


Maithuna, Sacred Sex You are Aphrodite and Adonis as soft flesh endlessly dances on flesh among the brilliant flowers of Mount Olympus. You are the roil and roll of the universe in the never ending movement of creation. You are mastodons in rut, but you are also a point of light beyond manifestation. That point explodes into a million fragments like fireworks in cosmic eternity. The two of you are one but even the one melts into nothingness. Finally, beyond thought, concept or even feeling at all is the indescribable ecstasy as your personality dies. Maithuna is the Sanskrit word for union. Sexual voyaging should take us on journeys to incredible spaces of consciousness and union with many levels of infinite reality, but that takes unlearning much of what religion has promulgated and our parents, in their ignorance, passed on to us. Making love is a way of getting high,perhaps ultimately the only way. So, ‘rule’ number one: it is of primary importance that orgasm is not the most important end to this union.
Oxygen Chemical element, symbol O and atomic number 8 All plants, animals, and fungi need oxygen for cellular respiration, which extracts energy by the reaction of oxygen with molecules derived from food and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. In tetrapods breathing brings oxygen into the lungs where gas exchange takes place, carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood, and oxygen diffuses into the blood. The body's circulatory system transports the oxygen to the cells, where cellular respiration takes place.[4][5] Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats, as do the major constituent inorganic compounds of animal shells, teeth, and bone. Oxygen was isolated by Michael Sendivogius before 1604, but it is commonly believed that the element was discovered independently by Carl Wilhelm Scheele, in Uppsala, in 1773 or earlier, and Joseph Priestley in Wiltshire, in 1774. History of study Discovery
SPIRITUAL SEX Here is your chance to spiritualize your sex life or to make your spiritual life more sexy by Walter Last Sexuality is closely related to spirituality in several ways. The idea of celibacy for priests, nuns and monks is to spiritualize sexual energies as in meditation, rituals and other devotional practices. There are various yoga and meditation techniques to transform sexual energy into kundalini or spiritual energy by oneself. Commonly esoteric teachings advise to curtail sexual activity and portray abstinence as an ideal in order to retain sexual energies for internal development. Furthermore, most of those with a chronic disease, and especially cancer, are emotionally rather fragile, and benefit greatly from a close-bonding loving relationship. What many individuals miss even more than sex is touching and hugging. Karezza I believe that regularly radiating love, and feel being loved, greatly helps to prevent and overcome cancer and other diseases. Meditative Sex Tantric Sex Sexual
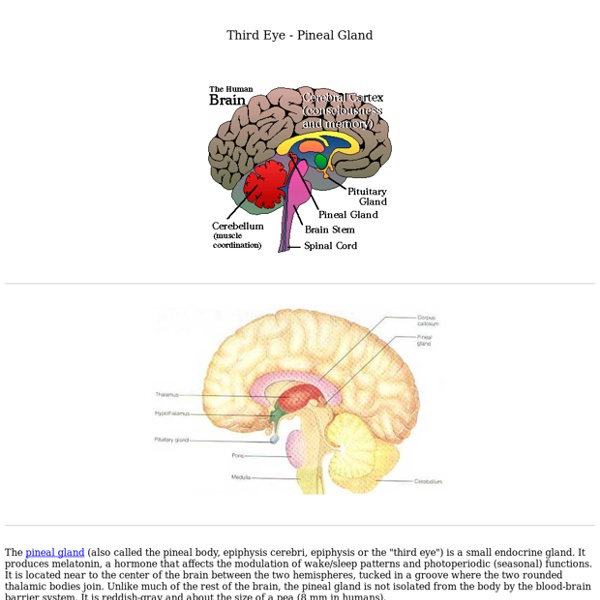
Fillmore Fulfilled: Pineal Gland « Back to Fillmore Fulfilled PINEAL GLAND (This drawing is a medial view of the right cerebral hemisphere; to the left is to the front of the cerebrum.) Charles Fillmore located the power of faith in the center of the head in the pineal gland. As with most of his other locations, Fillmore gave little or no explanation as to why he placed faith at the pineal gland. Therefore, we are left to view his designation from historical and other perspectives. In Eastern literature, the pineal gland was said to be the organ that correlated with the crown chakra. Medically, in Fillmore's day, little was known about the pineal gland and its function. It was not until the 1980s that scientists began to document that the pineal is an endocrine gland whose primary hormone, melatonin, helps to regulate the sleep-wake cycle. Thus, melatonin helps to regulate whether our cerebrum is in its conscious, awake state or mode, or in its subconscious, sleep state or mode. Permalink
List of martial arts There are a large number of distinct styles and schools of martial arts. Sometimes, schools or styles are introduced by individual teachers or masters, or as a brand name by a specific gym. Martial arts can be grouped by type or focus, or alternatively by regional origin. For hybrid martial arts, as they originated from the late 19th century and especially after 1950, it may be impossible to identify unique or predominant regional origins. A large portion of traditional martial arts can be categorized as folk wrestling (see the separate article), although in some cases a folk wrestling style and a modern combat sport may overlap or become indistinguishable from each other once the sport has been regulated. Africa[edit] Styles of stickfighting Folk wrestling Bare knuckle boxing Others Engolo (Angola) The Americas[edit] Mixed martial arts Barbados Bajan stick licking Bolivia Tinku Brazil Canada; Colombia Cuba El Juego de Maní Peru Bakom/Vacon Trinidad and Tobago Calinda United States Venezuela Asia[edit] China
Red blood cell In humans, mature red blood cells are flexible and oval biconcave disks. They lack a cell nucleus and most organelles, in order to accommodate maximum space for hemoglobin; they can be viewed as sacks of hemoglobin, with a plasma membrane as the sack. Approximately 2.4 million new erythrocytes are produced per second in human adults.[3] The cells develop in the bone marrow and circulate for about 100–120 days in the body before their components are recycled by macrophages. Packed red blood cells (pRBC) are red blood cells that have been donated, processed, and stored in a blood bank for blood transfusion. Structure Vertebrates There is an immense size variation in vertebrate red blood cells, as well as a correlation between cell and nucleus size. Mature red blood cells of birds have a nucleus, however in the blood of adult females of penguin Pygoscelis papua enucleated red blood cells (B) have been observed, but with very low frequency. Mammals Scanning electron micrograph of blood cells.
