How to Properly Use Reinforcement and Punishment - North Shore Pediatric Therapy
Reinforcement and punishment are common terms that most people have heard of and use on a daily basis, whether they realize it or not. Although the concepts seem easy to understand and implement, it can be easy to confuse the basic principles and/or implement them incorrectly. In order to understand the difference between reinforcement and punishment, it is important to understand the definitions of both terms. Reinforcement Reinforcement is a consequence following a behavior that increases the probability that the behavior will increase in the future. The consequence can be either positive or negative.
Teens May Learn Best with Positive Reinforcement
A new study finds that adolescents focus on rewards and are less able to learn to avoid punishment or consider the consequences of alternative actions. University College-London investigators compared how adolescents and adults learn to make choices based on the available information. Investigators tracked the way in which 18 volunteers aged 12-17 and 20 volunteers aged 18-32 completed tasks in which they had to choose between abstract symbols. Each symbol was consistently associated with a fixed chance of a reward, punishment, or no outcome. As the trial progressed, participants learned which symbols were likely to lead to each outcome and adjusted their choices accordingly.
Using Reinforcement and Punishment at Home
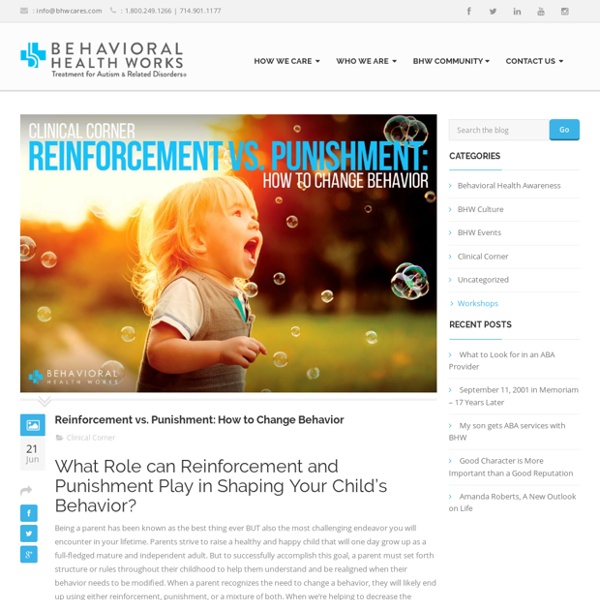
How do I get my child to listen to me at home? This is a common question I hear from parents. One solution is by using the basic principles of reinforcement and punishment. These principles will allow parents to gain control over their child’s behavior, and they will begin to see a decrease in negative behaviors and an increase in positive behaviors at home. Tips for Using Reinforcement at Home Reinforcement is a consequence following a behavior that increases the probability that the behavior will increase in the future.
Positive And Negative Reinforcement (Examples, Punishment) - Parenting For Brain
Reinforcement and punishment are often used as parenting tools to modify children’s behavior. Let’s review the difference between positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement, and the difference in outcomes between them. The Difference Between Positive And Negative Reinforcement In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is the introduction of a favorable condition that will make the desired behavior more likely to happen, continue or strengthen in the future1. Because the favorable condition acts as a reward, reinforcement is a reward-based operant conditioning. There are two types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement.
What Is 'positive Punishment'? Definition And Real-World Examples
Positive punishment is a popular concept in parenting. We'll explain what it is and how you can implement it with six examples. Parenting isn't always a walk in the park, and determining the best way to address your child's inevitable poor behavior can be a tricky line to walk. Techniques like positive punishment and negative reinforcement (two parenting "buzzwords" that you've probably heard a lot already) are just two of the ways parents and child care providers can try to correct a child's behavioral issues. [RELATED: "Parenting Styles: 4 Negative Reinforcement Examples "] If you decide to try out either -- or both -- of these parenting techniques, it's important that you first understand what they mean, what they do, and how you can incorporate this technique into your parenting style -- and how your babysitter or nanny can incorporate it into their care repertoire.
Rewarding behavior is key to parenting teens, study suggests
Parenting is hard, and parenting teens brings about an entirely new set of challenges, from keeping their rooms clean to getting them home before curfew. But, a new study suggests parents who want their teenagers to keep their grades up could have better success if they focus more on rewarding good behavior and less on threatening to punish the bad. According to the report, published in PLOS Computational Biology, British researchers have found that adolescents focus well on positive incentives, but have difficulty staying motivated to avoid penalties. The study shows that teens and adults learn in different ways, according to the study’s lead author Stefano Palminteri, a researcher with the Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience at University College London. It suggests that “in some cases positive feedback may have more of an effect than negative feedback on learning” in adolescents.
Punishing a child is effective if done correctly: Some children need consequences to succeed, psychologists say
While recently published parenting books have preached the effectiveness of positive parenting and "no drama" discipline, psychologists presenting at the American Psychological Association's 123rd Annual Convention said don't put timeout in timeout yet. "Parental discipline and positive parenting techniques are often polarized in popular parenting resources and in parenting research conclusions," presenter and researcher Robert Larzelere, PhD, of Oklahoma State University, said at a symposium. "But scientifically supported parenting interventions for young defiant children have found that timeouts and other types of assertive tactics can work if they're administered correctly." In his presentation, Larzelere said his research team interviewed 102 mothers who provided detailed descriptions of five times they had to discipline their toddlers for hitting, whining, defiance, negotiating or not listening. Longer-term effects revealed a different pattern.
10 Normal Teenage Behavior Problems And How To Handle Them
Image: iStock Understanding Teenage Behavior Problems Dealing with a teenager is not easy.
Positive Punishment: What Is It And How It Works? - MomJunction
Image: Shutterstock Positive punishment! Sounds like a perfect oxymoron. But how can a punishment be positive?
Positive Reinforcement: Changing The Behavior of Children For The Better
Home » Positive Education » Positive Reinforcement: Changing The Behavior of Children For The Better “The way positive reinforcement is carried out is more important than the amount.”– B.F. Skinner The purpose of reinforcement is to help increase the probability that a specific behavior will occur when a stimulus is delivered after a response is shown. When people think of reinforcement they immediately think of Pavlov, or at least I do. Pavlov and Skinner studied behavior and noted what it would take to produce a certain kind of behavior.