


Indian Fairs and Festivals Indus Valley Civilization The major sites of the Indus Valley Civilization imposed over modern borders The Indus Valley Civilization (IVC) was a Bronze Age civilization (3300–1300 BCE; mature period 2600–1900 BCE) extending from what today is northeast Afghanistan to Pakistan and northwest India (see map). Along with Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, it was one of three early civilizations of the Old World, and the most widespread among them, covering an area of 1.25 million km2.[3] It flourished in the basins of the Indus River, one of the major rivers of Asia, and the now dried up Sarasvati River,[4][5] which once coursed through northwest India and eastern Pakistan together with its tributaries flowed along a channel, presently identified as that of the Ghaggar-Hakra River on the basis of various scientific studies.[7][8][9] The Harappan language is not directly attested and its affiliation is uncertain since the Indus script is still undeciphered. Discovery and history of excavation Chronology Geography Cities
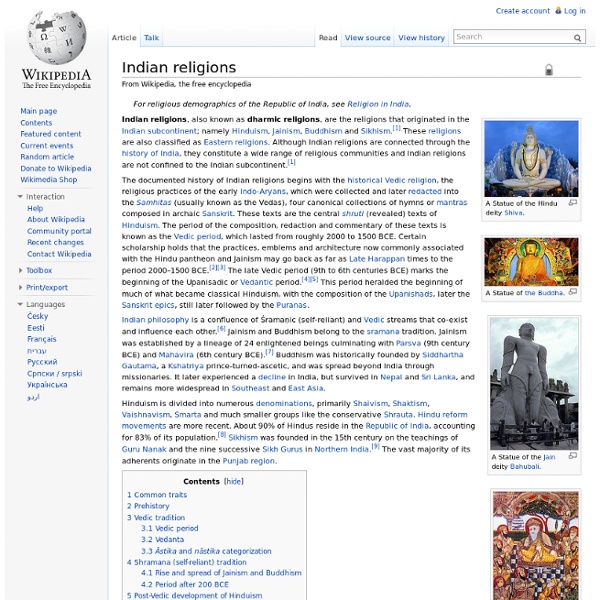
Jainism Jainism (/ˈdʒeɪnɪzəm/[1] or /ˈdʒaɪnɪzəm/[2]), traditionally known as Jin Sashana or Jain dharma (Sanskrit: जैन धर्म), is an Indian religion that prescribes a path of nonviolence (ahimsa) towards all living beings. Practitioners believe that nonviolence and self-control are the means by which they can obtain liberation. The three main principles of Jainism are non-violence (ahimsa), non-absolutism (anekantavada) and non-possessiveness (aparigraha). Followers of Jainism take 5 major vows: non-violence, non-lying, non-stealing, chastity, and non-attachment. Jainism is derived from the word Jina (conqueror) referring to a human being who has conquered inner enemies like attachment, desire, anger, pride, greed, etc. and possesses infinite knowledge (Kevala Jnana). Doctrine[edit] Non-violence (ahimsa)[edit] The hand with a wheel on the palm symbolizes Ahimsa (nonviolence). In addition to other humans, Jains extend the practice of nonviolence towards all living beings. Non-absolutism[edit]
History of India The history of India begins with evidence of human activity of Homo sapiens, as long as 75,000 years ago, or with earlier hominids including Homo erectus from about 500,000 years ago.[1] The Indus Valley Civilization, which spread and flourished in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent from c. 3300 to 1300 BCE in present-day Pakistan and northwest India, was the first major civilization in South Asia.[2] A sophisticated and technologically advanced urban culture developed in the Mature Harappan period, from 2600 to 1900 BCE.[3] This civilization collapsed at the start of the second millennium BCE and was later followed by the Iron Age Vedic Civilization, which extended over much of the Indo-Gangetic plain and which witness the rise of major polities known as the Mahajanapadas. In one of these kingdoms, Magadha, Mahavira and Gautama Buddha were born in the 6th or 5th century BCE and propagated their Shramanic philosophies. Prehistoric era[edit] Stone Age[edit] Bronze Age[edit]
Maurya Empire The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in ancient India, ruled by the Maurya dynasty from 322–185 BCE. Originating from the kingdom of Magadha in the Indo-Gangetic Plain (modern Bihar, eastern Uttar Pradesh) in the eastern side of the Indian subcontinent, the empire had its capital city at Pataliputra (modern Patna).[1][2] The Empire was founded in 322 BCE by Chandragupta Maurya, who had overthrown the Nanda Dynasty and rapidly expanded his power westwards across central and western India, taking advantage of the disruptions of local powers in the wake of the withdrawal westward by Alexander's Hellenic armies. By 316 BCE the empire had fully occupied Northwestern India, defeating and conquering the satraps left by Alexander.[3] Chandragupta then defeated the invasion led by Seleucus I, a Macedonian general from Alexander's army, gaining additional territory west of the Indus River.[4] History[edit] Chandragupta Maurya and Chanakya[edit] Bindusara[edit]
