


Hidden variable theory Albert Einstein, the most famous proponent of hidden variables, objected to the fundamentally probabilistic nature of quantum mechanics,[1] and famously declared "I am convinced God does not play dice".[2] Einstein, Podolsky, and Rosen argued that "elements of reality" (hidden variables) must be added to quantum mechanics to explain entanglement without action at a distance.[3][4] Later, Bell's theorem would suggest (in the opinion of most physicists and contrary to Einstein's assertion) that local hidden variables of certain types are impossible. The most famous nonlocal theory is de Broglie-Bohm theory. Motivation[edit] Under the orthodox Copenhagen interpretation, quantum mechanics is nondeterministic, meaning that it generally does not predict the outcome of any measurement with certainty. In other words, it is conceivable that the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics is an incomplete description of nature. "God does not play dice"[edit] Bohr-Einstein debates[edit] .
Copenhagen interpretation The Copenhagen interpretation is one of the earliest and most commonly taught interpretations of quantum mechanics.[1] It holds that quantum mechanics does not yield a description of an objective reality but deals only with probabilities of observing, or measuring, various aspects of energy quanta, entities that fit neither the classical idea of particles nor the classical idea of waves. The act of measurement causes the set of probabilities to immediately and randomly assume only one of the possible values. This feature of mathematics is known as wavefunction collapse. The essential concepts of the interpretation were devised by Niels Bohr, Werner Heisenberg and others in the years 1924–27. According to John Cramer, "Despite an extensive literature which refers to, discusses, and criticizes the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics, nowhere does there seem to be any concise statement which defines the full Copenhagen interpretation. Background[edit] Origin of the term[edit] 1. .
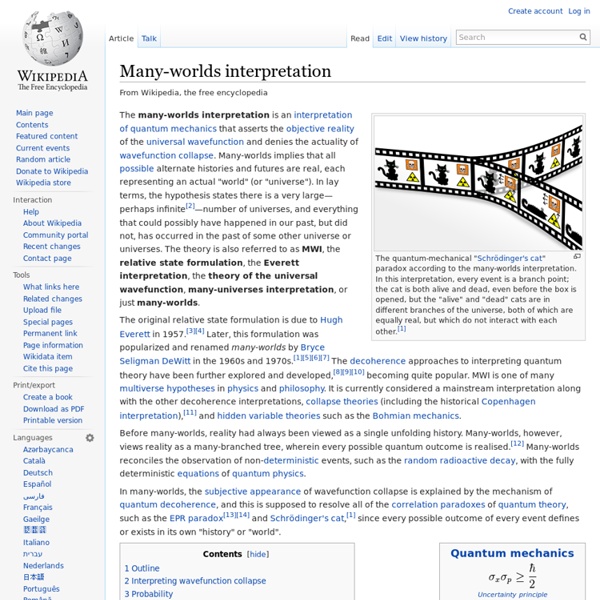
When the multiverse and many-worlds collide - physics-math - 01 June 2011 Read full article Continue reading page |1|2 Editorial: "God deserves a cosmological explanation" TWO of the strangest ideas in modern physics - that the cosmos constantly splits into parallel universes in which every conceivable outcome of every event happens, and the notion that our universe is part of a larger multiverse - have been unified into a single theory. This solves a bizarre but fundamental problem in cosmology and has set physics circles buzzing with excitement, as well as some bewilderment. The problem is the observability of our universe. Cosmologists reconcile this seeming contradiction by assuming that the superposition eventually "collapses" to a single state. This problem is captured in the famous thought experiment of Schrödinger's cat. Physicists call this process "decoherence". In the case of something as large as a cat, that may be possible in Schrödinger's theoretical sealed box. New Scientist Not just a website! More From New Scientist More from the web
Weird Universe Ensemble interpretation The ensemble interpretation, or statistical interpretation of quantum mechanics, is an interpretation that can be viewed as a minimalist interpretation; it is a quantum mechanical interpretation that claims to make the fewest assumptions associated with the standard mathematical formalization. At its heart, it takes to the fullest extent the statistical interpretation of Max Born for which he won the Nobel Prize in Physics.[1] The interpretation states that the wave function does not apply to an individual system – or for example, a single particle – but is an abstract mathematical, statistical quantity that only applies to an ensemble of similarly prepared systems or particles. Probably the most notable supporter of such an interpretation was Albert Einstein: To date, probably the most prominent advocate of the ensemble interpretation is Leslie E. Ballentine, Professor at Simon Fraser University, and writer of the graduate-level textbook "Quantum Mechanics, A Modern Development".[3]
70 Reminders to Help You Break Any Barrier I am pleased to introduce this guest article by a new friend John, the creator of HiLife2B, where he hopes to inspire people and to help them achieve their dreams. Follow him on Twitter: @janyasor 1. Believe that even the smallest compliment can save someone’s life 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70.
