


Serotonin Serotonin /ˌsɛrəˈtoʊnɨn/ or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract), platelets, and the central nervous system (CNS) of animals, including humans. It is popularly thought to be a contributor to feelings of well-being and happiness.[6] Serotonin secreted from the enterochromaffin cells eventually finds its way out of tissues into the blood. In addition to animals, serotonin is found in fungi and plants.[10] Serotonin's presence in insect venoms and plant spines serves to cause pain, which is a side-effect of serotonin injection. Functions[edit] Receptors[edit] Gauge of food availability (appetite)[edit] Serotonin functions as a neurotransmitter in the nervous systems of simple, as well as complex, animals. When humans smell food, dopamine is released to increase the appetite. Effects of food content[edit] In the digestive tract (emetic)[edit] [edit]
Conifer cone The male cone (microstrobilus or pollen cone) is structurally similar across all conifers, differing only in small ways (mostly in scale arrangement) from species to species. Extending out from a central axis are microsporophylls (modified leaves). Under each microsporophyll is one or several microsporangia (pollen sacs). The female cone (megastrobilus, seed cone, or ovulate cone) contains ovules which, when fertilized by pollen, become seeds. Female cones of the conifer families[edit] Pinaceae cones[edit] Intact and disintegrated fir cones The members of the pine family (pines, spruces, firs, cedars, larches, etc.) have cones that are imbricate (that is, with scales overlapping each other like fish scales). Araucariaceae cones[edit] Members of the Araucariaceae (Araucaria, Agathis, Wollemia) have the bract and seed scales fully fused, and have only one ovule on each scale. Podocarpaceae cones[edit] Berry-like Podocarpus cone Cupressaceae cones[edit] Sciadopityaceae cones[edit] Gallery[edit]
Endocrine system In addition to the specialised endocrine organs mentioned above, many other organs that are part of other body systems, such as bone, kidney, liver, heart and gonads, have secondary endocrine functions. For example the kidney secretes endocrine hormones such as erythropoietin and renin. A number of glands that signal each other in sequence are usually referred to as an axis, for example, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. As opposed to endocrine factors that travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system, other signaling molecules, such as paracrine factors involved in paracrine signalling diffuse over a relatively short distance. The word endocrine derives from the Greek words ἐνδο- endo- "inside, within," and κρίνειν krinein "to separate, distinguish". Endocrine organs and known secreted hormones[edit] Endocrine glands in the human head and neck and their hormones Hypothalamus[edit] Pineal body (epiphysis)[edit] Pituitary gland (hypophysis)[edit] Thyroid[edit] Skin[edit]
Pineal gland The pineal gland, also known as the pineal body, conarium or epiphysis cerebri, is a small endocrine gland in the vertebrate brain. It produces melatonin, a serotonin derived hormone, which affects the modulation of sleep patterns in both seasonal and circadian rhythms.[1][2] Its shape resembles a tiny pine cone (hence its name), and it is located in the epithalamus, near the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres, tucked in a groove where the two halves of the thalamus join. Nearly all vertebrate species possess a pineal gland. The gland has been compared to the photoreceptive, so-called third parietal eye present in the epithalamus of some animal species, which is also called the pineal eye. René Descartes believed the pineal gland to be the "principal seat of the soul" and viewed it as the third eye.[6] Structure[edit] Blood supply[edit] Innervation[edit] The pineal gland receives a sympathetic innervation from the superior cervical ganglion. Histology[edit] Development[edit]
Entheogen A group of peyotes, in cultivation. Peyote has been used in ritual contexts for thousands of years.[1][2][3] With the advent of organic chemistry, there now exist many synthetic drugs with similar psychoactive properties, many derived from these plants. Many pure active compounds with psychoactive properties have been isolated from these organisms and chemically synthesized, including mescaline, psilocybin, DMT, salvinorin A, ibogaine, ergine, and muscimol, respectively. Semi-synthetic (e.g. Etymology[edit] The neologism entheogen was coined in 1979 by a group of ethnobotanists and scholars of mythology (Carl A. Entheogen was coined as a replacement for the terms hallucinogen and psychedelic. Ruck et al. argued that the term hallucinogen was inappropriate owing to its etymological relationship to words relating to delirium and insanity. Entheogens[edit] Species[edit] High caffeine consumption has been linked to an increase in the likelihood of experiencing auditory hallucinations. L. Other
Dimethyltryptamine History[edit] Another historical milestone is the discovery of DMT in plants frequently used by Amazonian natives as additive to the vine Banisteriopsis caapi to make ayahuasca decoctions. Biosynthesis[edit] Biosynthetic pathway for N,N-dimethyltryptamine This transmethylation mechanism has been repeatedly and consistently proven by radiolabeling of SAM methyl group with carbon-14 (14C-CH3)SAM).[22][20][24][25][26] Evidence in mammals[edit] In 2013, researchers first reported DMT in the pineal gland microdialysate of rodents.[28] A study published in 2014 reported the biosynthesis of N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) in the human melanoma cell line SK-Mel-147 including details on its metabolism by peroxidases. [29] In a 2014 paper, a group first demonstrated the immunomodulatory potential of DMT and 5-MeO-DMT through the Sigma-1_receptor of human immune cells. INMT[edit] Endogenous DMT[edit] The first claimed detection of mammalian endogenous DMT was published in June 1965: German researchers F.