History of Ancient India Early Historic Period Vedic Period: The Aryans were the first to invade the country. They came out of the North in about 1500 BC and brought with them strong cultural traditions. Sanskrit, one of the most ancient languages spoken by them, was used in the first documentation of the Vedas, which date back to the 12th century BC and are believed to be oldest scriptures still in use. The Vedas are some of the oldest extant texts, next to those in Egypt and Mesopotamia. Mahajanapadas: This period saw the second major rise in urbanisation in India after the Indus valley Civilisation. Persian and Greek Conquests: Much of the Northwest subcontinent (currently Afghanistan and Pakistan) came under the rule of the Persian Achaemenid Empire in C. 520 BCE under the rule of Darius the Great and remained so for two centuries.
Middle kingdoms of India Middle kingdoms of India (or Classical India) refers to the political entities in India from the 3rd century BCE and the 13th century CE. This period begins after the decline of the Maurya Empire, and the corresponding rise of the Satavahana dynasty, beginning with Simuka, from 230 BC. The "Middle" period lasts for some 1,500 years, and ends in the 13th century, with the rise of the Delhi Sultanate and the end of the Chalukya Cholas (Rajendra Chola III died 1279). The period is known as the classical period of India, during which India is estimated to have had the largest economy of the world controlling between one third and one fourth of the world's wealth. The Northwest[edit] The Mauryan Empire, during the 2nd century BC, became a collage of regional powers with overlapping boundaries. The Indo-Scythian Sakas[edit] The Indo-Greeks[edit] The Yavanas[edit] The Yavanas or Yonas were described as living beyond Gandhara. The Indo-Parthians[edit] The Pahlavas[edit] The Western Satraps[edit]
Hinduism Indian religion Hinduism ()[1] is an Indian religion or dharma, a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide.[note 1][note 2] As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global population, known as Hindus.[2][3][web 1][web 2] The word Hindu is an exonym,[note 3] and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world,[note 4] many practitioners refer to their religion as Sanātana Dharma (Sanskrit: सनातन धर्म, lit. Etymology The word Hindū is derived from Indo-Aryan/Sanskrit root Sindhu, believed to be the name of the Indus River in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent. Definitions Because of the wide range of traditions and ideas covered by the term Hinduism, arriving at a comprehensive definition is difficult. The study of India and its cultures and religions, and the definition of "Hinduism", has been shaped by the interests of colonialism and by Western notions of religion. Art
Pala Empire The Pala Empire was a Buddhist imperial power in Classical India during the 8th to 12th century CE. The empire is named after its ruling dynasty, all of whose rulers bore names ending with the suffix -Pala ("protector"). The Palas were often described by opponents as the Lords of Gauda. Their empire was centered around the present-day Bengal-Bihar region, and at times, included what are now Assam, Orissa and parts of North India. The Palas ushered in a period of stability and prosperity in the Bengal region, which had been suffering from anarchy since the death of Shashanka. History[edit] The main sources of information about the Pala empire include:[3]:2–3 Pala accounts Various epigraphs, coins, sculptures and architectureRamacharita, a Sanskrit work by Abhinanda (9th century)Ramacharitam, a Sanskrit epic by Sandhyakar Nandi (12th century)Subhasita Ratnakosa, a Sanskrit compilation by Vidyakara (towards the end of the Pala rule) Other accounts Origins[edit] Establishment[edit] Expansion[edit]