Calculating Water Footprints: How Much Water in Your Food? The environmental impact of food production in terms of contribution to climate change is well documented. Fertilizer use, soil degradation, and transportation from far flung farms to the table are all sources of greenhouse gas emissions. However, food production also has a steep water footprint. In 2009, the Food Ethics Council (FEC) declared in a report that food products should come with water footprint information in addition to carbon information. As a general rule of thumb, crops like sugar and vegetables are more water-intensive than cereals. Another recently released report by WRAP and WWF examined how much water is wasted in the UK when food is thrown away. The report focuses on the water and carbon footprint of wasted household food and drink in the UK for the first time. According to the Water Footprint Network the water footprint of US citizens is 2840 cubic meter per year per capita. Scroll down to see comments.
the childhood beliefs site - I Used To Believe Objective collapse theory Objective collapse theories are an approach to the interpretational problems of quantum mechanics. They are realistic, indeterministic and reject hidden variables. The approach is similar to the Copenhagen interpretation, but more firmly objective. The most well-known examples of such theories are: Compared to other approaches[edit] Collapse theories stand in opposition to many-worlds interpretation theories, in that they hold that a process of wavefunction collapse curtails the branching of the wavefunction and removes unobserved behaviour. Variations[edit] Objective collapse theories regard the present formalism of quantum mechanics as incomplete, in some sense. Collapse is found "within" the evolution of the wavefunction, often by modifying the equations to introduce small amounts of non-linearity. Objections[edit] The fact that these theories seek to extend the formalism is considered as violation of the principle of parsimony by some. GRW collapse theories have unique problems.
Modality effect The modality effect is a term used in experimental psychology, most often in the fields dealing with memory and learning, to refer to how learner performance depends on the presentation mode of studied items. Description[edit] For serial recall, the modality effect is seen in an increased memory span for auditorally presented lists. Memory span is defined as the maximum number of items that participants correctly recall in 50% of trials. Some studies use the term modality to refer to a general difference in performance based upon the mode of presentation. Bennet Murdock used a basic free recall paradigm, with different types of lists, mixing auditorally and visually presented words. Glenberg[9] showed that the modality effect is also prevalent in long term memory, showing that to-be-remembered word pairs that are separated by distractor activity are better recalled if presented auditorally vs. visually. Several terms have been used to refer to the modality effect on recency.
Food and water for the poor -- not political lies via MD, GG and MS, I read an interesting interview with the Chairman of Nestle in which he says: There is no market for how that water is allocated and used. The result is waste, overuse and misuse of the water we have. If we don't do something about that, Mr. Brabeck-Letmathe fears, we will soon run ourselves dry.[snip]"If oil becomes scarce," he notes, "the oil price goes up. He makes two important points (that I have made many times on this blog and in my book). First, political interference has distorted food markets (via artificial stimulation of demand for biofuels and artificial blockages on GMOs), which is bad for farmers and the poor but good for food companies with political connections. Second, we need better markets for water, to ensure that it goes to highest and best use instead of political cronies with little need to be efficient (let alone care for the environment, human rights, etc.)
Consistent histories In quantum mechanics, the consistent histories approach is intended to give a modern interpretation of quantum mechanics, generalising the conventional Copenhagen interpretation and providing a natural interpretation of quantum cosmology.[1] This interpretation of quantum mechanics is based on a consistency criterion that then allows probabilities to be assigned to various alternative histories of a system such that the probabilities for each history obey the rules of classical probability while being consistent with the Schrödinger equation. In contrast to some interpretations of quantum mechanics, particularly the Copenhagen interpretation, the framework does not include "wavefunction collapse" as a relevant description of any physical process, and emphasizes that measurement theory is not a fundamental ingredient of quantum mechanics. Histories[edit] A homogeneous history (here labels different histories) is a sequence of Propositions specified at different moments of time is true at time
The Heroes of Myth and Folklore: Part One – Defining a Hero | Once Upon A Time… Herakles battling the Hydra There is a special genre of tales in the texts of Hellenic mythology that recounts the deeds of extraordinary men and women such as Herakles, Perseus, Jason and Medeia to name but a few. These larger-than-life people are called the Heroes. Their stories derive from the most ancient form of the oral tradition and have evolved through the ages into the symbolic and historical mythology of mortals who were granted immortality through their destinies and the homage and remembrance of their descendants. To study the heroes is both an historical and symbolic journey that explores how the world of the immortal Gods interacts with the world of mortal men and women. The Definition of a Hero The word hero in English has come to mean many things. (1) A person distinguished for valour, fortitude or bold enterprise (2) Anyone regarded as having displayed great courage, exceptional nobility or qualities that distinguished or exemplified the finest virtues of their gender. J.