


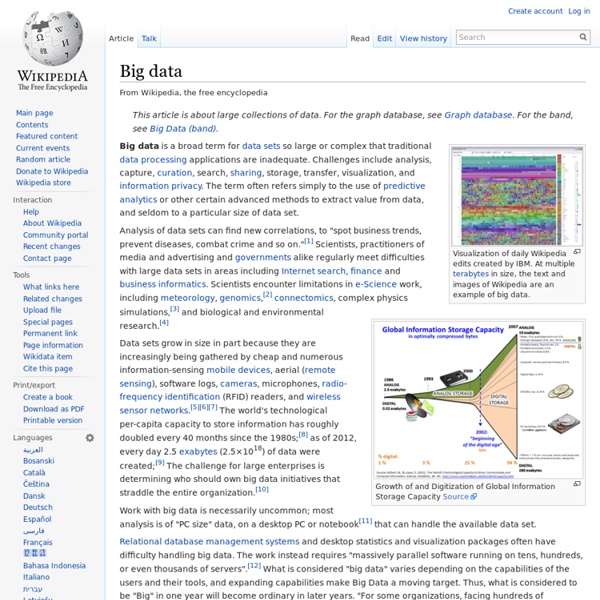
Big data Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre. Une visualisation des données créée par IBM[1] montre que les big data que Wikipedia modifie à l'aide du robot Pearle ont plus de signification lorsqu'elles sont mises en valeur par des couleurs et des localisations[2]. Croissance et Numérisation de la Capacité de Stockage Mondiale de L'information[3]. Dans ces nouveaux ordres de grandeur, la capture, le stockage, la recherche, le partage, l'analyse et la visualisation des données doivent être redéfinis. Certains supposent qu'ils pourraient aider les entreprises à réduire les risques et faciliter la prise de décision, ou créer la différence grâce à l'analyse prédictive et une « expérience client » plus personnalisée et contextualisée. Dimensions des big data[modifier | modifier le code] Le Big Data s'accompagne du développement d'applications à visée analytique, qui traitent les données pour en tirer du sens[15]. Volume[modifier | modifier le code] Variété[modifier | modifier le code]
Gartner - Big Data IT Glossary Gartner IT Glossary > Big Data Big Data inShare44 Big data is high-volume, high-velocity and/or high-variety information assets that demand cost-effective, innovative forms of information processing that enable enhanced insight, decision making, and process automation. FREE Webinar: Key Trends and Emerging Technologies in Advanced Analytics FREE Research: Answering Big Data’s 10 Biggest Vision and Strategy Questions Summary Article Name What is Big Data? Gartner, Inc. Description Big data is high-volume, high-velocity and high-variety information assets that demand cost-effective, innovative forms of information processing for enhanced insight and decision making. Related Research Report Highlight for Market Trends: How to Drive End-User Adoption of Big Data and Analytics in Eastern Europe and Russia Big data and analytics are becoming key enablers of business success in Eastern Europe and Russia. Report Highlight for Market Insight: How to Value CSPs' Big Data Potential Related Webinars
Technology | Narrative Science Fast and Efficient Delivery These data insights can be delivered on demand or on a schedule (hourly, daily, weekly, monthly) in your chosen format, including mobile, HTML, dashboard annotations or any document type. For mobile devices, whether via email or app, narrative content is ideally suited for consumption; much better than traditional methods like spreadsheets or graphs. Also, API options are available for integration with your existing systems and applications. You may think you know business intelligence, but Quill’s process of deriving data and developing narratives is unlike any other business intelligence platform on the market. Quill delivers stories that are understandable, precise and expressive.
2013 - (Peter Cochrane) Big Data v Data Mining Comment le Big Data va révolutionner 2013 "2012 a été l'année de l'évangélisation, 2013 sera l'année de la mise en place." Chez Atos, géant international du service informatique, pas de doute : cette année verra la multiplication des systèmes d'analyse dits de "Big Data". Plus qu'un concept, cette "grosse quantité de données" (littéralement) renvoie à de nouveaux systèmes informatiques qui promettent de "révolutionner la vie quotidienne". Le Big Data a émergé face à un constat. Chaque jour, 2,5 trillions d'octets de données sont générés dans le monde. "Internet a changé le monde des années 1990, le Big Data va changer celui des années 2010", anticipe Chuck Hollis, directeur technique du leader mondial du stockage EMC et gourou du Big Data. Prédire les crises cardiaques Mais dans la pratique, comment s'illustre ce Big Data ? Les applications du Big Data sont nombreuses. En octobre dernier, le canadien Research in Motion (RIM) a été victime d'une panne majeure sur ses téléphones BlackBerry. Big Data = Big brother ?
