


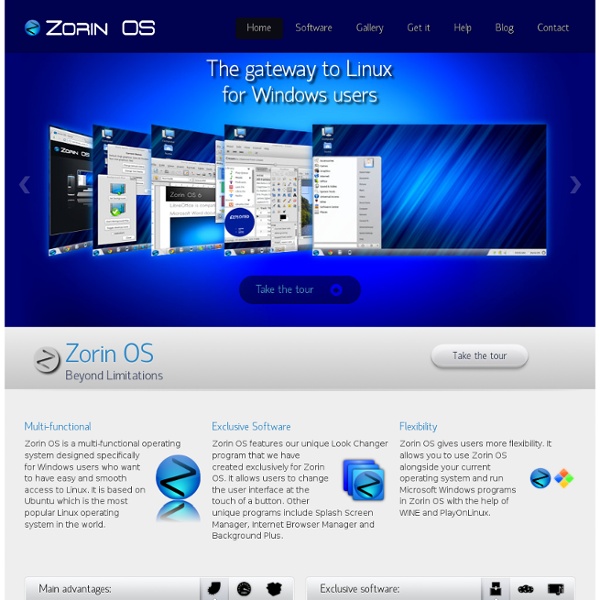
Slackware Fuduntu • Home Puppy Linux Pear Linux » Great new feature Pear Linux 6 is a fast, stable, and powerful operating system for everyday use. It’s completely free to use, study, and share. Pear Linux 6 is easy to use And it comes with thousands of free applications. Pear Linux 6 does everything you need it to. Pear Appstore gives you a handy way to choose and install desired applications by one click. Click on “Pear Linux 6″ (Top left of the screen) and the Launchpad open to show you your installed software : Each app is represented by an icon, and Launchpad creates as many pages of app icons as you need. Screen Shots Recommended Requirements Minimum System Requirements Personal computer with an Intel Pentium III 500 MHz or higher processor 512 MB physical RAM 8 GB available disk space 800×600 display resolution
KDE Oneiric - From Also see info about the most recent LTS version, Precise Pangolin (12.04 LTS). Introduction On October 14, 2011, Ubuntu 11.10 was released. It is codenamed Oneiric Ocelot and is the successor to Natty Narwhal 11.04 (Natty+1). General Notes General Notes This is the original Ubuntuguide. Menu -> File -> Open Terminal Text inside the grey dotted box like this should be put into the command-line Terminal. Many changes to the operating system can only be done by a User with Administrative privileges. sudo bash 'gksudo' can be used instead of 'sudo' when opening a Graphical Application through the "Run Command" dialog box or as a menu item. gksudo gedit /etc/apt/sources.list Many file management tasks can be accomplished with root Administrative privileges by starting the Nautilus file manager in a similar fashion. gksudo nautilus or sudo nautilus "man" command can be used to find help manual for a command. man sudo sudo apt-get install package Other versions Open the command terminal and type: Run:
SliTaz SliTaz GNU/Linux is a light-weight, community-based Linux distribution suitable for use on older hardware or as a Live CD or Live USB.[3][4][5][6] System requirements[edit] SliTaz GNU/Linux is supported on all machines based on the i486 or x86 Intel compatible processors.[2] The Live CD has four variants of SliTaz, requiring from 192 MB of RAM for the Core system to 48 MB for a text mode and X Window System.[2] Slitaz can even run in 16 megabytes of RAM and a little swap memory. [7] SliTaz can be booted from a Live CD, Live USB, floppy disk, or a local area network,[8] or can be installed, requiring approximately 100 MB of hard disk space.[9] Release history[edit] Gallery[edit] See also[edit] References[edit] External links[edit]
SliTaz GNU/Linux Internet U.S. Army soldiers "surfing the Internet" at Forward Operating Base Yusifiyah, Iraq The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to link several billion devices worldwide. It is a network of networks[1] that consists of millions of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The origins of the Internet date back to research commissioned by the United States government in the 1960s to build robust, fault-tolerant communication via computer networks.[2] This work, combined with efforts in the United Kingdom and France, led to the primary precursor network, the ARPANET, in the United States. Terminology The Internet, referring to the specific global system of interconnected IP networks, is a proper noun and written with an initial capital letter. History T3 NSFNET Backbone, c. 1992. Access
Application software Application software is all the computer software that causes a computer to perform useful tasks beyond the running of the computer itself. A specific instance of such software is called a software application, application program, application or app.[1] The term is used to contrast such software with system software, which manages and integrates a computer's capabilities but does not directly perform tasks that benefit the user. Application software applies the power of a particular computing platform or system software to a particular purpose. Terminology[edit] In information technology, an application is a computer program designed to help people perform an activity. In recent years, the shortened term "app" (coined in 1985[4]) has become particularly popular to refer to applications for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets, the shortened form matching their typically smaller scope in relation to applications used by PCs. Application software classification[edit] See also[edit]
Linux Linux ( History[edit] Antecedents[edit] With AT&T being required to license the operating system's source code to anyone who asked (due to an earlier antitrust case forbidding them from entering the computer business),[23] Unix grew quickly and became widely adopted by academic institutions and businesses. In 1984, AT&T divested itself of Bell Labs. Free of the legal obligation requiring free licensing, Bell Labs began selling Unix as a proprietary product. Linus Torvalds has said that if the GNU kernel had been available at the time (1991), he would not have decided to write his own.[26] Although not released until 1992 due to legal complications, development of 386BSD, from which NetBSD, OpenBSD and FreeBSD descended, predated that of Linux. MINIX, initially released in 1987, is an inexpensive minimal Unix-like operating system, designed for education in computer science, written by Andrew S. Creation[edit] Naming[edit] 5.25-inch floppy discs holding a very early version of Linux
Music This article is about music as a form of art. For history see articles for History of music and Music history. The creation, performance, significance, and even the definition of music vary according to culture and social context. Music ranges from strictly organized compositions (and their recreation in performance), through improvisational music to aleatoric forms. To many people in many cultures, music is an important part of their way of life. Etymology The word derives from Greek μουσική (mousike; "art of the Muses").[4] Music as form of art Jean-Gabriel Ferlan performing at a 2008 concert at the collège-lycée Saint-François Xavier Music is composed and performed for many purposes, ranging from aesthetic pleasure, religious or ceremonial purposes, or as an entertainment product for the marketplace. There are often many links between amateur and professional musicians. Composition Music can be composed for repeated performance or it can be improvised: composed on the spot. Notation Play
Yeah but if you were a complete noob to Linux and computers all together for that matter it would be a nice start by taranasus Jun 19