The Difference Between Positive/Negative Reinforcement and Positive/Negative Punishment [with Examples]
Reinforcement and punishment are often used as parenting tools to modify children’s behavior. Let’s review the difference between positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement, and the difference in outcomes between them. The Difference Between Positive And Negative Reinforcement In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is the introduction of a favorable condition that will make the desired behavior more likely to happen, continue or strengthen in the future1.
Real-Life Examples of Positive Punishment
“Positive” and “punishment” seem like two words that you wouldn’t use together. However, positive punishment will make complete sense once you learn the definition and explore some examples of positive punishment. Review how positive punishment is different from negative punishment and which is more effective. Understanding Positive Punishment “Positive punishment” might seem like an oxymoron. However, if you expand your thinking beyond positive to mean something “good” to positive meaning to add something, then a positive punishment makes a lot of sense.
Negative Punishment - Psychestudy
Punishment is an important concept used in the theory of Operant conditioning, whose main goal is to decrease the rate of certain undesired behavior from occurring again. There are two kinds of punishment This article will cover various aspects of Negative punishment. Negative punishment is the part of punishment, which also focuses on decreasing the rate of any specific undesired behavior from an individual. The concept works by removing a certain favorite or desired item from the individual’s life.
10 Positive Punishment Techniques & Their Effect
By: Ashley Brown Updated February 11, 2021 Medically Reviewed By: Laura Angers As a parent, it is natural to wonder about the best way to teach your child right from wrong. Punishing them is no fun, but sometimes it has to be done if you want their behavior to change.
(Positive Reinforcement examples) Positive Reinforcement in Psychology (Definition + 5 Examples)
If you read our earlier piece on positive punishment, you know that there are different methods of teaching and instilling good habits and behaviors. One of the most powerful and effective methods is one that you’re probably at least somewhat familiar with: positive reinforcement. Before you read on, we thought you might like to download our 3 Positive Psychology Exercises for free.
Operant Conditioning Examples
Burrhus Frederic Skinner was a psychologist and researcher credited with establishing the principles of operant conditioning. B.F. Skinner began with Thorndike's law of effect, which states that behaviors that cause satisfactory results will be repeated. Skinner considered satisfaction to be insufficiently specific to measure, and set out to design a means of measuring learned behaviors. The operant conditioning chamber, popularly known as a Skinner box, was his solution. He kept his test subjects, primarily pigeons and rats, in circumstances that allowed him to closely observe their behavior.
Positive Punishment: What It Is, Benefits, and Examples
Positive punishment is a form of behavior modification. In this case, the word “positive” doesn’t refer to something pleasant. Positive punishment is adding something to the mix that will result in an unpleasant consequence.
Positive Punishment: What It Is, Benefits, and Examples
Positive punishment is a form of behavior modification. In this case, the word “positive” doesn’t refer to something pleasant. Positive punishment is adding something to the mix that will result in an unpleasant consequence. The goal is to decrease the likelihood that the unwanted behavior will happen again in the future.
(Positive Punishment and Negative reinforcement examples) 12 Examples of Positive Punishment & Negative Reinforcement
You might be thinking that “positive punishment” sounds like an oxymoron, after all, how can punishment be positive? Not many people “like” punishment, right? The disconnect in understanding this concept comes from the usage of the word “positive;” here at PositivePsychology.com, we generally use the term “positive” to refer to things that are inherently good, things that are life-giving, and things that promote thriving and flourishing. The concept of positive punishment comes from a very different era and a very different perspective on psychology; namely, the 1930s and behaviorism. So, what actually is positive punishment and how does it relate to parenting, teaching, and even the workplace?
What Is Punishment Psychology, And Should You Use It?
Updated February 01, 2021 Medically Reviewed By: Tanya Harell Source: rawpixel.com We were all punished when we were younger at one time or another. However, it is how we are punished that can shape how we will behave in the future.
Adolescent learning: rewards, punishments, and the importance of context
Adolescents’ unique sensitivity to rewards is thought to be due to increased activity in and communication between areas of the brain that respond to rewards. However, we also know that many of the same brain areas also respond to punishment and that there are dynamic changes occurring throughout the brain during adolescence. Much like the complexity of brain development, the story about how adolescents learn from reinforcement might not be so simple. “The way that adolescents learn from the choices that they have made in the past will ultimately influence their future choices and actions.” An in-depth review of studies examining how we learn from reinforcement across age shows mixed results.



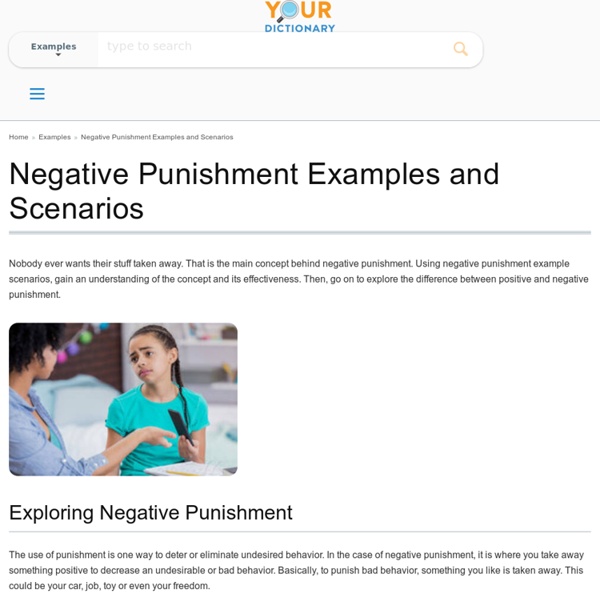
In this instance, the teen’s parents are taking away her speaker (something she values and enjoys) as punishment for missing curfew. By taking away her speaker, they hope that the teen will not miss curfew again. by dioriviemae Mar 27