWL propertiesBuild your own basic ontology, step by stepEstimated time: 5 minutes You should have already understood the following tutorial (and pre-requisites) before you begin:
Quality System - Quality Management Plans
A Quality Management Plan documents how an organization will plan, implement, and assess the effectiveness of its quality assurance and quality control operations. Specifically, it describes how an organization structures its quality system, the quality policies and procedures, areas of application, and roles, responsibilities, and authorities. The elements of a quality system are documented in a Quality Management Plan. Both EPA organizations and organizations performing data collection activities funded by EPA are required to document their quality systems. The Quality Management Plan is an organization or program-specific document; it describes the general practices of an organization or program. Project-specific details of individual projects of the organization or program are documented in a Quality Assurance Project Plan (see QA Project Plans).
Human resource management
Human resource management (HRM, or simply HR) is a function in organizations designed to maximize employee performance in service of their employer’s strategic objectives.[1] HR is primarily concerned with how people are managed within organizations, focusing on policies and systems.[2] HR departments and units in organizations are typically responsible for a number of activities, including employee recruitment, training and development, performance appraisal, and rewarding (e.g., managing pay and benefit systems).[3] HR is also concerned with industrial relations, that is, the balancing of organizational practices with regulations arising from collective bargaining and governmental laws.[4] In startup companies, HR's duties may be performed by trained professionals. In larger companies, an entire functional group is typically dedicated to the discipline, with staff specializing in various HR tasks and functional leadership engaging in strategic decision making across the business.
OntoWiki — Agile Knowledge Engineering and Semantic Web
CubeViz -- Exploration and Visualization of Statistical Linked Data Facilitating the Exploration and Visualization of Linked Data Supporting the Linked Data Life Cycle Using an Integrated Tool Stack Increasing the Financial Transparency of European Commission Project Funding Managing Multimodal and Multilingual Semantic Content Improving the Performance of Semantic Web Applications with SPARQL Query Caching
Change management
Change management is an approach to transitioning individuals, teams, and organizations to a desired future state.[1] In a project management context, change management may refer to a project management process wherein changes to the scope of a project are formally introduced and approved.[2][3] History[edit] 1960s[edit] Everett Rogers wrote the book Diffusion of Innovations in 1962.
Organizational culture
Encompasses values and behaviours that contribute to the unique social and psychological environment of an organization Schein (1992), Deal and Kennedy (2000), and Kotter (1992) advanced the idea that organizations often have very differing cultures as well as subcultures.[5][6][7] Although a company may have its "own unique culture," in larger organizations there are sometimes co-existing or conflicting subcultures because each subculture is linked to a different management team.[8] Flamholtz and Randle (2011) suggest that one can view organizational culture as "corporate personality."[9][10] They define it as it consisting of the values, beliefs, and norms which influence the behavior of people as members of an organization.[11]
MooWheel: a javascript connections visualization library
View the project on Google Code 06.29.2008 version 0.2 now available! get it. What's new? Looking for version 0.1 instead? The purpose of this script is to provide a unique and elegant way to visualize data using Javascript and the <canvas> object.
change management principles, process, tips and change theory and models
Instead, change needs to be understood and managed in a way that people can cope effectively with it. Change can be unsettling, so the manager logically needs to be a settling influence. Check that people affected by the change agree with, or at least understand, the need for change, and have a chance to decide how the change will be managed, and to be involved in the planning and implementation of the change.
Economic efficiency
In microeconomics, economic efficiency is, roughly speaking, a situation in which nothing can be improved without something else being hurt. Depending on the context, it is usually one of the following two related concepts: Strands of thought[edit] There are two main standards of thought on economic efficiency, which respectively emphasize the distortions created by governments (and reduced by decreasing government involvement) and the distortions created by markets (and reduced by increasing government involvement). These are at times competing, at times complementary—either debating the overall level of government involvement, or the effects of specific government involvement.