Marijuana Smokers Breathe Easy Says The University of Alabama As of January 10, 2012, a new study has been published in the Journal of the American Medical Association exonerating marijuana from the bad reputation of being as harmful to your lungs when smoked as tobacco cigarettes. Researchers at the University of California San Francisco and the University of Alabama at Birmingham completed a twenty-year study between 1986 and 2006 on over 5,000 adults over the age of 21 in four American cities. Study co-author Dr. Lung function was determined by testing the volume of expiration in the first second of exhaling and the amount of air a person can force out in one second after taking a deep breath. Basically, though these studies do not depict what the consequences are of inhaling marijuana smoke, their findings suggest that occasional use of marijuana may not be linked with unfavorable consequences on pulmonary function.
Blood cell Red blood cells (erythrocytes)White blood cells (leukocytes)Platelets (thrombocytes) Together, these three kinds of blood cells add up to a total 45% of the blood tissue by volume, with the remaining 55% of the volume composed of plasma, the liquid component of blood.[1] Red blood cells[edit] Red and white human blood cells as seen under a microscope using a blue slide stain Red blood cells or erythrocytes, primarily carry oxygen and collect carbon dioxide through the use of hemoglobin. RBCs are formed in the red bone marrow from hematopoietic stem cells in a process known as erythropoiesis. Mature red blood cells are unique among cells in the human body in that they lack a nucleus (although erythroblasts do have a nucleus). The condition of having too few red blood cells is known as anemia, while having too many is polycythemia. White blood cells[edit] Artificially colored electron micrograph of blood cells. Platelets[edit] If the number of platelets is too low, excessive bleeding can occur.
Cannabidiol helps neuropathy pain Cannabidiol—a compound derived from marijuana—may be a promising new treatment to prevent the development of painful neuropathy in patients receiving the chemotherapy drug paclitaxel, according to animal experiments reported in the October issue of Anesthesia & Analgesia, official journal of the International Anesthesia Research Society (IARS). "Our preliminary findings…indicate that cannabidiol may prevent the development of paclitaxel-induced allodynia in mice and therefore be effective at preventing dose-limiting paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy in humans," according to the report by Sara Jane Ward, Ph.D., and colleagues of Temple University School of Pharmacy, Philadelphia. In Female Mice, Cannabidiol Reduces Paclitaxel-Induced Neuropathy Paclitaxel—commonly used in the treatment of advanced breast or ovarian cancer—can cause nerve damage (neuropathy), leading to symptoms like pain, numbness, or tingling. Further Study Needed to Evaluate Cannabidiol's Effects in Humans
Enteric nervous system The enteric nervous system (ENS) or intrinsic nervous system is one of the main divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) and consists of a mesh-like system of neurons that governs the function of the gastrointestinal tract.[1] It is capable of acting independently of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, although it may be influenced by them. The ENS is also called the second brain.[2][3] It is derived from neural crest cells.[4][5] Structure[edit] The enteric nervous system in humans consists of some 500 million neurons[6] (including the various types of Dogiel cells),[1][7] one two-hundredth of the number of neurons in the brain, five times as many as the one hundred million neurons in the human spinal cord,[8] and about 2/3 as many as in the whole nervous system of a cat. Function[edit] Complexity[edit] The enteric nervous system has been described as a "second brain" for several reasons. Additional images[edit] The myenteric plexus of a rabbit. See also[edit]
Toke of the Town - Cannabis news, rumor and humor