


Your Brain & Nervous System Listen How do you remember the way to your friend's house? Why do your eyes blink without you ever thinking about it? Where do dreams come from? Your brain is in charge of these things and a lot more. In fact, your brain is the boss of your body. Your brain has many different parts that work together. cerebrum (say: suh-REE-brum) cerebellum (say: sair-uh-BELL-um) brain stem pituitary (say: puh-TOO-uh-ter-ee) gland hypothalamus (say: hy-po-THAL-uh-mus) The Biggest Part: the Cerebrum The biggest part of the brain is the cerebrum. <a href=" your favorite way to challenge your brain? When you're thinking hard, you're using your cerebrum. The cerebrum has two halves, with one on either side of the head. Listen The Cerebellum's Balancing Act Next up is the cerebellum. Because of your cerebellum, you can stand upright, keep your balance, and move around. Brain Stem Keeps You Breathing — and More Another brain part that's small but mighty is the brain stem.
cells of the nervous system Types of Neurons (Nerve Cells) The human body is made up of trillions of cells. Cells of the nervous system, called nerve cells or neurons, are specialized to carry "messages" through an electrochemical process. The human brain has approximately 86 billion neurons. To learn how neurons carry messages, read about the action potential. Neurons come in many different shapes and sizes. Neurons are similar to other cells in the body because: Neurons are surrounded by a cell membrane.Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes.Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other organelles.Neurons carry out basic cellular processes such as protein synthesis and energy production. However, neurons differ from other cells in the body because: Neurons have specialize cell parts called dendrites and axons. The Neuron One way to classify neurons is by the number of extensions that extend from the neuron's cell body (soma). Pseudounipolar cells (example: dorsal root ganglion cells).
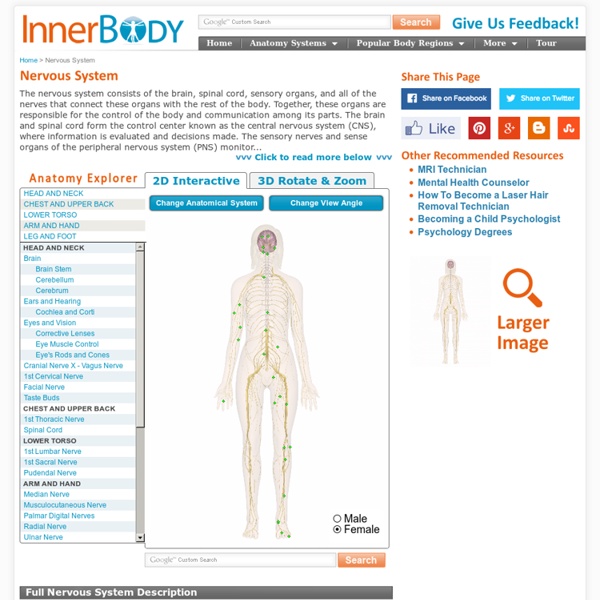
Nervous System The nervous system is an organ system in charge of sending messages to and from the brain and spinal cord to and from all parts of the body. It consists of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. Another important part of the nervous system is the sense organs to which a special page is devoted. Sense Organs Jobs of the nervous system It controls and coordinates the body functions. It receives sensory impulses from the sensory organs through sensory nerve fibers, analyzes and interprets this information and starts the motor impulses which are carried to muscles and glands which act on these impulses and cause the body to react. It helps the body learn from experience and stores these memories. It coordinates all parts of the body to keep everything in balance. Parts of the nervous system Central nervous system: Made up of the brain and the spinal cord. Peripheral nervous system: Neurons: These are nerve cells. Brain: Spinal Cord: Enteric nervous system: Diagram of the Cerebrum
Enrichment: Activity Discussion: The more frequently we are called on to do a certain task, the easier the task becomes. This is because our brain learns by doing. Each time we repeat a task, nerve cell connections in our brains are strengthened. Materials: jigsaw puzzle of no more than 12 pieces (preferably one new to the class) clock with second hand Procedure: Time a volunteer doing the jigsaw puzzle and record the score on the board. How are the person's times different?