(Hurwitz et al) Data Mining for Big Data Data mining involves exploring and analyzing large amounts of data to find patterns for big data. The techniques came out of the fields of statistics and artificial intelligence (AI), with a bit of database management thrown into the mix. Generally, the goal of the data mining is either classification or prediction. In classification, the idea is to sort data into groups. These are two classes. Typical algorithms used in data mining include the following: Classification trees: A popular data-mining technique that is used to classify a dependent categorical variable based on measurements of one or more predictor variables. Here's a classification tree example. Of course, you can find many more attributes than this. The data set is broken into training data and a test data set. The algorithm is run over the training data and comes up with a tree that can be read like a series of rules. These rules are then run over the test data set to determine how good this model is on “new data.”
Peut-on être contre les big data ? L'article présente les thèses d'Alan Mitchell, le directeur de la stratégie du cabinet Ctrl+shift. Selon lui, "les Big Data auraient presque un côté contre-révolutionnaire : le chant du cygne d’une informatique productiviste, centralisatrice, centrée sur les grandes organisations." L'effort consenti - notamment en R&D - pour développer cette informatique et ses applications aurait été mieux employé à développer le pouvoir de création des individus, et à les aider à produire eux-mêmes les arbitrages qui leurs sont proposés par cette informatique massive. Daniel Kaplan lui-même reconnaît, à la fin de l'article, que le propos est peut-être un peu fort et qu'il est peu adapté, par exemple, aux les sciences dures. Je m'arrête sur cet article parce qu'on me pose de plus en plus de questions sur ce phénomène big data dont j'ai parlé très tôt. Mais de là à contester l'existence même, l'intérêt et la puissance du phénomène big data, il y a un pas que l'on ne peut franchir.
Big Data Big Data : un marché de 24 milliards de dollars en 2016 Ce n’est pas en 2013 qu’on cessera d’entendre parler du Big Data, même si la concrétisation en termes de projets n’est sans doute pas à l’heure actuelle à la hauteur du marketing entourant ce concept. Mais la taille de ce marché a de quoi aiguiser les appétits. D’après IDC, qui se livre à une évaluation, le Big Data, soit les services et technologies associés, est promis à une forte croissance annuelle de l’ordre de 31,7%. De quoi faire gonfler le gâteau jusqu’à 23,8 milliards de dollars en 2016. +53,4% pour le segment stockage Naturellement, nouveau concept ne signifie pas la création d’un marché totalement nouveau. IDC précise ainsi que ce marché du Big Data englobe certes de nouveaux segments, mais aussi de nombreuses activités déjà établies, notamment dans les secteurs du stockage et de la BI. La croissance annuelle attendue par le cabinet entre 2012 et 2016 se répartit ainsi de la manière suivante : +53,4% pour le stockage et +21,1% pour les services.
ExplainingComputers - Big Data Big Data Hot on the heels of Web 2.0 and cloud computing , Big Data may well be the Next Big Thing in the IT world. Whereas Web 2.0 links people and things online, and cloud computing is about the transition to an online computing infrastructure, Big Data generates value from the storage and processing of very large quantities of digital information that cannot be analyzed with traditional computing techniques. By the end of 2015, Cisco estimate that global Internet traffic will reach 4.8 zettabytes a year . That's 4.8 billion terabytes, and signals both the Big Data challenge and the Big Data opportunity on the horizon. The quantity of computer data being generated on Planet Earth is growing exponentially for a number of related reasons. As vision recognition improves, it is additionally starting to become possible for computers to glean useful information and data relationships from still images and video. Big data velocity also raises a number of key issues.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2025-08-03 17:43
by raviii Aug 4