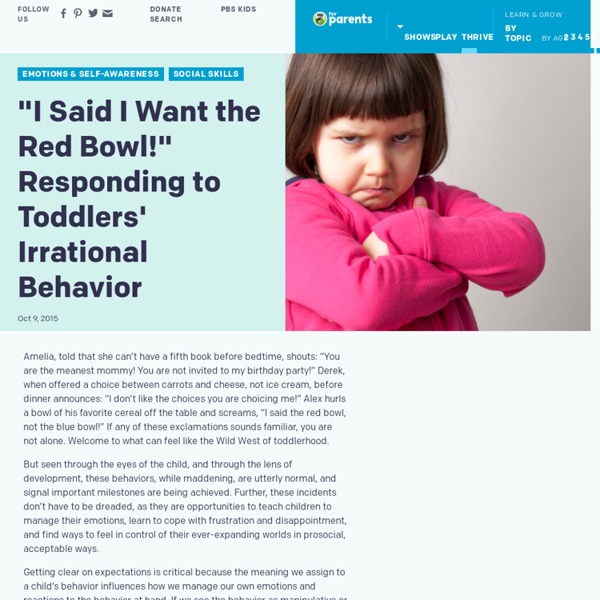
Does my toddler have a short attention span because she won’t sit still for a story?
A: It is perfectly normal for toddlers to not sit still very long—period. Most don’t like to stay in one place for long now that they can explore in so many new ways—by running, jumping, and climbing. So, an adult’s idea of snuggling on the couch to hear a story may not be the same idea a toddler has for story-time. You may only be able to read or talk about a few pages in a book at a time.
Schemas in Children’s Play
Written by Clare CaroSchemas in Children’s Play are such an important concept when it comes to the development of our children that it’s worth taking the time to understand them so you can facilitate them when you see them.What are these schemas?Well it’s really a fancy word for the urges that children have to do things like climb, throw things and hide in small places. They appear through play; perhaps it is the way they choose to do things, or what they desperately need to do out of the blue! Bringing It All TogetherAfter looking at each schema individually to get to grips with what each 'urge' is all about we may already be able to recognise some of the different ways they can appear in your child.Rotation, Trajectory, Enveloping, Orientation, Positioning, Connection, Enclosure/Container, Transporting and Transformation are urges that show in all children starting as early as their first birthday, some times before.How Can Knowing About These Urges Help Us?
Schema and Fairies
Schemas are one of those things that divide practitioners, like fairies at the bottom of the garden. You either believe in them and are in absolute awe at how amazing they are, or you just don’t believe they exist. It’s really interesting when you discuss this with people and it’s extra exciting when a ‘non-believer’ suddenly says “That describes my key child exactly!!”
Teaching English to learners with Special Educational Needs (SENs) – Myths and realities
‘I know I have children with special educational needs in my class, I want to help them and we are supposed to promote inclusion, but I really am not sure how to do this’ Vera, primary teacher from Spain ‘Some of the children in my class are really badly behaved, they can’t sit still, don’t finish their work and are always calling out.
How can parents and teachers best educate young children?
What principles can both teachers and parents bring to the education of very young children? Gillian Craig, who was part of the Learning Time with Shaun and Timmy writing team, explains. As teachers and parents, we follow certain principles in our roles. Often though, these principles overlap and all we need to do is recognise and reinforce these areas. Ask (the right) questions
MIT Brain Study: Back-And-Forth Talk Key To Developing Kids' Verbal Skills
New MIT research finds that for children's brain development, parents don't just need to talk to their kids — it's important to talk with them, in back-and-forth exchanges. "What we found is, the more often parents engaged in back-and-forth conversation with their child, the stronger was the brain response in the front of the brain to language," said cognitive neuroscience professor John Gabrieli. Story continues below Most Viewed Stories That stronger brain response, measured as children ages 4 to 6 lay in a scanner listening to simple stories, reflects a deeper, more intimate engagement with language, said graduate student Rachel Romeo.
Surprisingly Simple Techniques for Challenging Behaviour - Kathy Brodie Early Years Training
I often get asked about children’s behaviour. It is a massive topic, with many facets. However, I would always start from the perspective that all behaviour, good or unacceptable, is a form of communication. It is how we, as practitioners and adults, respond to that communication that makes all the difference.
Taking Playtime Seriously
So part of encouraging play is pulling back on how much programmed goal-directed learning we expect from very young children, to leave them time for the fun of exploration, curiosity and, well, fun. But another important part may be creating environments that foster children’s play and parents’ participation and attention. Dr. Hirsh-Pasek, who is a senior fellow at the Brookings Institution, cited its Learning Landscapes Initiative, which aims to set up learning opportunities in public places where people will encounter them. One of these, the Urban Thinkscape project in Philadelphia, involves puzzle benches at bus stops, with puzzles designed to build STEM skills.
Deconstructing Role Play – Provide the Resources, Step Back and Watch Children’s Learning Flourish
Hospital, vet’s surgery, post office, travel agent – themed role play areas are often seen as a must for an early years setting. They are often meticulously prepared to be aesthetically pleasing, covered in laminated words and pictures with the aim of enticing children in. But this is where I encountered a problem: in these areas, children are expected to come together to play out adult scenarios that are consistent with these themes.
How you talk to your child changes their brain
Most parents know that talking to their child helps them develop. But a new study has revealed that it’s how you talk to your child that really matters for their brain growth. Rather than just spewing complex words at them, or showing flashcards in the hope of enriching their vocabulary, the key is to engage them in “conversational turns” – in other words, a good old chat. In a study of children between the ages of 4 and 6, cognitive scientists at MIT found that such back-and-forth conversation changes the child’s brain. Specifically, it can boost the child’s brain development and language skills, as measured both by a range of tests and MRI brain scans. This was the case regardless of parental income or education.
The Brain-Changing Power of Conversation
The Science Researchers used highly faithful audio recorders — a system called Language Environment Analysis (known as LENA) — to capture every word spoken or heard by 36 4–6 year olds from various socioeconomic backgrounds over two full days. The recordings were analyzed to measure the number of words spoken by each child, the number of words spoken to each child, and the number of conversational turns — back-and-forth exchanges initiated by either adult or child.