Explore the Brain Advertisement. EnchantedLearning.com is a user-supported site. As a bonus, site members have access to a banner-ad-free version of the site, with print-friendly pages.Click here to learn more. (Already a member? Click here.) THE FUNCTIONS OF THE BRAIN The human brain is a complex organ that allows us to think, move, feel, see, hear, taste, and smell. The brain produces electrical signals, which, together with chemical reactions, let the parts of the body communicate. The average human brain weighs about 3 pounds (1300-1400 g). At birth, the human brain weighs less than a pound (0.78-0.88 pounds or 350-400 g). The brain consists of gray matter (40%) and white matter (60%) contained within the skull. The brain has three main parts: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brain stem (medulla). NOURISHMENT OF THE BRAIN Although the brain is only 2% of the body's weight, it uses 20% of the oxygen supply and gets 20% of the blood flow. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surrounds the brain.
Object moved The brain is what it is because of the structural and functional properties of interconnected neurons. The mammalian brain contains between 100 million and 100 billion neurons, depending on the species. Each mammalian neuron consists of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon. The cell body contains the nucleus and cytoplasm. Dendrites extend from the neuron cell body and receive messages from other neurons. When neurons receive or send messages, they transmit electrical impulses along their axons, which can range in length from a tiny fraction of an inch (or centimeter) to three feet (about one meter) or more. The brain contains at least ten times more glia than neurons.
Your Lungs & Respiratory System Listen Time for Talk Your lungs are important for breathing . . . and also for talking! Above the trachea (windpipe) is the larynx (say: LAIR-inks), which is sometimes called the voice box. Across the voice box are two tiny ridges called vocal cords, which open and close to make sounds. When you exhale air from the lungs, it comes through the trachea and larynx and reaches the vocal cords. The amount of air you blow out from your lungs determines how loud a sound will be and how long you can make the sound. Experiment with different sounds and the air it takes to make them — when you giggle, you let out your breath in short bits, but when you burp, you let swallowed air in your stomach out in one long one! Love Your Lungs Your lungs are amazing. Keeping your lungs looking and feeling healthy is a smart idea, and the best way to keep your lungs pink and healthy is not to smoke. You can also show your love for your lungs by exercising!
Nervous tissue - Wikipedia Main component of the nervous system Functions of the nervous system are sensory input, integration, control of muscles and glands, homeostasis, and mental activity. Structure[edit] Nervous tissue is composed of neurons, also called nerve cells, and neuroglial cells. Components[edit] Neurons are classified both functionally and structurally. Functional classification:[5] Sensory neurons (afferent): Relay sensory information in the form of an action potential (nerve impulse) from the PNS to the CNSMotor neurons (efferent): Relay an action potential out of the CNS to the proper effector (muscles, glands)Interneurons: Cells that form connections between neurons and whose processes are limited to a single local area in the brain or spinal cord Structural classification:[5] Multipolar neurons: Have 3 or more processes coming off the soma (cell body). Neuroglia encompasses the non-neural cells in nervous tissue that provide various crucial supportive functions for neurons. Endoneurium. Tumours[edit]
The Constitution for Kids (4th-7th Grade) This file is intended for students in grades 4 through 7. Other versions of this page are available: Want to change this page's colors? Choose a new skin! If you have any questions about any words or ideas on this page, please ask your parents or teachers for help. Understanding the Constitution is important for all Americans, even kids! If there is anything that could be improved on this page, please let the Webmaster know! The Basics The Constitution is the highest law in the United States. The Constitution can be changed. History The Constitution was written in 1787. From May to September 1787 a group of men known as the Framers met. At that time there were only 13 states. After the Convention, the Constitution had to be approved. Amendments When the Constitution was written, the Framers knew their creation was not perfect. The Framers added an amendment process. Originally, some people did not want to ratify the Constitution. Soon, the new government started meeting. Slavery Women
Animal Systems: Nervous System Since you're reading this page, we figure you've got a nervous system. If you were an insect you would also have a nervous system, but it would be a lot simpler. Even animals that don't think have simple nervous systems called nerve nets that help them move. Your nervous system is divided into two parts. Your central nervous system includes your brain and your spinal cord. Your peripheral nervous system is made up of the network of neurons that spans your organs, muscles, and body. The nervous system is about action and senses. The nervous system also senses activity inside of your body. Your nervous system interacts with every other system in your body. There are many hidden interactions going on within your body. The nervous system is made up of nervous tissues that are, in turn, made up of many types of neurons. Your peripheral nervous system has two types of neurons that are constantly at work.