Royal Society
national academy of science in the United Kingdom The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge,[1] is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. Founded on 28 November 1660, it was granted a royal charter by King Charles II as "The Royal Society".[1] It is the oldest national scientific institution in the world.[2] The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, recognising excellence in science, supporting outstanding science, providing scientific advice for policy, fostering international and global co-operation, education and public engagement. It also performs these roles for the smaller countries of the Commonwealth. The society is governed by its Council, which is chaired by the Society's President, according to a set of statutes and standing orders. History[edit]
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
18th/19th-century German writer, artist, and politician A literary celebrity by the age of 25, Goethe was ennobled by the Duke of Saxe-Weimar, Karl August, in 1782 after taking up residence in Weimar in November 1775 following the success of his first novel, The Sorrows of Young Werther (1774). He was an early participant in the Sturm und Drang literary movement. During his first ten years in Weimar, Goethe became a member of the Duke's privy council, sat on the war and highway commissions, oversaw the reopening of silver mines in nearby Ilmenau, and implemented a series of administrative reforms at the University of Jena. He also contributed to the planning of Weimar's botanical park and the rebuilding of its Ducal Palace.[4][b] Goethe's first major scientific work, the Metamorphosis of Plants, was published after he returned from a 1788 tour of Italy.
www.iep.utm
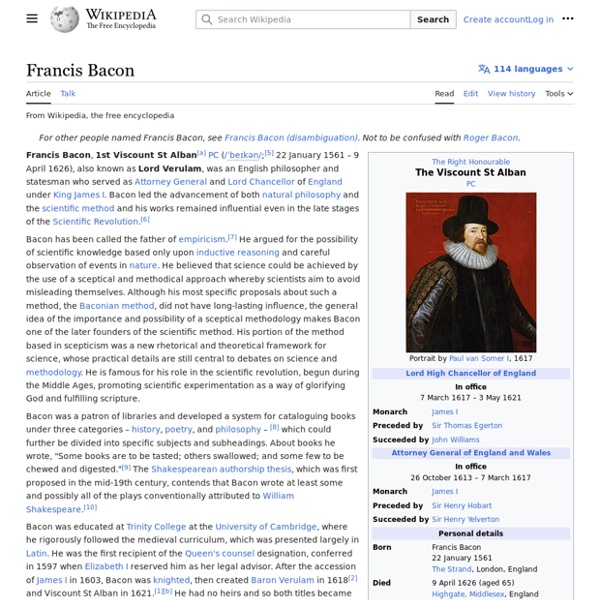
Sir Francis Bacon (later Lord Verulam and the Viscount St. Albans) was an English lawyer, statesman, essayist, historian, intellectual reformer, philosopher, and champion of modern science. Early in his career he claimed “all knowledge as his province” and afterwards dedicated himself to a wholesale revaluation and re-structuring of traditional learning.
Gulliver's Travels
1726 novel by Jonathan Swift Gulliver's Travels, or Travels into Several Remote Nations of the World. In Four Parts. By Lemuel Gulliver, First a Surgeon, and then a Captain of Several Ships is a prose satire[1][2] of 1726 by the Irish writer and clergyman Jonathan Swift, satirising both human nature and the "travellers' tales" literary subgenre. It is Swift's best known full-length work, and a classic of English literature. Swift claimed that he wrote Gulliver's Travels "to vex the world rather than divert it".
Plotinus
Biography[edit] Plotinus had an inherent distrust of materiality (an attitude common to Platonism), holding to the view that phenomena were a poor image or mimicry (mimesis) of something "higher and intelligible" [VI.I] which was the "truer part of genuine Being". This distrust extended to the body, including his own; it is reported by Porphyry that at one point he refused to have his portrait painted, presumably for much the same reasons of dislike. Likewise Plotinus never discussed his ancestry, childhood, or his place or date of birth. From all accounts his personal and social life exhibited the highest moral and spiritual standards.
www.britannica
John Milton, (born December 9, 1608, London, England—died November 8?, 1674, London?), English poet, pamphleteer, and historian, considered the most significant English author after William Shakespeare. Top Questions
Ernst Mayr
German-American evolutionary biologist His theory of peripatric speciation (a more precise form of allopatric speciation which he advanced), based on his work on birds, is still considered a leading mode of speciation, and was the theoretical underpinning for the theory of punctuated equilibrium, proposed by Niles Eldredge and Stephen Jay Gould. Mayr is sometimes credited with inventing modern philosophy of biology, particularly the part related to evolutionary biology, which he distinguished from physics due to its introduction of (natural) history into science. Biography[edit]
Plutarch
Plutarch (/ˈpluːtɑrk/; Greek: Πλούταρχος, Ploútarkhos, Koine Greek: [plǔːtarkʰos]; later named, on his becoming a Roman citizen, Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (Λούκιος Μέστριος Πλούταρχος);[a] c. 46 – 120 AD),[1] was a Greek historian, biographer, and essayist, known primarily for his Parallel Lives and Moralia.[2] He is considered today to be a Middle Platonist. Early life[edit] Ruins of the Temple of Apollo at Delphi, where Plutarch served as one of the priests responsible for interpreting the predictions of the oracle.
en.m.wikipedia
Italian poet Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri (Italian: [duˈrante deʎʎ aliˈɡjɛːri]; Latin: Dantes), commonly known by his pen name Dante Alighieri or simply as Dante (,[1][2] also ,[3] Italian: [ˈdante]; c. 1265 – 1321), was an Italian poet. His Divine Comedy, originally called Comedìa (modern Italian: Commedia) and later christened Divina by Giovanni Boccaccio, is widely considered the most important poem of the Middle Ages and the greatest literary work in the Italian language.[4][5] In the Late Middle Ages, most poetry was written in Latin, making it accessible only to the most educated readers. In De vulgari eloquentia (On Eloquence in the Vernacular), however, Dante defended the use of the vernacular in literature.