Gurjara-Pratihara The Gurjar Pratihara (गुर्जर-प्रतिहार), often simply called Pratihara Empire, was an imperial Indian dynasty that ruled much of Northern India from the 8th to the 11th centuries. At its peak of prosperity and power (c. 836–910), the Gurajara-Pratihara Empire rivaled or even exceeded the Gupta Empire in the extent of its territory. The Pratihara Empire started to decline in the early 10th century after it had to face several invasions by the south Indian Rashtrakuta dynasty.[1] Kannauj was the capital of imperial Gurjara Pratiharas.[2][3][4] The Gurjara Pratihara rulers in the tenth century was entitled as Maharajadhiraja of Āryāvarta ("Great King over Kings of the abode of the Aryans". i.e. Etymology[edit] The word "Pratihara" means protector or "who takes over the enemy/opponent" and was used by the Gurjara-Pratihara rulers as self-designation. Origin[edit] Several scholars including D. Rulers[edit] Early rulers[edit] Expansion[edit] Conquest of Kannauj and further expansion[edit]
Rashtrakuta dynasty A stanza from the 9th century Kannada classic Kavirajamarga, praising the people for their literary skills Rashtrakuta (Kannada: ರಾಷ್ಟ್ರಕೂಟ, Sanskrit: राष्ट्रकूट rāṣṭrakūṭa), was a royal dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian Subcontinent between the sixth and the 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant that mentions their rule from Manpur in the Malwa region of modern Madhya Pradesh. Other ruling Rashtrakuta clans from the same period mentioned in inscriptions were the kings of Achalapur (modern Elichpur in Maharashtra) and the rulers of Kannauj. The clan that ruled from Elichpur was a feudatory of the Badami Chalukyas and during the rule of Dantidurga, it overthrew Chalukya Kirtivarman II and went on to build an empire with the Gulbarga region in modern Karnataka as its base. During their rule, Jain mathematicians and scholars contributed important works in Kannada and Sanskrit. History[edit] Administration[edit]
Gupta Empire The high points of this cultural creativity are magnificent architecture, sculptures and paintings.[7] The Gupta period produced scholars such as Kalidasa, Aryabhata, Varahamihira, Vishnu Sharma and Vatsyayana who made great advancements in many academic fields.[8][9] Science and political administration reached new heights during the Gupta era.[10] Strong trade ties also made the region an important cultural center and set the region up as a base that would influence nearby kingdoms and regions in Burma, Sri Lanka, and Southeast Asia.[11] The earliest available Indian epics are also thought to have been written around this period. The empire gradually declined because of many factors such as substantial loss of territory and imperial authority caused by their own erstwhile feudatories and the invasion by the Huna peoples from Central Asia.[12] After the collapse of the Gupta Empire in the 6th century, India was again ruled by numerous regional kingdoms. Origin of the Guptas[edit]
Sikhism Sikhism, known in Punjabi as Sikhi,[note 1] (/ˈsiːkɨzəm/ or /ˈsɪkɨzəm/; Punjabi: ਸਿੱਖੀ, sikkhī, IPA: [ˈsɪkːʰiː]) is a monotheistic religion founded during the 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, by Guru Nanak[3] and continued to progress through the ten successive Sikh gurus (the eleventh and last guru being the holy scripture Guru Granth Sahib. The Guru Granth Sahib is a collection of the Sikh Gurus' writings that was compiled by the 5th Sikh Guru). It is the fifth-largest organized religion in the world, with approximately 30 million adherents.[4][5] Punjab, India is the only state in the world with a majority Sikh population. Adherents of Sikhism are known as Sikhs (students or disciples). According to the ninth Sikh Guru, Tegh Bahadhur, the ideal Sikh should have both Shakti (power that resides in the temporal), and Bhakti (spiritual meditative qualities). Philosophy and teachings[edit] The Sikh concept of God[edit] Liberation[edit] Worldly illusion[edit]