Tryptamine Tryptamine is a monoamine alkaloid found in plants, fungi, and animals. It contains an indole ring structure, and is structurally similar to the amino acid tryptophan, from which it derives its name. Tryptamine is found in trace amounts in the brains of mammals and is believed to play a role as a neuromodulator or neurotransmitter.[2] The tryptamine chemical structure is the backbone for a group of compounds termed collectively tryptamines. The concentration of tryptamine in rat brains is about 3.5 pmol/g.[3] Plants containing tryptamine[edit] Many plants contain small amounts of tryptamine, for example, as a possible intermediate in one biosynthetic pathway to the plant hormone indole-3-acetic acid.[4] Higher concentrations can be found in many Acacia species. Role in vertebrates[edit] Tryptamine acts as a serotonin releasing agent[5] and a serotonergic activity enhancer.[6] It is metabolised by MAO-A and MAO-B.[7] Tryptamine derivatives[edit] General structure of substituted tryptamines
Psychedelia Psychedelia is a name given to the subculture of people who use psychedelic drugs, and a style of psychedelic artwork and psychedelic music derived from the experience of altered consciousness that uses highly distorted and surreal visuals, sound effects and reverberation, and bright colors and full spectrums and animation (including cartoons) to evoke and convey to a viewer or listener the artist's experience while using such drugs. The term "psychedelic" is derived from the Ancient Greek words psuchē (ψυχή - psyche, "mind") and dēlōsē (δήλωση - "manifest"), translating to "mind-manifesting". Psychedelic states may be elicited by various techniques, such as meditation, sensory stimulation[1] or deprivation, and most commonly by the use of psychedelic substances. When these psychoactive substances are used for religious, shamanic, or spiritual purposes, they are termed entheogens. Etymology[edit] To make this mundane world sublime, Take half a gram of phanerothyme History[edit] In art[edit]
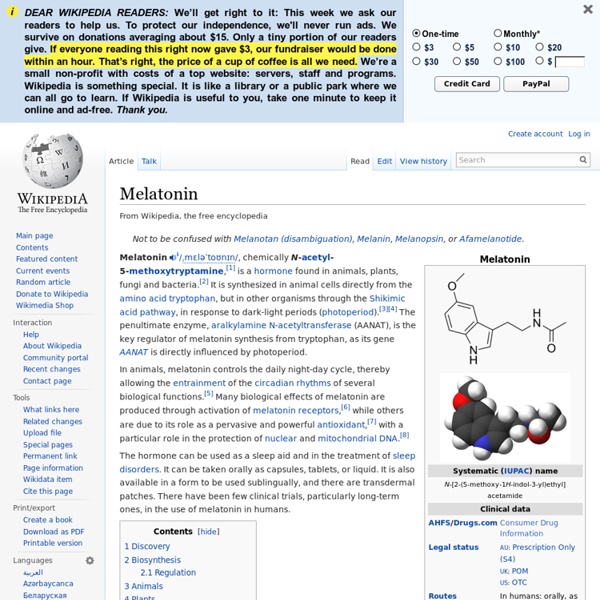
In humans, melatonin is produced by the pineal gland, a small endocrine gland[26] located in the center of the brain but outside the blood–brain barrier. The melatonin signal forms part of the system that regulates the sleep-wake cycle by chemically causing drowsiness and lowering the body temperature, but it is the central nervous system (specifically the suprachiasmatic nuclei, or SCN)[26] that controls the daily cycle in most components of the paracrine and endocrine systems[27][28] rather than the melatonin signal (as was once postulated). by oddsalom Mar 17